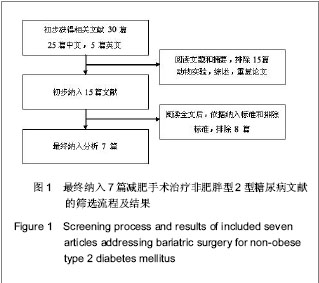
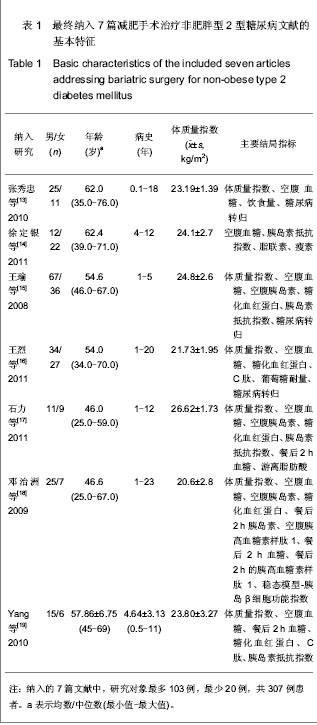
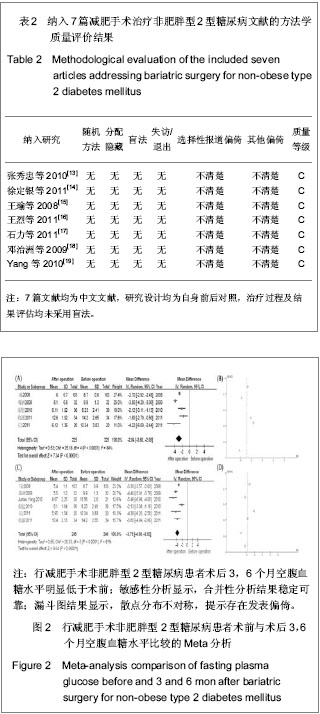
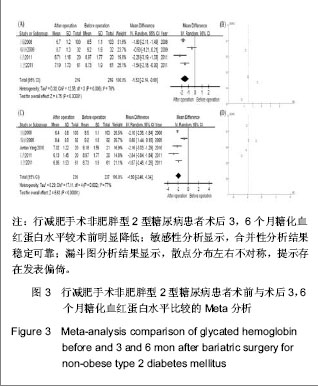
| [1] Zimmet P, Shaw J, Alberti KG. Preventing type 2 diabetes and the dysmetabolic syndrome in the real world: a realistic view. Diabet Med. 2003; 20(9): 693-702. [2] Yang W, Lu J, Wang J, et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in china. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(12): 1090-1101. [3] Mihardja L, Delima, Manz HS, et al. Prevalence and determinants of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance in Indonesia (a part of basic health research/riskesdas). Acta Med Indones. 2009;41(4): 169-174. [4] Zeng W, Huang XB, Jia Y, et al. Zhongguo Gonggong Weisheng. 2010;26(9): 1095-1097.曾伟, 黄晓波, 贾勇, 等. 不同肥胖指标对糖尿病风险预测效果分析[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2010, 26(9): 1095-1097. [5] Wang Z, Zhang H, Shen XH, et al. Zhongguo Gonggong Weisheng. 2010;28(6): 759-762.王珍, 张红, 沈旭慧, 等. 心血管病传统危险因素与糖尿病及其前期关系[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2010, 28(6): 759-762.[6] Dixon JB, O’Brien PE, Playfair J, et al. Adjustable gastric banding and conventional therapy for type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2008;299(3): 316-323. [7] Buchwald H, Williams SE. Bariatric surgery worldwide 2003. Obes Surg. 2004;14(9): 1157-1164. [8] Cummings DE, Flum DR. Gastrointestinal surgery as a treatment for diabetes. JAMA. 2008;299(3): 341-343. [9] Buchwald H, Estok R, Fahrbach K, et al. Weight and type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2009;122(3): 248-256. [10] Wang K, Gong J, Yang GC, et al. Yixue Linchuang Yanjiu. 2012;29(7): 1234-1238.王坤, 宫建, 杨国春, 等. 中国大陆地区胃转流手术治疗2型糖尿病的Meta分析[J]. 医学临床研究, 2012, 29(7): 1234-1238. [11] Higgins J, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1. 0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2011. [12] Cui W, Gong J, Wang Q, et al. Myocardial Protection with Sevofurane in Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Surgery. Pak J Med Sci. 2012; 28(4): 761-766. [13] Zhang XZ, Ren ZQ, Zhang PB. Shandong Yiyao. 2010;50(44): 89-90.张秀忠, 任泽强, 张蓬波. 胃转流术对非肥胖型2型糖尿病的降糖效果[J]. 山东医药, 2010, 50(44): 89-90. [14] Xu DY, Jin K, Dai HW. Shiyong Yixue Zazhi. 2011;27(5): 795-797.徐定银, 金凯, 戴华卫. 胃转流手术对2型糖尿病患者糖代谢的影响[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2011, 27(5): 795-797. [15] Wang Y, Wang YT, Wang L. Zhongguo Putong Waike Zazhi. 2008;17(10): 1003-1006.王瑜, 王燕婷, 王烈. 胃转流术对非肥胖型2型糖尿病的治疗作用[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2008, 17(10): 1003-1006. [16] Wang L, Zhang ZZ, Huang S, et al. Zhongguo Shiyong Waike Zazhi. 2011;31(3): 234-237.王烈, 张再重, 黄盛, 等. 不同吻合方式胃转流术对2型糖尿病疗效对比研究[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2011, 31(3): 234-237.[17] Shi L, Tang LJ, Chen T, et al. Zhongguo Putong Waike Zazhi. 2011;20(9): 960-962.石力, 汤礼军, 陈涛, 等. 2型糖尿病患者胃转流术后游离脂肪酸的改变及其意义[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2011, 20(9): 960-962.[18] Deng ZZ, Wang L, Lin YY, et al. Zhongguo Puwai Jichu yu Linchuang Zazhi. 2009;16(6): 466-469.邓治洲, 王烈, 林忆阳, 等. 胃转流术对非肥胖型2型糖尿病的疗效观察及其对胰高血糖素样肽-1的影响[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2009, 16(6): 466-469.[19] Yang J, Li C, Liu H, et al. Effects of subtotal gastrectomy and roux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy on the clinical outcome of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Surg Res. 2010;164: e67-e71. [20] Cummings DE, Overduin J, Foster-Schubert KE.Gastric bypass for obesity: mechanisms of weight loss and diabetes resolution. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(6): 2608-2015.[21] Zhang YD, Tang XJ, Li G, et al. Zhongguo Gonggong Weisheng. 2010;26(9): 1112-1113.张阳丹, 唐晓君, 李革, 等. 肥胖及血脂异常与2型糖尿病关系[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2010, 26(9): 1112-1113.[22] Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(6): 393-403. [23] Jia WP, Xiang KS, Chen L, et al. Epidemiological study on obesity and its comorbidities in urban Chinese older than 30 years of age in Shanghai, China. Obes Rev. 2002;3(3): 157-165.[24] Qiu H, Zhang MR, Tian R, et al. Zhongguo Gonggong Weisheng. 2009;25(12): 157-165.邱泓, 张茂镕, 田荣, 等. 昆明市糖尿病患病情况及危险因素分析[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2009, 25(12): 157-165.[25] Nkondjockl A, Reeveu O. Fish-seafood consumption,obesity,and risk of type 2 diabetes: an ecological study.Diabetes Metab. 2003;29(6):635-642. [26] Lyssenko V, Lupi R, Marchetti P, et al. Mechanisms by which common variants in the TCF7L2 gene increase risk of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(8): 2155-2163. [27] Nauck MA, Kemmeries G, Holst JJ, et al. Rapid tachyphylaxis of the glucagon-like peptide 1-induced deceleration of gastric emptying in humans. Diabetes. 2011;60(5):1561-1565. [28] Gong J. Xibu Yixue. 2012;24(12): 352-355.宫建. 循证医学中“循证”问题的探讨[J]. 西部医学, 2012, 24(12): 352-355. [29] Gong J, Pan W, Huang XY, et al. Zhongguo Xunzheng Yixue Zazhi. 2012;24(12): 352-355.宫建, 潘雯, 黄晓艳, 等. 中国内地2型糖尿病患者胃转流术后1年疗效的Meta分析[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2012, 24(12): 352-355. [30] Zheng X. Zhongguo Gonggong Weisheng. 2011;27(7): 937-938.郑新. 地方性氟中毒与农村学龄儿童氟斑牙关系Meta分析[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2011, 27(7): 937-938.[31] Yu HH, Shi JP. Zhongguo Gonggong Weisheng. 2011;27(9): 1195-1196.于慧会, 时景璞. 汉族人群ApoA5基因多态性与冠心病关联Meta分析[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2011, 27(9): 1195-1196. |