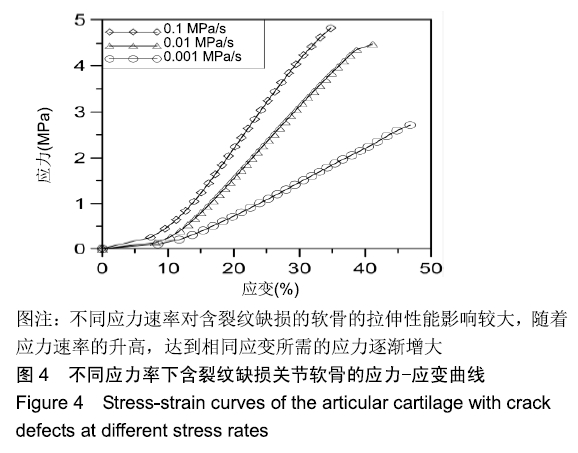
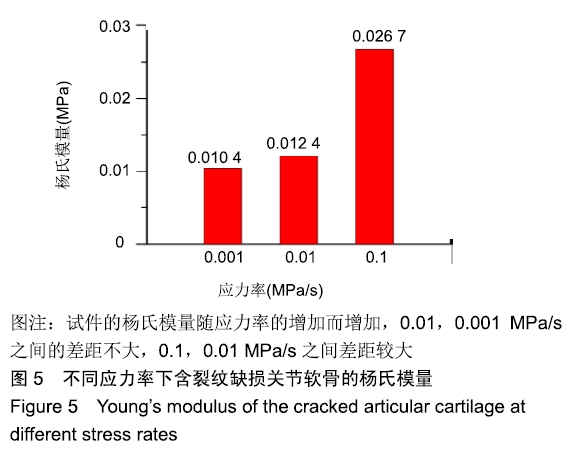
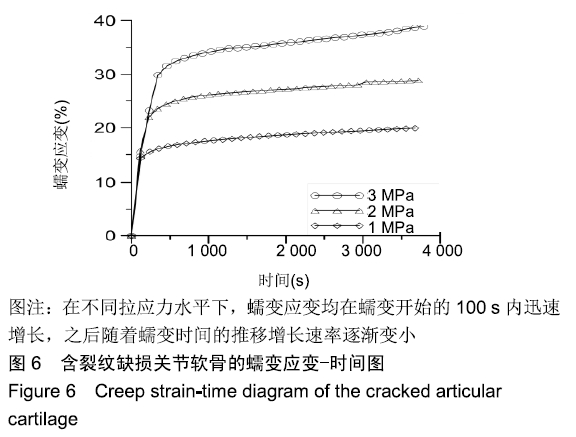
[1] CHEN D, SHEN J, ZHAO W, et al.Osteoarthritis: toward a comprehensive understanding of pathological mechanism. Bone Res.2017;5:16044.
[2] ALTMAN RD, MANJOO A, FIERLINGER A, et al.The mechanism of action for hyaluronic acid treatment in the osteoarthritic knee:a systematic review.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2015;16(1):321.
[3] ZAITSEVA EM, ALEXEEVA LI.Knee joint osteoarthrosis:Risk factors of rapid progression.Ter Arkh.2012;84(5):42-45.
[4] 陈焱,单德龙,秦春耀,等.关节镜下成形联合缝合术治疗不稳定型外侧盘状半月板临床分析[J].系统医学,2017,2(6):37-39.
[5] JULIEN F,JOLLES BM.Gait analysis of patients with knee osteoarthritis highlights a pathological mechanical pathway and provides a basis for therapeutic interventions.EFORT Open Rev. 2016;1(10):368-374.
[6] 寇海龙.骨关节炎病人关节软骨中HIF,VEGF,MEF2C的表达及意义[D].兰州:兰州大学,2016.
[7] BRODY LT.Knee osteoarthritis:Clinical connections to articular cartilage structure and function.Phys Ther Sport. 2015;16(4): 301-316.
[8] HOSSEINI SM, WU Y, ITO K, et al.The importance of superficial collagen fibrils for the function of articular cartilage.Biomech Model Mechanobiol.2014;13(1):41-51.
[9] GAO LL, QIN XY, ZHANG CQ, et al.Ratcheting behavior of articular cartilage under cyclic unconfined compression.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2015;57:371-377.
[10] 张子峰.关节软骨-软骨下骨界面的形态学特征和力学意义[D].上海:上海交通大学,2011.
[11] 那键,刘艺,马克勇,等.老年性骨关节炎的分子生物学机制及治疗展望[J].中国老年学杂志,2010,30(20):3035-3037.
[12] 陈凯,张德坤,戴祖明,等.牛膝关节软骨的力学承载特性及其有限元仿真分析[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(6):675-680.
[13] HAYES WC, MOCKROS LF.Viscoelastic properties of human articular cartilage.J Appl Physiol.1971;31(4):562-568.
[14] KELLY PA, O'CONNOR JJ.Transmission of rapidly applied loads through articular cartilage.Part 1:Uncracked cartilage.Proc Inst Mech Eng H.1996;210(1):27-37.
[15] 李振宇,马洪顺,姜鸿志.关节软骨力学性能实验研究[J].工程与试验, 1989,28(2):7-9.
[16] 余存泰,徐中和,黄公怡.应力导致关节软骨退变机制的实验研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2004,10(5):411-414.
[17] FLACHSMANN R, KISTLER M, RENTZIOS A, et al.Influence of an Initiating Microsplit on the Resistance to Compression- Induced Rupture of the Articular Surface.Connect Tissue Res. 2006;47(2):77-84.
[18] 李源尚.猪髌骨关节软骨压痕力学性能及粘弹性研究[D].长春:吉林大学, 2018.
[19] SADEGHI H, SHEPHERD DET, ESPINO DM.Effect of the variation of loading frequency on surface failure of bovine articular cartilage.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2015;23(12):2252-2258.
[20] 李锋,李元超,贾晓峰,等.关节软骨模拟运动摩擦磨损行为研究[J].摩擦学学报,2011,31(1):30-35.
[21] 周海宇.关节软骨的生物摩擦学机理研究[D].上海:上海交通大学, 2014.
[22] 钱善华,刘利国,倪自丰,等.两种润滑介质下关节软骨摩擦行为的对比研究[J].摩擦学学报,2013,33(5):488-494.
[23] 李锋,王安敏,王成焘.天然关节软骨与医用不锈钢摩擦磨损行为研究[J].摩擦学学报,2016,36(1):42-47.
[24] WANG CC, DENG JM, ATESHIAN GA, et al.An automated approach for direct measurement of two-dimensional strain distributions within articular cartilage under unconfined compression.J Biomech Eng. 2002;124(5):557-567.
[25] MEDER R, VISSER SKD, BOWDEN JC, et al.Diffusion tensor imaging of articular cartilage as a measure of tissue microstructure. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2006;14(9):875-881.
[26] 刘志动,高丽兰,张春秋,等.关节软骨不同层区的率相关性能研究[J].医用生物力学,2014,29(2):141-145.
[27] SADEGHI H, LAWLESS BM, ESPINO DM, et al.Effect of frequency on crack growth in articular cartilage.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;77:40-46.
[28] 张学喜.关节软骨的红外光谱显微成像及偏最小二乘法应用研究[D].南京:南京航空航天大学,2016.
[29] MENG Q, AN S, DAMION RA, et al.The effect of collagen fibril orientation on the biphasic mechanics of articular cartilage.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2017;65:439-453.
|