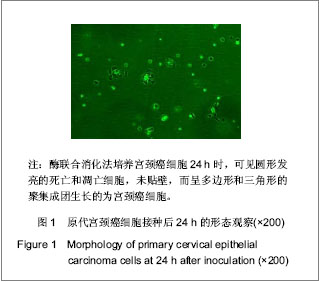
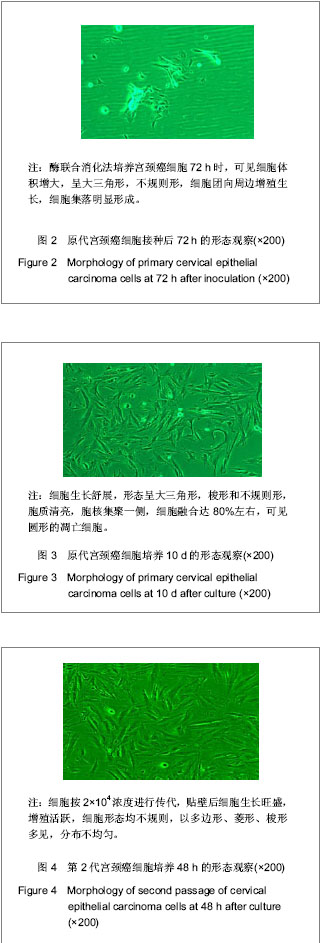
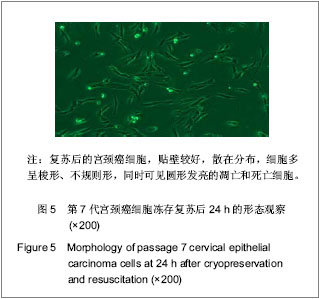
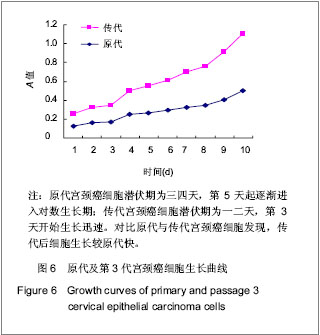
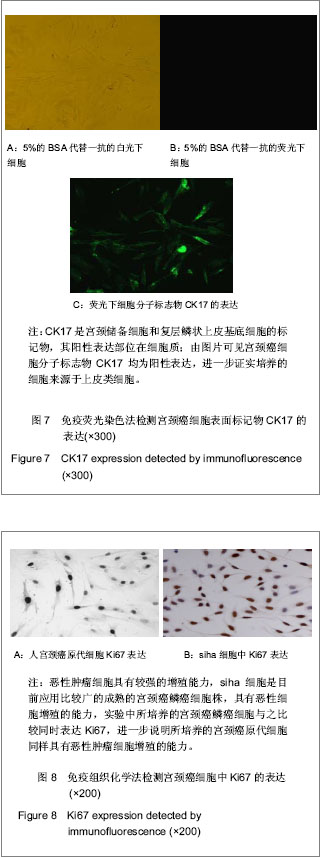
| [1] Situ ZQ,Wu JZ. Xi’an: Xi’an world Publishing Corporation. 2004:33-320.司徒镇强,吴军正.细胞培养[M].西安:世界图书出版社,2004: 33-320.[2] Ma XP,Cheng JX,Zhang Y,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(11):1959-1962.马秀萍,程静新,张瑜,等.人宫颈癌细胞的体外培养及鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(11):1959-1962.[3] E Z.Beijing: Peking Union Medical College Press. 2004: 311-321.鄂征.组织培养技术及其在医学研究中的应用[M].北京:中国协和医科大学出版社, 2004: 311-321.[4] Ding L,Yang YG,Mei X,et al. Zhenduan Binglixue Zazhi. 2009; 16(3):174-176.丁岚,杨永国,梅霞,等. CK17和p16在宫颈鳞状上皮不成熟化生和宫颈上皮内瘤变中的表达及意义[J].诊断病理学杂志,2009, 16(3):174-176.[5] Regauer S, Reich O.CK17 and p16 expression patterns distinguish (atypical) immature squamous metaplasia from high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN III). Histopathology. 2007;50(5):629-6.[6] Wang CH. Zhongguo Xiandai Yisheng. 2010; 48(16): 14-15, 19.王川红. 宫颈癌中p- STAT3与Ki67的表达与意义[J].中国现代医生, 2010, 48(16): 14-15, 19. [7] Fan SZ,Yuan ZF. Zhengzhou Daxue Xuebao. 2010;45(1): 81-84.樊素珍,苑中甫. 宫颈癌组织中Annexin A2和Ki-67蛋白的表达[J].郑州大学学报,2010,45(1):81-84.[8] Pectasides D, Kamosioras K, Papaxoinis G, et al. Chemotherapy for recurrent cervical cancer. Cancer Treatment Reviews. 2008; 34(7): 603-613.[9] Zhao EF, Bao L, Li C,et al. Changes in epidemiology and clinical characteristics of cervical cancer over the past 50 years.Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao. 2005;25(6):605-609.[10] Qin JL,Gulinar Kuerban,Meiliban Tuerxun,et al.Jiepou Kexue Jinzhan. 2010; 16(2): 113-116, 120.秦积龙, 古力娜尔•库尔班, 美力班•吐尔逊, 等. 新疆维吾尔族妇女宫颈上皮内瘤变及宫颈癌中FHIT、P16INK4a、RARβ蛋白的表达及意义[J]. 解剖科学进展, 2010, 16(2): 113-116, 120.[11] Meiliban Tuerxun, Gulinar Kuerban, Qin JL,et al. Jiepou Kexue Jinzhan. 2011; 17(3): 206-210.美力班•吐尔逊, 古力娜尔•库尔班, 秦积龙, 等. 新疆维吾尔族妇女宫颈上皮内瘤变及宫颈癌中树突状细胞的检测及意义[J]. 解剖科学进展, 2011, 17(3): 206-210.[12] Yang J,Chen XL,Su BS,et al. Xi’an Jiaotong Daxue Xuebao. 2008; 29(6): 717-719.杨军,陈晓黎,苏宝山,等.增强型绿色荧光蛋白标记的Hela细胞株的建立[J].西安交通大学学报:医学版, 2008, 29(6): 717-719.[13] Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF,et al. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells.Nature. 2001;414(6859):105-111.[14] Marx J.Cancer research. Mutant stem cells may seed cancer. Science. 2003;301(5638):1308-1310.[15] Couzin J. Tracing the steps of metastasis, cancer's menacing ballet.Science. 2003;299(5609):1002-1006.[16] Al-Hajj M, Becker MW, Wicha M, et al. Therapeutic implications of cancer stem cells.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004; 14(1):43-47.[17] Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF,et al. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells.Nature. 2001;414(6859):105-111.[18] Jiang SQ,Tu SA,Zhou JL,et al. Zhongguo Fuyou Baojian. 2006; 21(4): 524-526.姜淑清,土送爱,周俊兰,等. 新疆策勒县妇女病现状调查与分析[J].中国妇幼保健,2006, 21(4): 524-526.[19] Ablimit Tangnur,Turgan Muyassaer, Abliz Guzalnur,et al.Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi. 2011;32(5): 477-480.唐努尔•阿布力米提, 穆也沙尔•吐尔干, 古扎丽努尔•阿不力孜,等. 新疆宫颈癌高发区维吾尔族人群人乳头瘤病毒亚型的研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2011,32(5): 477-480.[20] Rockett JC, Larkin K, Darnton SJ, et al. Five newly established oesophageal carcinoma cell lines: phenotypic and immunological characterization. Br J Cancer. 1997;75(2): 258-263.[21] Zhao XF,Wang JK,Zhang XL,et al. Hebei Beifang Yixue Xuebao. 2007;24(1):35-37.赵秀芳,王金科,张晓丽,等.乳腺癌原代细胞培养及化疗药敏的研究[J].河北北方医学学报,2007,24(1):35-37.[22] Lu ZT,Li M,Zou ZQ,et al. Guoji Zhongliuxue Zazhi. 2008;35(7): 553-556.卢兆桐,李明,邹志强,等. 食管癌细胞体外培养药敏试验与P—gp、LRP表达的相关性研究[J].国际肿瘤学杂志,2008,35(7): 553-556.[23] Liu DC,Guo YH. Xiandai Zhongliu Yixue. 2009;17(4):699-701.刘德传,郭以河.MTT 法测定大肠癌对化疗药物敏感性的实验研究[J].现代肿瘤医学,2009,17(4):699-701.[24] Hao WP,Yao YS,Wang JW,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(50):9348-9351.郝维平,姚友生,王家伟,等.人类膀胱移行上皮细胞的体外培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(50): 9348-9351.[25] Cai HY,Yu B,Bai X,et al. Linchuang Junyi Zazhi. 2011;39(4): 611-612.蔡慧云,于波,白雪,等.简便人大肠癌原代细胞培养方法的探讨[J].临床军医杂志, 2011,39(4):611-612.[26] Fang LJ,Song E,Luan Y,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(45):8450-8454.方立建,宋鄂,栾瑛,等.人脐带血内皮祖细胞体外培养和鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(45):8450-8454.[27] Liu N,Hu C,Ren Y,et al. Yatai Chuantong Yiyao. 2011;7(3): 12-14.刘念,胡超,任野,等.人子宫内膜细胞体外培养技术的改良研究[J].亚太传统医药,2011,7(3):12-14 |