| [1] Hirabayashi K, Watanabe K, Wakano K,et al. Expansive open-door laminoplasty for cervical spinal stenotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983;8(7):693-699.[2] Wang MY, Shah S, Green BA. Clinical outcomes following cervical laminoplasty for 204 patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy.Surg Neurol. 2004;62(6):487-492.[3] Hale JJ, Gruson KI, Spivak JM. Laminoplasty: a review of its role in compressive cervical myelopathy.Spine J. 2006;6 (6 Suppl): 289S-298S.[4] Kaner T, Sasani M, Okteno?lu T,et al. Clinical outcomes following cervical laminoplasty for 19 patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy.Turk Neurosurg. 2009;19(2):121-126.[5] Hardman J, Graf O, Kouloumberis PE,et al. Clinical and functional outcomes of laminoplasty and laminectomy. Neurol Res. 2010;32(4):416-420.[6] Chiba K, Ogawa Y, Ishii K,et al. Long-term results of expansive open-door laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy--average 14-year follow-up study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(26):2998-3005.[7] Matsumoto M, Chiba K, Toyama Y. Surgical treatment of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and its outcomes: posterior surgery by laminoplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(5):E303-308.[8] Sakaura H, Hosono N, Mukai Y,et al. Long-term outcome of laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy due to disc herniation: a comparative study of laminoplasty and anterior spinal fusion.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(7):756-759.[9] Nakamura K,Toyama Y, Hoshino Y. Cervical pain after laminoplasty .In:Cervical Laminoplasty.New York: Springer, 2003:169-174.[10] Shiraishi T, Fukuda K, Yato Y,et al. Results of skip laminectomy-minimum 2-year follow-up study compared with open-door laminoplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(24): 2667-2672.[11] Luk KD, Kamath V, Avadhani A,et al.Cervical laminoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(2):347-348.[12] Kawaguchi Y, Kanamori M, Ishihara H,et al. Minimum 10-year followup after en bloc cervical laminoplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(411):129-139.[13] Yoshida M, Tamaki T, Kawakami M,et al. Does reconstruction of posterior ligamentous complex with extensor musculature decrease axial symptoms after cervical laminoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(13):1414-1418.[14] Takeshita K, Peterson ET, Bylski-Austrow D,et al. The nuchal ligament restrains cervical spine flexion.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(18):E388-393.[15] Liu J, Ebraheim NA, Sanford CG Jr,et al. Preservation of the spinous process-ligament-muscle complex to prevent kyphotic deformity following laminoplasty.Spine J. 2007;7(2): 159-164. [16] Stemper BD, Marawar SV, Yoganandan N,et al.Quantitative anatomy of subaxial cervical lateral mass: an analysis of safe screw lengths for Roy-Camille and magerl techniques.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(8):893-897.[17] Xin XH,Wu Q,Tang HJ,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(4):662-666.席新华,吴强,唐华军,等.成人下颈椎椎体与关节突关节倾角的X射线测量数据[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(4): 662-666.[18] Chu G,Bai JP,Xilin•Baoleri. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(13):2460-2464.楚戈,白靖平,锡林•宝勒日,等.无X射线引导下颈椎侧块钉置入技术的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(13): 2460-2464.[19] Barrey C, Mertens P, Rumelhart C,et al. Biomechanical evaluation of cervical lateral mass fixation: a comparison of the Roy-Camille and Magerl screw techniques.J Neurosurg. 2004;100(3 Suppl Spine):268-276.[20] Chiewvit P, Tritrakarn SO, Phawjinda A,et al. Predictive value of magnetic resonance imaging in cervical spondylotic myelopathy in prognostic surgical outcome.J Med Assoc Thai. 2011;94(3):346-354.[21] Cho WS, Chung CK, Jahng TA,et al. Post-laminectomy kyphosis in patients with cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament : does it cause neurological deterioration. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008;43(6):259-264.[22] Greiner-Perth R, Elsaghir H, Böhm H,et al. The incidence of C5-C6 radiculopathy as a complication of extensive cervical decompression: own results and review of literature. Neurosurg Rev. 2005;28(2):137-142.[23] Nassr A, Eck JC, Ponnappan RK,et al.The incidence of C5 palsy after multilevel cervical decompression procedures: a review of 750 consecutive cases.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(3):174-178.[24] Sakaura H, Hosono N, Mukai Y,et al. C5 palsy after decompression surgery for cervical myelopathy: review of the literature.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(21):2447-2451.[25] Hashimoto M, Mochizuki M, Aiba A,et al. C5 palsy following anterior decompression and spinal fusion for cervical degenerative diseases. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(10):1702-1710.[26] Kong Q, Zhang L, Liu L,et al. Effect of the decompressive extent on the magnitude of the spinal cord shift after expansive open-door laminoplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(13):1030-1036.[27] Minoda Y, Nakamura H, Konishi S,et al. Palsy of the C5 nerve root after midsagittal-splitting laminoplasty of the cervical spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(11):1123-1127.[28] Imagama S, Matsuyama Y, Yukawa Y,et al. C5 palsy after cervical laminoplasty: a multicentre study.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(3):393-400.[29] Zhang W,Li PF,Yang DL,et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2011;19(1):11-14.张为,李鹏飞,杨大龙,等.颈椎后路减压术后脊髓后移的临床意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(1):11-14.[30] Iizuka H, Nakajima T, Iizuka Y,et al. Cervical malalignment after laminoplasty: relationship to deep extensor musculature of the cervical spine and neurological outcome.J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;7(6):610-614.[31] Rhee JM, Register B, Hamasaki T,et al. Plate-only open door laminoplasty maintains stable spinal canal expansion with high rates of hinge union and no plate failures.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(1):9-14.[32] Zhang CL,Jiang Y,Zhong CN,et al. Zhengzhou Daxue Xuebao: Yixueban. 2007;43(2):584-586.张春霖,姜岩,钟楚楠,等.脊髓型颈椎病钛板双向固定颈椎管扩大成形术治疗58例体会[J].郑州大学学报:医学版,2007,43(2): 584-586.[33] Takeuchi K, Yokoyama T, Aburakawa S,et al. Axial symptoms after cervical laminoplasty with C3 laminectomy compared with conventional C3-C7 laminoplasty: a modified laminoplasty preserving the semispinalis cervicis inserted into axis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(22):2544-2549.[34] Hosono N, Sakaura H, Mukai Y,et al. C3-6 laminoplasty takes over C3-7 laminoplasty with significantly lower incidence of axial neck pain.Eur Spine J. 2006;15(9):1375-1379.[35] Fujibayashi S, Neo M, Yoshida M,et al. Neck muscle strength before and after cervical laminoplasty: relation to axial symptoms.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(3):197-202.[36] Takeshita K, Seichi A, Akune T,et al. Can laminoplasty maintain the cervical alignment even when the C2 lamina is contained. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(11):1294-1298.[37] Iizuka H, Nakajima T, Iizuka Y,et al.Cervical malalignment after laminoplasty: relationship to deep extensor musculature of the cervical spine and neurological outcome.J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;7(6):610-614.[38] Kotani Y, Abumi K, Ito M,et al. Minimum 2-year outcome of cervical laminoplasty with deep extensor muscle-preserving approach: impact on cervical spine function and quality of life.Eur Spine J. 2009;18(5):663-671.[39] Dong FL,Shen CL,Jiang S,et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2008;16(9):682-686,701.董福龙,申才良,江曙,等.颈椎椎管容积的动态CT测量及其临床意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(9):682-686,701. |
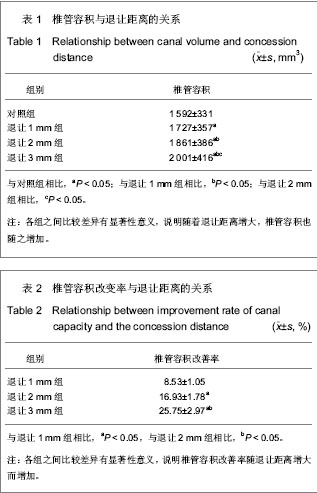
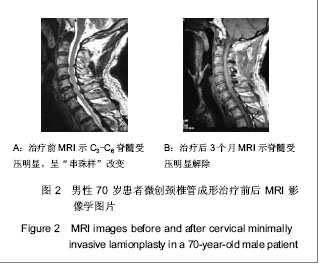
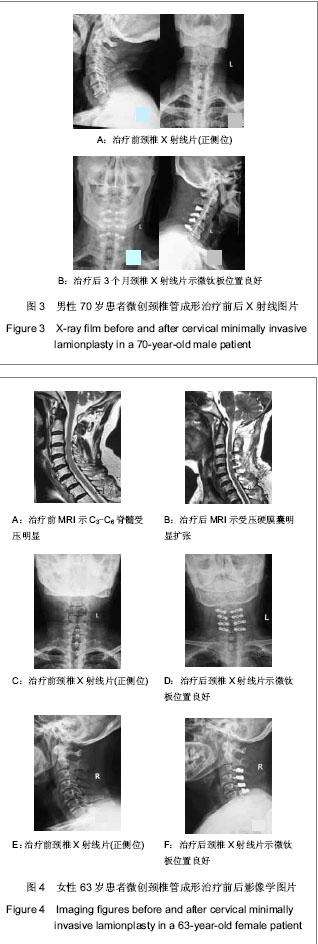
.jpg)