| [1] Xia L, Sakban RB, Qu Y, et al. Tethered spheroids as an in vitro hepatocyte model for drug safety screening. Biomaterials. 2012;33(7):2165-2176.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Tethered+spheroids+as+an+in+vitro+hepatocyte+model+for+drug+safety+screening.[2]Bierwolf J, Lutgehetmann M, Feng K, et al. Primary rat hepatocyte culture on 3D nanofibrous polymer scaffolds for toxicology and pharmaceutical research. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2011;108(1):141-150.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Primary+rat+hepatocyte+culture+on+3D+nanofibrous+polymer+scaffolds+for+toxicology+and+pharmaceutical+research.[3] Hui EE, Bhatia SN. Micromechanical control of cell-cell interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(14):5722-5726.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17389399[4] Ohashi K, Yokoyama T, Yamato M, et al. Engineering functional two- and three-dimensional liver systems in vivo using hepatic tissue sheets. Nat Med. 2007;13(7):880-885.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Engineering+functional+two-+and+three-dimensional+liver+systems+in+vivo+using+hepatic+tissue+sheets.[5] Kim K, Ohashi K, Utoh R, et al. Preserved liver-specific functions of hepatocytes in 3D co-culture with endothelial cell sheets. Biomaterials. 2012;33(5):1406-1413.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Preserved+liver-specific+functions+of+hepatocytes+in+3D+co-culture+with+endothelial+cell+sheets.[6] Rhim JA, Sandgren EP, Degen JL, et al. Replacement of diseased mouse liver by hepatic cell transplantation. Science. 1994;263(5150):1149-1152.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8108734[7] Ohashi K, Park F, Kay MA. Hepatocyte transplantation: clinical and experimental application. J Mol Med (Berl). 2001;79(11):617-630.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=J+Mol+Med+(Berl).+2001%3B+11(79)%3A617-630[8] Goto Y, Ohashi K, Utoh R, et al. Hepatocyte transplantation through the hepatic vein: a new route of cell transplantation to the liver. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(8):1259-1270.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Hepatocyte+transplantation+through+the+hepatic+vein%3A+a+new+route+of+cell+transplantation+to+the+liver.[9] Carpentier B, Gautier A, Legallais C. Artificial and bioartificial liver devices: present and future. Gut. 2009;58(12):1690-1702.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19923348[10] lin JM, Kneip B, Vaulont S, et al. Dependence of hepatocyte-specific gene expression on cell-cell interactions in primary culture. EMBO J. 1985;4(10):2487-2491.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Dependence+of+hepatocyte-specific+gene+expression+on+cell-cell+interactions+in+primary+culture.[11] Ben-Ze'ev A, Robinson GS, Bucher NL, et al. Cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions differentially regulate the expression of hepatic and cytoskeletal genes in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988;85(7):2161-2165.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Cell-cell+and+cell-matrix+interactions+differentially+regulate+the+expression+of+hepatic+and+cytoskeletal+genes+in+primary+cultures+of+rat+hepatocytes.[12] Oda H, Yoshida Y, Kawamura A, et al. Cell shape, cell-cell contact, cell-extracellular matrix contact and cell polarity are all required for the maximum induction of CYP2B1 and CYP2B2 gene expression by phenobarbital in adult rat cultured hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;75(5):1209-1217.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Biochem+Pharmacol.+2008%3B+5(75)%3A1209-1217[13] Mooney D, Hansen L, Vacanti J, et al. Switching from differentiation to growth in hepatocytes: control by extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1992;151(3):497-505.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1295898[14] Dunn JC, Tompkins RG, Yarmush ML. Long-term in vitro function of adult hepatocytes in a collagen sandwich configuration. Biotechnol Prog. 1991;7(3):237-245.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Long-term+in+vitro+function+of+adult+hepatocytes+in+a+collagen+sandwich+configuration.[15] Dunn JC, Yarmush ML, Koebe HG, et al. Hepatocyte function and extracellular matrix geometry: long-term culture in a sandwich configuration. FASEB J. 1989;3(2):174-177.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=FASEB+J.+1989%3B+2(3)%3A174-177[16] Wu FJ, Friend JR, Hsiao CC, et al. Efficient assembly of rat hepatocyte spheroids for tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1996;50(4):404-415.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Efficient+assembly+of+rat+hepatocyte+spheroids+for+tissue+engineering+applications.[17] Pulavendran S, Rose C, Mandal AB. Hepatocyte growth factor incorporated chitosan nanoparticles augment the differentiation of stem cell into hepatocytes for the recovery of liver cirrhosis in mice. J Nanobiotechnology. 2011;9:15.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Hepatocyte+growth+factor+incorporated+chitosan+nanoparticles+augment+the+differentiation+of+stem+cell+into+hepatocytes+for+the+recovery+of+liver+cirrhosis+in+mice.[18] Ananthanarayanan A, Narmada BC, Mo X, et al. Purpose-driven biomaterials research in liver-tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2011;29(3):110-118.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Purpose-driven+biomaterials+research+in+liver-tissue+engineering.[19] Feng ZQ, Chu X, Huang NP, et al. The effect of nanofibrous galactosylated chitosan scaffolds on the formation of rat primary hepatocyte aggregates and the maintenance of liver function. Biomaterials. 2009;30(14):2753-2763.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Biomaterials.+2009%3B+14(30)%3A2753-2763[20] Cushing MC, Anseth KS. Materials science. Hydrogel cell cultures. Science. 2007;316(5828):1133-1134.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Hydrogel+cell+cultures.+Science.+2007%3B+5828(316)%3A1133-1134[21] Seliktar D. Designing cell-compatible hydrogels for biomedical applications. Science. 2012;336(6085):1124-1128.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Designing+cell-compatible+hydrogels+for+biomedical+applications.[22] Kim M, Lee JY, Jones CN, et al. Heparin-based hydrogel as a matrix for encapsulation and cultivation of primary hepatocytes. Biomaterials. 2010;31(13):3596-3603.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Heparin-based+hydrogel+as+a+matrix+for+encapsulation+and+cultivation+of+primary+hepatocytes.[23] Fu Y, Xu K, Zheng X, et al. 3D cell entrapment in crosslinked thiolated gelatin-poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2012;33(1):48-58.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Biomaterials.+2012%3B+1(33)%3A48-58[24] Ricard-Blum S. The collagen family. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011;3(1):a004978.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21421911[25] Friess W. Collagen--biomaterial for drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1998;45(2):113-136.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=European+Journal+of+Pharmaceutics+and+Biopharmaceutics.+1998%3B+2(45)%3A113-136[26] Nagamoto Y, Tashiro K, Takayama K, et al. The promotion of hepatic maturation of human pluripotent stem cells in 3D co-culture using type I collagen and Swiss 3T3 cell sheets. Biomaterials. 2012;33(18):4526-4534.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=The+promotion+of+hepatic+maturation+of+human+pluripotent+stem+cells+in+3D+co-culture+using+type+I+collagen+and+Swiss+3T3+cell+sheets.[27] Yuan T, Zhang L, Feng L, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation and immunological properties of mesenchymal stem cells in collagen type I hydrogel. Biotechnol Prog. 2010;26(6):1749-1758.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Biotechnol+Prog.+2010%3B+6(26)%3A1749-1758[28] Zheng L, Sun J, Chen X, et al. In vivo cartilage engineering with collagen hydrogel and allogenous chondrocytes after diffusion chamber implantation in immunocompetent host. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(8):2145-2153.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=In+vivo+cartilage+engineering+with+collagen+hydrogel+and+allogenous+chondrocytes+after+diffusion+chamber+implantation+in+immunocompetent+host.[29] Oh SA, Lee HY, Lee JH, et al. Collagen three-dimensional hydrogel matrix carrying basic fibroblast growth factor for the cultivation of mesenchymal stem cells and osteogenic differentiation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(9-10):1087-1100.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Three-Dimensional+Hydrogel+Matrix+Carrying+Basic+Fibroblast+Growth+Factor+for+the+Cultivation+of+Mesenchymal+Stem+Cells+and+Osteogenic+Differentiation.[30] Zhao Y, Xu Y, Zhang B, et al. In vivo generation of thick, vascularized hepatic tissue from collagen hydrogel-based hepatic units. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(4):653-659.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=In+vivo+generation+of+thick%2C+vascularized+hepatic+tissue+from+collagen+hydrogel-based+hepatic+units.[31] Seglen PO. Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:29-83.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Seglen+PO.+Preparation+of+isolated+rat+liver+cells.+Methods+Cell+Biol+1976%3B13%3A[32] Zhao YS, Xu YX, Zhang BF, et al. Experimental study of implantable engineered liver tissue using type I collagen gel as scaffold. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007;87(29):2065-2068.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Experimental+study+of+implantable+engineered+liver+tissue+using+type+I+collagen+gel+as+scaffold.[33] Wang S, Nagrath D, Chen PC, et al. Three-dimensional primary hepatocyte culture in synthetic self-assembling peptide hydrogel. Tissue Eng Part A. 2008;14(2):227-236.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Three-dimensional+primary+hepatocyte+culture+in+synthetic+self-assembling+peptide+hydrogel.[34] Saha K, Pollock JF, Schaffer DV, et al. Designing synthetic materials to control stem cell phenotype. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2007;11(4):381-387.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Designing+synthetic+materials+to+control+stem+cell+phenotype[35] Levenberg S, Huang NF, Lavik E, et al. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells on three-dimensional polymer scaffolds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(22):12741-12746.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14561891[36] Tibbitt MW, Anseth KS. Hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics for 3D cell culture. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2009;103(4):655-663.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19472329[37] Shea LD, Smiley E, Bonadio J, et al. DNA delivery from polymer matrices for tissue engineering. Nat Biotechnol. 1999;17(6):551-554.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10385318[38] Semino CE, Merok JR, Crane GG, et al. Functional differentiation of hepatocyte-like spheroid structures from putative liver progenitor cells in three-dimensional peptide scaffolds. Differentiation. 2003;71(4-5):262-270.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Differentiation.+2003%3B+4-5(71)%3A262-270[39] Silva GA, Czeisler C, Niece KL, et al. Selective differentiation of neural progenitor cells by high-epitope density nanofibers. Science. 2004;303(5662):1352-1355.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Selective+differentiation+of+neural+progenitor+cells+by+high-epitope+density+nanofibers.[40] Nicodemus GD, Bryant SJ. Cell encapsulation in biodegradable hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2008;14(2):149-165.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18498217[41] Egawa EY, Kato K, Hiraoka M, et al. Enhanced proliferation of neural stem cells in a collagen hydrogel incorporating engineered epidermal growth factor. Biomaterials. 2011;32(21):4737-4743.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Enhanced+proliferation+of+neural+stem+cells+in+a+collagen+hydrogel+incorporating+engineered+epidermal+growth+factor[42] Hammond JS, Gilbert TW, Howard D, et al. Scaffolds containing growth factors and extracellular matrix induce hepatocyte proliferation and cell migration in normal and regenerating rat liver. J Hepatol. 2011;54(2):279-287.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=J+Hepatol.+2011%3B+2(54)%3A279-287[43] Sellaro TL, Ranade A, Faulk DM, et al. Maintenance of human hepatocyte function in vitro by liver-derived extracellular matrix gels. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(3):1075-1082.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Maintenance+of+human+hepatocyte+function+in+vitro+by+liver-derived+extracellular+matrix+gels.[44] Berthiaume F, Moghe PV, Toner M, et al. Effect of extracellular matrix topology on cell structure, function, and physiological responsiveness: hepatocytes cultured in a sandwich configuration. FASEB J. 1996;10(13):1471-184.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Effect+of+extracellular+matrix+topology+on+cell+structure%2C+function%2C+and+physiological+responsiveness+hepatocytes+cultured+in+a+sandwich+configuration.[45] Page JL, Johnson MC, Olsavsky KM, et al. Gene expression profiling of extracellular matrix as an effector of human hepatocyte phenotype in primary cell culture. Toxicol Sci. 2007;97(2):384-397.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Gene+expression+profiling+of+extracellular+matrix+as+an+effector+of+human+hepatocyte+phenotype+in+primary+cell+culture.[46] Zavan B, Brun P, Vindigni V, et al. Extracellular matrix-enriched polymeric scaffolds as a substrate for hepatocyte cultures: in vitro and in vivo studies. Biomaterials. 2005;26(34):7038-7045.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Extracellular+matrix-enriched+polymeric+scaffolds+as+a+substrate+for+hepatocyte+cultures%3A+in+vitro+and+in+vivo+studies.+Biomaterials.[47] Shen C, Meng Q. Prediction of cytochrome 450 mediated drug-drug interactions by three-dimensional cultured hepatocytes. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2012;12(10):1028-1036.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Prediction+of+cytochrome+450+mediated+drug-drug+interactions+by+three-dimensional+cultured+hepatocytes.[48] Li J, Ning G, Duncan SA. Mammalian hepatocyte differentiation requires the transcription factor HNF-4alpha. Genes Dev. 2000;14(4):464-474.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10691738[49] Schrem H, Klempnauer J, Borlak J. Liver-enriched transcription factors in liver function and development. Part II: the C/EBPs and D site-binding protein in cell cycle control, carcinogenesis, circadian gene regulation, liver regeneration, apoptosis, and liver-specific gene regulation. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56(2):291-330.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Pharmacol+Rev.+2004%3B+2(56)%3A291-330[50] Dean S, Tang JI, Seckl JR, et al. Developmental and tissue-specific regulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha (HNF4-alpha) isoforms in rodents. Gene Expr. 2010;14(6):337-344.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Developmental+and+tissue-specific+regulation+of+hepatocyte+nuclear+factor+4-alpha+(HNF4-alpha)+isoforms+in+rodents.[51] Takaki Y, Hirai S, Manabe N, et al. Dynamic changes in protein components of the tight junction during liver regeneration. Cell Tissue Res. 2001;305(3):399-409.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Dynamic+changes+in+protein+components+of+the+tight+junction+during+liver+regeneration.[52] Sawada N, Murata M, Kikuchi K, et al. Tight junctions and human diseases. Med Electron Microsc. 2003;36(3):147-156.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Med+Electron+Microsc.+2003%3B+3(36)%3A147-156[53] Bhatia SN, Balis UJ, Yarmush ML, et al. Effect of cell-cell interactions in preservation of cellular phenotype: cocultivation of hepatocytes and nonparenchymal cells. FASEB J. 1999;13(14):1883-1900.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10544172[54] Nishikawa M, Kojima N, Komori K, et al. Enhanced maintenance and functions of rat hepatocytes induced by combination of on-site oxygenation and coculture with fibroblasts. J Biotechnol. 2008;133(2):253-260.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Enhanced+maintenance+and+functions+of+rat+hepatocytes+induced+by+combination+of+on-site+oxygenation+and+coculture+with+fibroblasts.[55] Zinchenko YS, Culberson CR, Coger RN. Contribution of non-parenchymal cells to the performance of micropatterned hepatocytes. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(8):2241-2251.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Contribution+of+Non-parenchymal+Cells+to+the+Performance+of+Micropatterned+Hepatocytes.+Tissue+Eng+Part+A.+2006%3B |
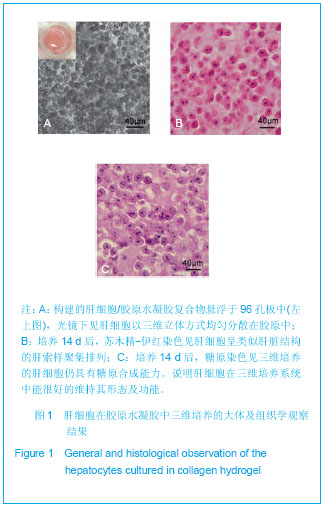
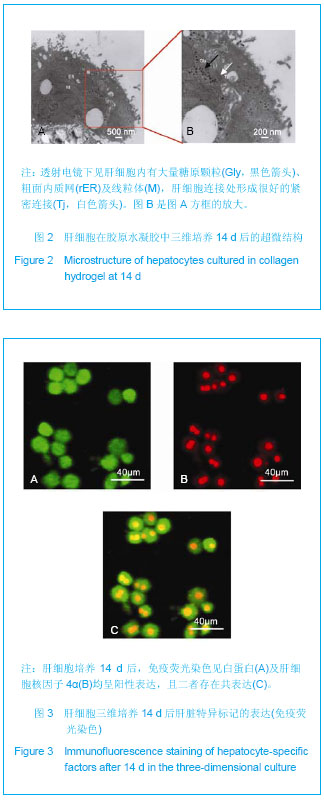
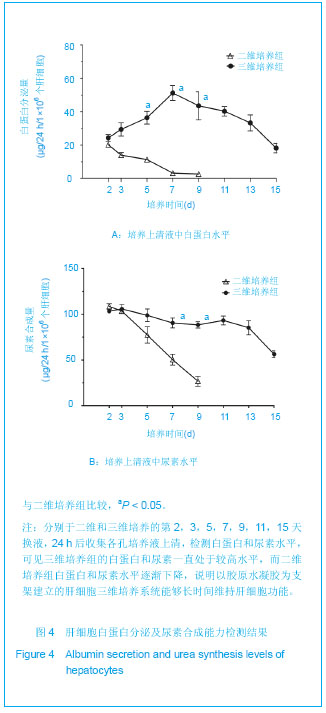
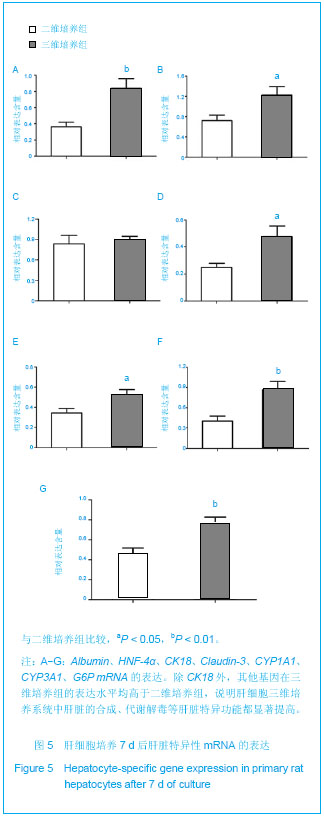
.jpg)
.jpg)