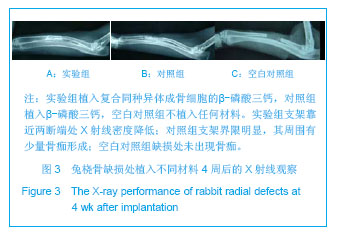
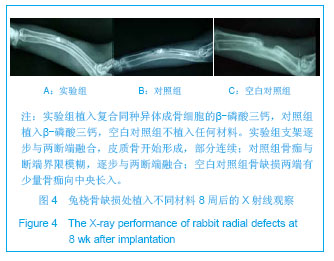
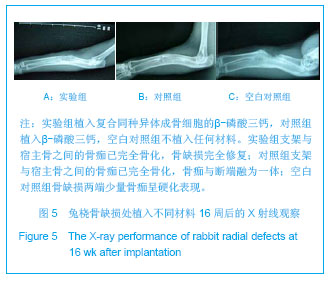
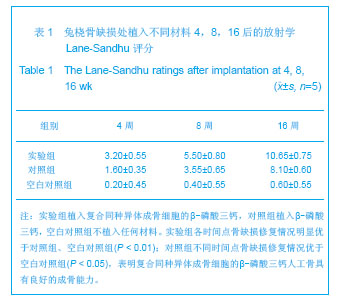
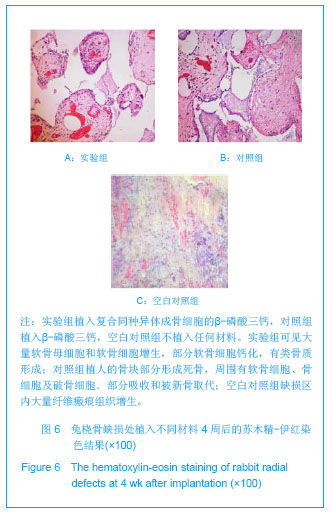
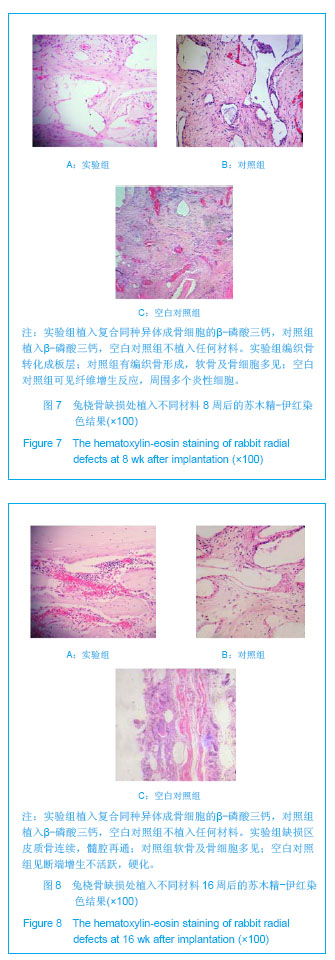
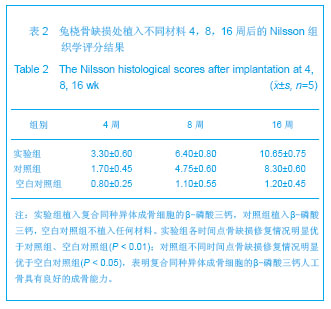
| [1]Hirokazu K,Takaaki T,Masaaki C,et al.Repair of segmental bone defects in rabbit tibiae using a complex of b-tricalcium phosphate, type I collagen, and fibroblast growth factor-2. Biomaterials.2006;27(6):5118–5126.[2]Boos AM,Arkudas A,Kneser U,et al.Bone tissue engineering for bone defect therapy.Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir.2010; 42(6): 360-368.[3]Horner EA,Kirkham J,Wood D,et al.Long bone defect models for tissue engineering applications: criteria for choice.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2010;16(2):263-271.[4]Drosse I,Volkmer E,Capanna R,et al.Tissue engineering for bone defect healing: an update on a multi-component approach. Injury.2008;Suppl 2:S9-20.[5]Hatten HP,Voor MJ.Bone healing using a bi-phasic ceramic bone substitute demonstrated in human vertebroplasty and with histology in a rabbit cancellous bone defect model.Interv Neuroradiol.2012;18(1):105-113.[6]Henmi A,Nakamura M,Echigo S,et al.Involvement of sensory neurons in bone defect repair in rats.J Electron Microsc (Tokyo).2011;60 (6):393-400.[7]Mehta M,Duda GN,Perka C,et al.Influence of gender and fixation stability on bone defect healing in middle-aged rats: a pilot study.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2011;469(11):3102-3110.[8]Garcia-Cimbrelo E,Garcia-Rey E,Cruz-Pardos A.The extent of the bone defect affects the outcome of femoral reconstruction in revision surgery with impacted bone grafting: a five- to 17-year follow-up study.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2011; 93(11):1457-1464.[9]Dos Santos PL,Santiago JF,Ponzoni D,et al. Maxillary bone defect reconstruction using porous polyethylene implants.J Craniofac Surg.2011;22(6):2337-2340.[10]Sheyn D,Kallai I,Tawackoli W,et al.Gene-modified adult stem cells regenerate vertebral bone defect in a rat model.Mol Pharm. 2011;8 (5):1592-1601.[11]Kasai T,Matsumura S,Iizuka T,et al.Carbon nanohorns accelerate bone regeneration in rat calvarial bone defect. Nanotechnology.2011;22(6):65-72. [12]Luca L,Rougemont AL,Walpoth BH,et al.Injectable rhBMP-2-loaded chitosan hydrogel composite: osteoinduction at ectopic site and in segmental longbone defect.J Biomed Mater Res A.2011;96(1):66-74.[13]Knothe UR,Dolejs S,Matthew Miller R,et al.Effects of mechanical loading patterns,bone graft,and proximity to periosteum on bone defect healing.J Biomech.2010;43(14): 2728-2737.[14]Kneser U,Voogd A,Ohnolz J,et al.Fibrin gel-immobilized primary osteoblasts in calcium phosphate bone cement: in vivo evaluation with regard to application as injectable biological bone substitute. Cells Tissues Organs.2005;179: 158.[15]Mai R,Hagedorn MG,Gelinsky M,et al.Ectopic bone formation in nude rats using human osteoblasts seeded poly(3) hydroxybutyrate embroidery and hydroxyapatite-collagen tapes constructs.J Craniomaxillofac Surg.2006;34 Suppl 2:101-109.[16]Damron TA.Use of 3D beta-tricalcium phosphate (Vitoss) scaffolds in repairing bone defects.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2007;2(6):763-775. [17]王玮,章莹,吴文.骨唾液酸蛋白-β-磷酸三钙人工骨的研制及释放实验[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(1): 27-30.[18]Tanaka T,Kumagae Y,Saito M,et al.Bone formation and resorption in patients after implantation of beta-tricalcium phosphate blocks with 60% and 75% porosity in opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2008;86(2):453-459.[19]Hirata M,Murata H,Takeshita H,et al.Use of purified beta-tricalcium phosphate for filling defects after curettage of benign bone tumours.Int Orthop.2006;30(6):510-513. [20]侯喜君,王春华,李霖,等.β-磷酸三钙煅烧骨修复兔股骨远端骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(3):400-406. [21]Declercq H,Van den Vreken N,De Maeyer E,et al.Isolation, proliferation and differentiation of osteoblastic cells to study cell/biomaterial interactions: comparison of different isolation techniques and source. Biomaterials.2004;25(5):757-768.[22]Coopre LE,Masuda T,Whitson SW,et al.Formation of mineralizing osteoblast cultures no machined titanium oxide grit-blasted,and plasma-sprayed titanium surfaces.Inr J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002;17(1):37-42.[23]Lane JM,Sandhu HS.Current approaches to experimental bone grafting. Orthop Clin North Am.1987;18(2):213-225.[24]Nilsson OS,Urist MR,Dawson EG,et al.Bone repair induced by morphogenetic protein in ulnar defects in dogs.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986;68(4):635-642.[25]Hirokazu K,Takaaki T,Masaaki C,et al.Repair of segmental bone defects in rabbit tibiae using a complex of b-tricalcium phosphate, type I collagen, and fibroblast growth factor-2.Biomaterials.2006;27(6):5118–5126. [26]Ei Y,Haider HKh,Shujia J,et al.Therapeutic angiogenesis. Devising new strategies based on past experiences.Basic Res Cardiol.2008;99(2): 121-132. [27]Ummers BN,Eisenstein SM.Donor site pain from the ilium: a complication of lumbar spine fusion.J Bone Jt Surg Br.1989;7: 677–680. |