| [1] Erskine JG, Fraser C, Simpson R, et al.Blood loss with knee joint replacement. JR Coll Surg Edinb.1981; 26(5): 295-297.[2] Mesa-Romas F,Mesa-Romas M,Maquieira-Canosa C.Predictors for blood transfusion following total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study. Acta Orthop Belg, 2008; 74(1): 83-89.[3] 罗吉伟,金大地,黄美贤,等.全膝关节置换术围手术期失血量的评估[J].南方医科大学学报, 2006, 26(11):1606-1608.[4] 余存泰,覃健,侯之启,等.全膝关节置换术隐性失血的初步研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2006, 21(10):784-786.[5] 覃健,余存泰,徐中和,等.全髋关节及全膝关节置换术后隐性失血的临床影响[J].中华骨科杂志, 2006, 26(5):323-326.[6] Prasad N, Padmanabhan V, Mullaji A. Blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of risk factors.Int Orthop. 2007; 31(1): 39-44.[7] Bierbaum BE, Callaghan JJ, Galante JO,et al.An analysis of blood management in patients having a total hip or knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:2-10.[8] Ralley FE, Berta D, Binns V, Howard J. One intraoperative dose of tranexamic acid for patients ha ving primary hip or knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468(7): 1905-1911.[9] Malone KJ, Matuszak S, Mayo D,et al. The effect of intra-articular epinephrine lavage on blood loss following total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2009; 32(2):100-103.[10] Molloy DO, Archbold HA, Ogonda L,et al. Comparison of topical fibrin spray and tranexamic acid on blood loss after total knee replacement: a prospective, randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89(3):306-309.[11] Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis.1957;16(4):494-502.[12] Healy WL, Della Valle CJ, Iorio R,et al.Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty: Standardized List and Definitions of The Knee Society. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2012 Jul 19.[13] Lotke PA, Faralli VJ, Orenstein EM,et al.Blood loss after total knee replacement. Effects of tourniquet release and continuous passive motion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991; 73(7):1037-1040.[14] Gross JB.Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiolog.1983;58(3):277-280.[15] Ward CF, Meathe EA,Benumof JL, et al. A computer nomogram for blood loss replacement. Anesthesiology.1980; 53(3):126-130.[16] Nadler SB, Hidalgo JH, Bloch T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery.1962;51(2):224-232.[17] Fahmy NR, Patel DG.Hemostatic changes and postoperative deep-vein thrombosis associated with use of a pneumatic tourniquet. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1981;63: 461-465.[18] Ho KM, Ismail H. Use of intravenous tranexamic acid to reduce allogeneic blood transfusion in total hip and knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2003; 31:529-537.[19] Camarasa MA, Olle G, Serra-Prat M,et al. Efficacy of aminocaproic, tranexamic acids in the control of bleeding during total knee replacement: a randomized clinical trial. Br J Anaesth. 2006;96:576-582. [20] Hersekli MA, Akpinar S, Okoc G, et al. The timing of tourniquet release and its influence on blood loss after total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2004;28:138-141.[21] Newman JH, Bowers M, Murphy J.The clinical advantages of autologous transfusion. A randomized, controlled study after knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79(4): 630-632.[22] Sehat KR, Evans R, Newman JH. How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty?. Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee. 2000;7(3):151-155.[23] Salido JA, Marín LA, Gómez LA,et al. Preoperative hemoglobin levels and the need for transfusion after prosthetic hip and knee surgery: analysis of predictive factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84: 216-220.[24] Shen HL, Li Z, Feng ML, et al.Analysis on hidden blood loss of total knee arthroplasty in treating knee osteoarthritis. Chin Med J (Engl).2011;124(11):1653-1656.[25] Hekmat K, Jacobsson L, Nilsson JÅ,et al.Decrease in the incidence of total hip arthroplasties in patients with rheumatoid arthritis--results from a well defined population in south Sweden. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(5):130.[26] Bongartz T, Halligan CS, Osmon DR,et al.Incidence and risk factors of prosthetic joint infection after total hip or knee replacement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59(12):1713-1720.[27] Matsuda K, Nozawa M, Katsube S,et al.Reinfusion of unwashed salvaged blood after total knee arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int Orthop. 2009; 33(6): 1615-1618.[28] 高乐才,吴文元,魏金栋,等.术后抗凝对膝关节置换术后隐性失血影响的临床观察[J].河北医药,2013,35(6):880-882. [29] 詹学华.人工全膝关节置换术后膝周冰袋冷敷对隐性失血的影响分析[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2011,19(8):38-39.[30] 朱苏南. 全髋全膝术后应用低分子肝素与隐性失血相关性研究[J].求医问药:下半月,2012,10(10):530-531. [31] 许杰,马若凡,李亮平,等.应用低分子肝素对初次全髋及全膝关节置换后失血的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(48): 8963-8967. [32] 高玉镭,李佩佳,田敏,等.人工全膝关节置换术隐性失血的发生机制及影响因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(3):209-212. [33] 丛宇,曾晓峰,包倪荣,等.人工关节置换术后隐性失血的影响因素及相关机制[J]. 医学研究生学报,2011,24(6):611-614. [34] 丛宇.人工关节置换术后失血的相关研究[J].医学研究生学报, 2010,23(12):1332-1336.[35] 肖鹏,吴学建,刘宏建. 人工关节置换术后隐性失血的相关分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(4):635-638.[36] 陈德胜,金群华,李亚平,等. 隐性失血对双侧人工全膝关节同期置换手术的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(17):1290- 1292.[37] 邱旭升,陈东阳,徐志宏,等.全膝关节置换术后隐性失血危险因素的分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(6):510-512.[38] 杨越华,蒋雷生.髋膝关节置换及髋部骨折内固定术后隐性失血[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(5):289-292. [39] 高玉镭,王东辰;李佩佳,等.人工全髋关节置换术隐性失血量的估算及原因分析[J].实用医药杂志,2012,29(6):490-492.[40] Chen FY, Yang FE, Chen Q.Total knee arthroplasty for the treatment of hemophilic arthropathy of the knee. Zhongguo Gu Shang.2011;24(12):1001-1004. |

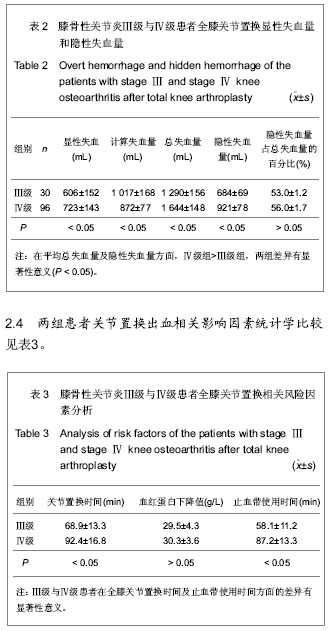

.jpg)