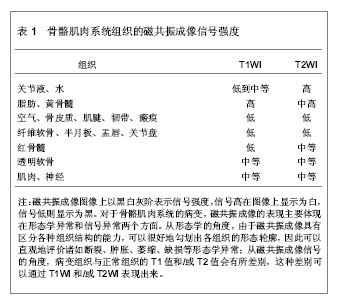
| [1] 戴刚,张卫东,王东武,等.关节镜下手术治疗膝半月板损伤478例流行病学调查分析[J].重庆医学,2006,35(13):1168-1170. [2] 凃茜,罗述祥,刘园园,等.MRI和X线检查在膝关节外伤诊断中的比较[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2005,3(1):54-56.[3] 互动百科.半月板损伤[DB/OL].2012-11-06. http://www.baike.com/wikdoc/sp/qr/history/version.do?ver=22&hisiden=o,W1lBVUVHBQAIQ1xaX,UdcQg[4] 张国兴.膝关节盘状半月板的MRI诊断分析[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2009,12(12):1917-1918.[5] 陈国云,杨兵,李吉华,等.膝关节半月板损伤的MRI与关节镜对照研究[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2005,3(1):54-56.[6] 燕树义,高晓荣,李学民,等.中老年人半月板损伤的关节镜诊断治疗[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2006,20(6):623-626.[7] Lowery DJ,Farley TD,Wing DW,et al.A clinical composite score accurately detects meniscal pathology.Arthroscopy. 2006;22(11):1174-1179.[8] Takeda Y,Ikata T,Yoshida S,et al.MRI high-signal intensity in the menisci of asymptomatic children.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998;80(3):463-467.[9] Akseki D,Ozcan O,Boya H,et al.A new weight-bearing meniscal test and a comparison with McMurray's test and joint line tenderness.Arthroscopy.2004;20(9):951-958.[10] Vincken PW,ter Braak BP,van Erkell AR,et al.Effectiveness of MR imaging in selection of patients for arthroscopy of the knee. Radiology.2002;223(3):739-746.[11] 陈海南,董启榕,汪益,等.低场强磁共振成像诊断半月板撕裂的准确性研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2004,20(2):83-84.[12] 董启榕,汪益.膝关节磁共振成像与关节镜图谱[M].郑州:郑州大学出版社,2004:109.[13] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2012-12-27. https://www.cnki.net[14] SCI数据库.Web of Sciencevia ISI Web of Knowledge[DB/OL]. 2012-12-27.http://ip-science.thomsonreuters.com/mjl[15] 常光辉,孙西河,刘秀娟,等.膝关节半月板损伤的MRI诊断与手术对照分析[J].潍坊医学院学报,2002,24(3):163-165.[16] 陈宏.不同磁共振扫描方法对膝关节前交叉韧带的评价[J].新疆医科大学学报,2006,29(7):639-640.[17] Rubin DA, Paletta GA Jr.Current concepts and controversies in meniscal imaging.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am.2000; 8(2):243-270.[18] Escobedo EM,Hunter JC,Zink-Brody GC,et al.Usefulness of turbo spin-echo MR imaging in the evaluation of meniscal tears: comparison with a conventional spin-echo sequence.AJR Am J Roentgenol.1996;167(5):1223-1227.[19] 李培,郑卓肇,袁亮.膝关节盘状半月板的MRI征象分析[J].中国民康医学(上半月),2008,20(19):2229-2231.[20] Rohren EM,Kosarek FJ,Helms CA.Discoid lateral meniscus and the frequency of meniscal tears.Skeletal Radiol. 2001; 30(6):316-320.[21] McCauley TR,Jee WH,Galloway MT,et al.Grade 2C signal in the meniscus [correction of mensicus] on MR imaging of the knee.AJR Am J Roentgenol.2002;179(3):645-648.[22] 刘泽坤.膝关节盘状半月板分型及损伤的MRI诊断表现分析[J].中外医疗,2012,31(5):172.[23] Kaplan PA,Gehl RH,Dussault RG,et al.Bone contusions of the posterior lip of the medial tibial plateau (contrecoup injury) and associated internal derangements of the knee at MR imaging.Radiology.1999;211(3):747-753.[24] Lee K,Siegel MJ,Lau DM,et al.Anterior cruciate ligament tears: MR imaging-based diagnosis in a pediatric population. Radiology. 1999;213(3):697-704.[25] Stoller DW,Martin C,Crues JV 3rd,et al.Meniscal tears: pathologic correlation with MR imaging.Radiology. 1987; 163(3):731-735.[26] Silverman JM,Mink JH,Deutsch AL.Discoid menisci of the knee: MR imaging appearance.Radiology. 1989; 173(2): 351-354.[27] Auge WK 2nd,Kaeding CC.Bilateral discoid medial menisci with extensive intrasubstance cleavage tears: MRI and arthroscopic correlation.Arthroscopy.1994;10(3):313-318.[28] De Smet AA,Tuite MJ.Use of the "two-slice-touch" rule for the MRI diagnosis of meniscal tears.AJR Am J Roentgenol.2006; 187(4):911-914.[29] Boxheimer L,Lutz AM,Zanetti M,et al.Characteristics of displaceable and nondisplaceable meniscal tears at kinematic MR imaging of the knee.Radiology.2006;238(1):221-231.[30] Wright RW,Boyer DS.Significance of the arthroscopic meniscal flounce sign: a prospective study.Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(2):242-244.[31] 赵文,高克勇,王飞,等.急性膝关节损伤磁共振诊断及临床意义[J].实用医技杂志,2007,14(19):2571-2573.[32] 王旭,李金亭.膝关节半月板损伤的MR检查技术[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2011,8(4):348-351.[33] 360doc个人图书馆.运动创伤的影像学诊断[DB/OL]. 2012-05-23. http://www.360doc.com/content/12/0523/11/ 420868_213086103.shtml[34] Boyd KT,Myers PT.Meniscus preservation; rationale, repair techniques and results.Knee.2003;10(1):1-11.[35] Macarini L,Murrone M,Marini S,et al.MR in the study of knee cartilage pathologies: influence of location and grade on the effectiveness of the method.Radiol Med.2003;105(4): 296-307.[36] 陈兴灿,潘永清,刘淼,等.正常和损伤膝关节半月板低场MRI研究(附损伤半月板关节镜所见比较)[J].中国临床医学影像杂志, 2005,16(12):710-712.[37] 李仕臣,王文革,吕晓波,等.关节镜与核磁共振对膝关节损伤诊断的对比观察[J].山西医药杂志,2006,35(5):413-415.[38] 高友富,高强,廖海燕等.盘状半月板42例的磁共振成像诊断分析[J].实用医学影像杂志,2013,14(1):79-80.[39] 谢海柱,王滨,苏续清.膝关节损伤磁共振成像诊断及临床价值[J].实用放射学杂志,2005,21(7):760-762.[40] Matava MJ,Eck K,Totty W,et al.Magnetic resonance imaging as a tool to predict meniscal reparability.Am J Sports Med. 1999;27(4):436-443. |