| [1] Ludwig B, Rotem A, Schmid J, et al. Improvement of islet function in a bioartificial pancreas by enhanced oxygen supply and growth hormone releasing hormone agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(13):5022-5027. [2] Teramura Y, Iwata H. Bioartificial pancreas microencapsulation and conformal coating of islet of Langerhans. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2010;62(7-8):827-840.[3] De Vos P, Van Straaten JF, Nieuwenhuizen AG, et al. Why do microencapsulated islet grafts fail in the absence of fibrotic overgrowth? Diabetes. 1999;48(7):1381-1388.[4] Chang TM. Artificial Cells for cell and organ replacements. Artif Organs. 2004;28(3):265-270.[5] Luo R, Li H, Lam KY. Modeling the effect of environmental solution pH on the mechanical characteristics of glucose-sensitive hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2009;30(4): 690-700.[6] Lee SJ, Park K. Synthesis and characterization of sol-gel phase-reversible hydrogels sensitive to glucose. J Mol Recognit. 1996;9(5-6):549-557.[7] Makino K, Mack EJ, Okano T, et al. Self-regulated delivery of insulin from microcapsules. Biomater Artif Cells Immobilization Biotechnol. 1991;19(1):219-228.[8] Tanna S, Joan Taylor M, Sahota TS, et al. Glucose-responsive UV polymerised dextran-concanavalin A acrylic derivatised mixtures for closed-loop insulin delivery. Biomaterials. 2006;27(8):1586-1597.[9] Cheng SY, Constantinidis I, Sambanis A. Use of glucose-responsive material to regulate insulin release from constitutively secreting cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006;93(6): 1079-1088.[10] Wu Z, Zhang S, Zhang X, et al. Phenylboronic acid grafted chitosan as a glucose-sensitive vehicle for controlled insulin release. J Pharm Sci. 2011;100(6):2278-2286.[11] Huguet ML, Dellacherie E. Calcium alginate beads coated with chitosan: Effect of the structure of encapsulated materials on their release. Process Biochem. 1996;31(8): 745-751.[12] Hari PR, Chandy T, Sharma CP. Chitosan/calcium-alginate beads for intestinal delivery of nitrofurantoin. J Microencapsul. 1996;13(3):319-329.[13] Silva CM, Ribeiro AJ, Figueiredo IV, et al. Alginate microspheres prepared by internal gelation: Development and effect on insulin stability. Int J Pharm. 2006;311(1-2):1-10.[14] Mi FL, Sung HW, Shyu SS. Drug release from chitosan-alginate complex beads reinforced by a naturally occurring cross-linking agent. Carbohyd Polym. 2002;48(1): 61-72.[15] Pan XP, Li LJ. Advances in cell sources of hepatocytes for bioartificial liver. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2012;11(6): 594-605.[16] 刘映薇,于炜婷,刘袖洞,等.海藻酸钠-壳聚糖-海藻酸钠(ACA)微胶囊的蛋白质通透性研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2006, 25(3):370-373.[17] 周晶,张英,王为,等.谷氨酰胺对微囊化重组CHO细胞生长代谢及内皮抑素表达的影响[J].生物工程学报,2006,22(1):162-166.[18] Lee CS, Chu IM. Characterization of modified alginate-poly-l-lysine microcapsules. Artif Organs. 1997; 21(9):1002-1006.[19] Dove A. Cell-based therapies go live. Nat Biotechnol. 2002; 20(4):339-343.[20] Kang J, Erdodi G, Kennedy JP, et al. Toward a bioartificial pancreas: diffusion of insulin and IgG across immunoprotective membranes with controlled hydrophilic channel diameters. Macromol biosci. 2010;10(4):369-377. [21] de Vos P, Spasojevic M, de Haan BJ, et al. The association between in vivo physicochemical changes and inflammatory responses against alginate based microcapsules. Biomaterials. 2012;33(22):5552-5559.[22] de Vos P, Faas MM, Strand B, et al. Alginate-based microcapsules for immunoisolation of pancreatic islets. Biomaterials. 2006;27(32):5503-5617.[23] Veriter S, Aouassar N, Adnet PY, et al. The impact of hyperglycemia and the presence of encapsulated islets on oxygenation within a bioartificial pancreas in the presence of mesenchymal stem cells in a diabetic Wistar rat model. Biomaterials. 2011;32(26):5945-5956. [24] Kitano S, Koyama Y, Kataoka K, et al. A novel drug delivery system utilizing a glucose responsive polymer complex between poly (vinyl alcohol) and poly (N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) with a phenylboronic acid moiety. J Control Release. 1992; 19(1-3):161-170.[25] Voigt A, Zintl F. Hybridoma cell growth and anti-neuroblastoma monoclonal antibody production in spinner flasks using a protein-free medium with microcarriers. J Biotechnol. 1999;68(2-3):213-226. |
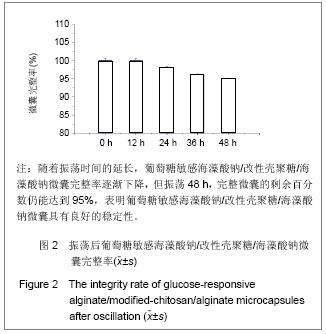
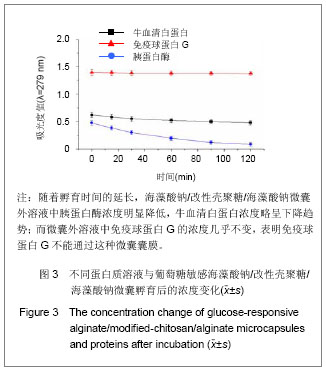
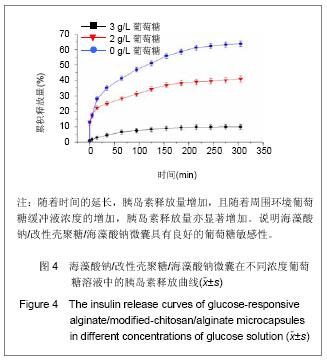
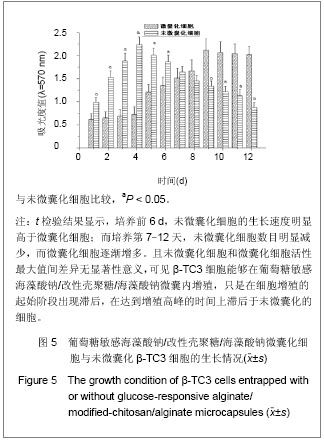
.jpg)