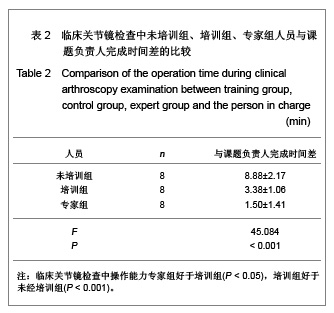
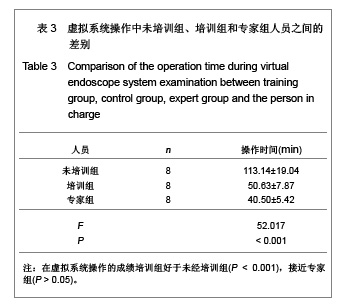
| [1] Wang LD.Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2009;17 (19): 1447-1448. 王立德.我国膝关节镜外科发展的历史进程[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009,17(19):1447-1448.[2] Bigony L. Arthroscopic surgery: a historical perspective. Orthopaedic Nursing.2008;27(6):349-354,quiz 355-356.[3] Andersen C, Winding TN, Vesterby MS. Development of simulated arthroscopic skills. Acta Orthop.2011;82(1): 90-95. [4] Zhang H.Xibei Yixue Jiaoyu. 2010;18(01):48-51. 张晗.虚拟现实技术在医学教育中的应用探讨[J].西北医学教育, 2010,18(01):48-51. [5] Rosen JM, Soltanian H, Redett R, et al.Evolution of virtural reality. IEEE Engineering in Medical and Biology.1996;15(2): 16-22. [6] Justo-Janeiro JM, Pedroza-Meléndez A, et al.A new laparoscopic simulator. Cir Cir. 2007;75(1):19-23.[7] Pedowitz RA, Esch J, Snyder S. Evaluation of a virtual reality simulator for arthroscopy skills development. Arthroscopy. 2002;18:E2[8] Verdaasdonk EG, Stassen LP, Schijven MP, et al. Construct validity and assessment of the learning curve for the SIMENDO endoscopic simulator. Surg Endosc. 2007;21(8): 1406-1412. [9] Maher SA, Rodeo SA, Doty SB, et al. Evaluation of a porous polyurethane scaffold in a partial meniscal defect ovine model. Arthroscopy. 2010; 26(11):1510-1519. [10] Scanzello CR, McKeon B, Swaim BH, et al. Synovial inflammation in patients undergoing arthroscopic meniscectomy: molecular characterization and relationship to symptoms. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(2):391-400. [11] Thein R, Haviv B, Kidron A, et al. Intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid following arthroscopic partial meniscectomy of the knee. Orthopedics. 2010;33(10):724. [12] Han SB, Shetty GM, Lee DH, et al. Unfavorable results of partial meniscectomy for complete posterior medial meniscus root tear with early osteoarthritis: a 5- to 8-year follow-up study. Arthroscopy. 2010; 26(10):1326-1332. [13] Sturnieks DL, Besier TF, Mills PM, et al. Knee joint biomechanics following arthroscopic partial meniscectomy. J Orthop Res. 2008; 26(8):1075-1080.[14] Bu JM,Fan LH,Xiao Y.Zhongguo Yiliao Shebei. 2009;24(11): 62-63,47. 步金梅,范林华,肖毅.计算机仿真技术在临床教学中的应用研究[J].中国医疗设备,2009;24(11):62-63,47. [15] Howell SM. The role of arthroscopy in treating osteoarthritis of the knee in the older patient. Orthopedics. 2010;33(9):652. [16] Spahn G, Klinger HM, Mückley T, et al. Four-year results from a randomized controlled study of knee chondroplasty with concomitant medial meniscectomy: mechanical debridement versus radiofrequency chondroplasty. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(9 Suppl):S73-80.[17] Netravali NA, Giori NJ, Andriacchi TP. Partial medial meniscectomy and rotational differences at the knee during walking. J Biomech. 2010;43(15): 2948-2953. [18] Zhang Y,Liu GT,Zhang ZH.Zhongguo Yiliao Shebei. 2010; 25(06):69-71,74. 张媛,刘国通,张志华.消化内镜模拟训练系统在医师培训中的应用[J].中国医疗设备,2010,25(06):69-71,74. [19] Fisher L, Ormonde DG, Riley RH, et al. Endoscopic skills training in a simulated clinical setting. Simul Healthc. 2010;5(4):232-237.[20] López-Vázquez E, Juan JA, Vila E, et al.Reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament with a Dacron prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73(9):1294-300[21] Tan K,Guo GY,Pan XH,et al.Jisuanji Fangzhen. 2009;26(12): 290-293,324. 谭珂,郭光友,潘新华,等.膝关节镜手术仿真训练系统设计[J].计算机仿真,2009,26(12):290-293,324.[22] Luo W,Li SS.Shengwu Yixue Gongchengxue Jinzhan. 2010; 31(03):149-152. 罗伟,李珊珊.仿真手术刀在虚拟外科手术系统中的应用与研究[J].生物医学工程学进展,2010,31(03):149-152. [23] Gketsis ZE, Tzagkas D, Hatzilias PV, et al. Laparoscopic image analysis for robotic arm guidance. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006;1:148-151.[24] Wang YK, Zhu JF. Zhangauo Weichuang Waike Zazhi. 2010; 10(3):278-280. 王永坤,朱江帆.虚拟内镜技术在消化系统疾病诊断中的应用[J].中国微创外科杂志,2010,10(03):278-280.[25] Spahn G, Klinger HM, Mückley T, et al.Four-year results from a randomized controlled study of knee chondroplasty with concomitant medial meniscectomy: mechanical debridement versus radiofrequency chondroplasty. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(9 Suppl):S73-80.[26] Netravali NA, Giori NJ, Andriacchi TP. Partial medial meniscectomy and rotational differences at the knee during walking. J Biomech. 2010;43(15): 2948-2953. [27] Stein T, Mehling AP, Welsch F, et al. Long-term outcome after arthroscopic meniscal repair versus arthroscopic partial meniscectomy for traumatic meniscal tears. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(8):1542-1548. [28] Justo-Janeiro JM, Pedroza-Meléndez A, et al.A new laparoscopic simulator. Cir Cir. 2007;75(1):19-23.[29] Vosburgh KG, San José Estépar R,et al. Natural Orifice Transluminal Endoscopic Surgery (NOTES): an opportunity for augmented reality guidance. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2007;125:485-490.[30] Xiong YS, Xu K, Wang YZ, et al. Guofang Keji Daxue Xuebao. 2007;29(1):66-72. 熊岳山,徐凯,王彦臻,等.虚拟膝关节镜手术仿真系统的关键技术研究[J].国防科技大学学报,2007,29(1):66-72.[31] Xie XH, Chen WJ. Xiandai Dianzi jishu. 2012,35(18):139-145. 谢晓辉,陈为坚.虚拟关节内窥镜手术训练系统[J].现代电子技术, 2012,35(18):139-145.[32] Fan LD, Li SG, Zhang ZG, et al. Chang shang Waike Zazhi. 2008;10(6):567-570. 范立冬,李曙光,张治刚,等.虚拟现实技术在医学训练中的应用[J].创伤外科杂志,2008,10(6):567-570. |