| [1] Mellado-Valero A,Ferrer-García JC,Calvo-Catalá J,et al. Implant treatment in patients with osteoporosis. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal.2010;15(1): e52-57.[2] Bornstein MM,Cionca N,Mombelli A Systemic conditions and treatments as risks for implant therapy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2009;24 (Suppl): 12-27. [3] van Steenberghe D,Jacobs R,Desnyder M,et al. The relative impact of local and endogenous patient-related factors on implant failure up to the abutment stage. Clin Oral Implants Res.2002;13: 617-622. [4] Miettinen SS,Jaatinen J,Pelttari A,et al. Effect of locally administered zoledronic acid on injury-induced intramembranous bone regeneration and osseointegration of a titanium implant in rats. J Orthop Sci.2009;14: 431-436.[5] Maïmoun L, Brennan TC,Badoud I, et al. Strontium ranelate improves implant osseointegration. Bone.2010;46: 1436-1441. [6] Neale SD,Sabokbar A,Howie DW,et al. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-6 release by periprosthetic cells stimulates osteoclast formation and bone resorption. J Orthop Res.1999;17: 686-694.[7] Marco F,Milena F,Gianluca G.et al. Peri-implant osteogenesis in health and osteoporosis. Micron.2005;36: 630-644.[8] 袁旭敏,傅远飞,张富强,等. 羟基磷灰石涂层钛种植体结合强度及稳定性的研究进展[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2007,12(3): 193-195.[9] 陈海军,张安生,林均舟,等. 锌对钛种植体骨融合的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(51):9518-9522.[10] Wang X,Ito A,Sogo Y,et al.Zinc-containing apatite layers on external fixation rods promoting cell activity. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:962-968.[11] Wang Y,Zhang S,Zeng X,et al. Osteoblastic cell response on fluoridated hydroxyapatite coatings. Acta Biomater.2007;3: 191-197.[12] Cai YL,Zhang JJ,Zhang S,et al.Osteoblastic cell response on fluoridated hydroxyapatite coatings: the effect of magnesium incorporation.Biomed Mater.2010;5: 054114.[13] Oxlund BS,Ortoft G,Andreassen TT,et al.Low-intensity, high-frequency vibration appears to prevent the decrease in strength of the femur and tibia associated with ovariectomy of adult rats. Bone. 2003;32:69-77.[14] Kurth AH,Eberhardt C,Muller S,et al.The bisphosphonate ibandronate improves implant integration in osteopenic ovariectomized rats. Bone. 2005;37:204-210.[15] Gao Y,Luo E,Hu J, et al. Effect of combined local treatment with zoledronic acid and basic fibroblast growth factor on implant fixation in ovariectomized rats.Bone.2009;44: 225-232.[16] Berzins A,Shah B,Weinans H,et al.Nondestructive measurements of implant-bone interface shear modulus and effects of implant geometry in pull-out tests.J Biomed Mater Res.1997;34:337-340.[17] Avila G,Misch K,Galindo-Moreno P,et al.Implant surface treatment using biomimetic agents.Implant Dent.2009; 18: 17-26.[18] Starck WJ,Epker BN.Failure of osseointegrated dental implants after diphosphonate therapy for osteoporosis: A case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.1995;10:74-78.[19] Narai S,Nagahata S. Effects of alendronate on the removal torque of implants in rats with induced osteoporosis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003;18:218-223.[20] Yang L,Perez-Amodio S,Barrere-de Groot FY,et al. The effects of inorganic additives to calcium phosphate on in vitro behavior of osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Biomaterials. 2010; 31:2976-2989.[21] Kawamura H,Ito A,Miyakawa S,et al.Stimulatory effect of zinc-releasing calcium phosphate implant on bone formation in rabbit femora. J Biomed Mater Res.2000;50:184-190.[22] Kempen DH,Lu L,Heijink A,et al. Effect of local sequential vegf and bmp-2 delivery on ectopic and orthotopic bone regeneration.Biomaterials. 2009;30:2816-2825.[23] Cooper LF,Zhou Y,Takebe J,et al. Fluoride modification effects on osteoblast behavior and bone formation at tio2 grit-blasted c.P. Titanium endosseous implants. Biomaterials. 2006;27: 926-936.[24] 王丹宁,赵宝红,张伟,等. 纯钛表面应用微弧氧化法制备不同浓度锌涂层对成骨细胞生物学特性影响的研究[J].口腔医学,2011, 31(10):577-581.[25] 赵宝红,封伟,尚德浩,等. 纯钛表面微弧氧化法制备含钙锌涂层的抗菌性能研究[J].上海口腔医学,2012,21(3):266-269. |
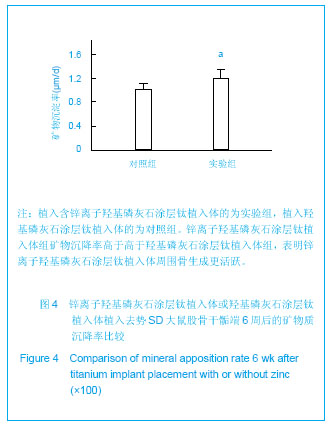
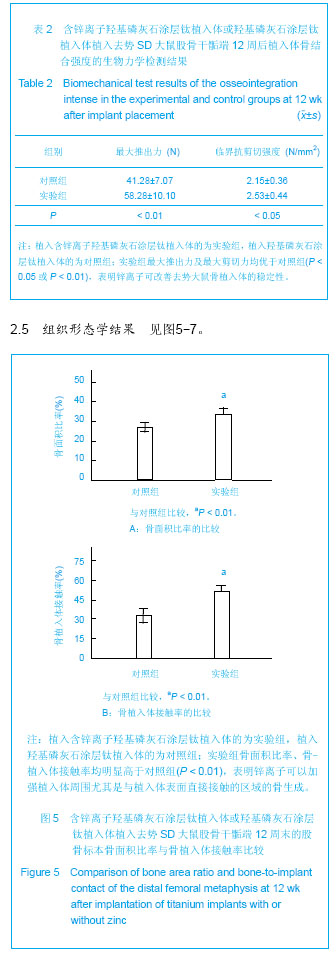

.jpg)
.jpg)