| [1] Drake MT, Clarke BL, Lewiecki EM. The Pathophysiology and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Clin Ther. 2015;37(8):1837-1850.[2] Jilka RL, O'Brien CA, Roberson PK, et al. Dysapoptosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes increases cancellous bone formation but exaggerates cortical porosity with age. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(1):103-117.[3] 章振林,金小岚,夏维波.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017版)要点解读[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2017,10(5): 411-412.[4] Jonasson G, Rythén M. Alveolar bone loss in osteoporosis: a loaded and cellular affair. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2016;8: 95-103.[5] 宋慧婷,侯建明.骨髓间充质干细胞对骨质疏松的治疗作用概述[J].创伤与急诊电子杂志, 2017,5(1):40-43.[6] 张娜,符晓华,于才红,等.不同体重雌性大鼠对维甲酸反应的研究[J].湖南师范大学学报(医学版), 2008, 5(4):28-30,32.[7] 杨娟,张锡宝.维甲酸受体及其作用机制研究进展[J].皮肤性病诊疗学杂志, 2014,21(5):423-426.[8] 孙宇强,王雪,关兴芳,等.维甲酸及其受体与肿瘤关系的研究进展[J].生命科学, 2014, 26(3): 295-301.[9] Yang J, Wu N, Peng J, et al. Prevention of retinoic acid-induced osteoporosis in mice by isoflavone-enriched soy protein. J Sci Food Agric. 2016;96(1):331-338.[10] Allen SP, Maden M, Price JS. A role for retinoic acid in regulating the regeneration of deer antlers. Dev Biol. 2002; 251(2):409-423.[11] 潘理平,曾茜.治疗骨质疏松症药物及其不良反应[J].药学实践杂志, 2006, 24(6):328-330.[12] 张雅蓉,唐舸,刘杉,等.5种常用大鼠骨质疏松动物模型的特点[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2013,40(5):629-633.[13] 杜一飞,周薇娜,胡旭,等.去势法大鼠骨质疏松症模型建立的探讨[J].口腔医学,2010, 30(7):399-401.[14] 王键,龚颜,曾荣,等.去势雌性大鼠骨质疏松模型的研究[J].海南医学,2013, 24(3):424-426.[15] 许鹏,郭雄,张银刚,等. 维甲酸诱导骨质疏松模型大鼠的效果及机理[J].四川大学学报(医学版), 2005, 36(2):229-232.[16] 朱虎虎,孙炜,孙建新,等.维甲酸诱导雌性大鼠骨质疏松模型建立的效果观察[J].当代医学, 2013,19(14):24-26.[17] Ranhotra HS. The interplay between retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptors and human diseases. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2012;32(4):181-189.[18] 贾启生,何华伟,郑东翔.小鼠骨质疏松模型成骨细胞的体外特征研究[J].北京口腔医学, 2016, 24(3):138-141.[19] Liu Q, Zhang X, Jiao Y, et al. In vitro cell behaviors of bone mesenchymal stem cells derived from normal and postmenopausal osteoporotic rats. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(2): 669-678.[20] Pino AM, Rosen CJ, Rodríguez JP. In osteoporosis, differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) improves bone marrow adipogenesis. Biol Res. 2012;45(3):279-287.[21] 郭鱼波,马如风,王丽丽,等.骨质疏松动物模型及其评价方法的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015,21(9):1149-1154.[22] 刘绪立.兔骨质疏松模型的快速建立和硫酸钙复合bBMP在椎体强化中的实验研究[D]. 西安:第四军医大学, 2009.[23] 虞惊涛,马信龙,马剑雄.骨质疏松动物模型评价方法[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2014,7(1):66-70.[24] 莫文秋.骨质疏松动物模型评价方法的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2016, 22(7):1330-1332.[25] 贾婷婷,张云涛,刘顺振,等. 维甲酸诱导大鼠骨质疏松模型的制作[J].口腔医学研究, 2012, 28(5):420-422.[26] 代学俊,岑蔼儿,张春梅,等. 骨质疏松症抑制人间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2014, 35(5):723-729.[27] 李良,李冬菊,吴江,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞在去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松发病机理中潜在的作用[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2006,23(1): 129-135.[28] 逯伟达.人骨髓间充质干细胞来源的脂肪细胞抑制成骨细胞分化的机制研究[D].济南:山东大学, 2012.[29] 王勇平,廖燚,蒋垚.成骨细胞的体外培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2011, 15(33):6231-6234.[30] 李娟,申广浩,程光,等.组织块法培养SD大鼠的成骨细胞及鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(46):8571-8574.[31] Wang A, Ding X, Sheng S, et al. Retinoic acid inhibits osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;375(3):435-439.[32] 何倩婷,盛士虎,陈丹,等.全反式维甲酸诱导大鼠骨髓间充质细胞脂肪化[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版), 2010,4(6): 577-582.[33] 黄帆,刘映孜,杨秋珺,等.全反式维甲酸增强骨形态蛋白9诱导间充质干细胞成骨分化作用[J].第三军医大学学报, 2013,35(4): 328-331.[34] 李清,邹丽影,曾嘉颖,等.全反式维甲酸抑制大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化信号通路中Fosl1直接调控PPARγ2[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2017, 33(6):1104-1111.[35] 王云,梁辉,陶荣. ATRA对人骨髓间充质干细胞成脂肪细胞分化及瘦素生成的影响[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2010, 30(3):299-304. |
.jpg)
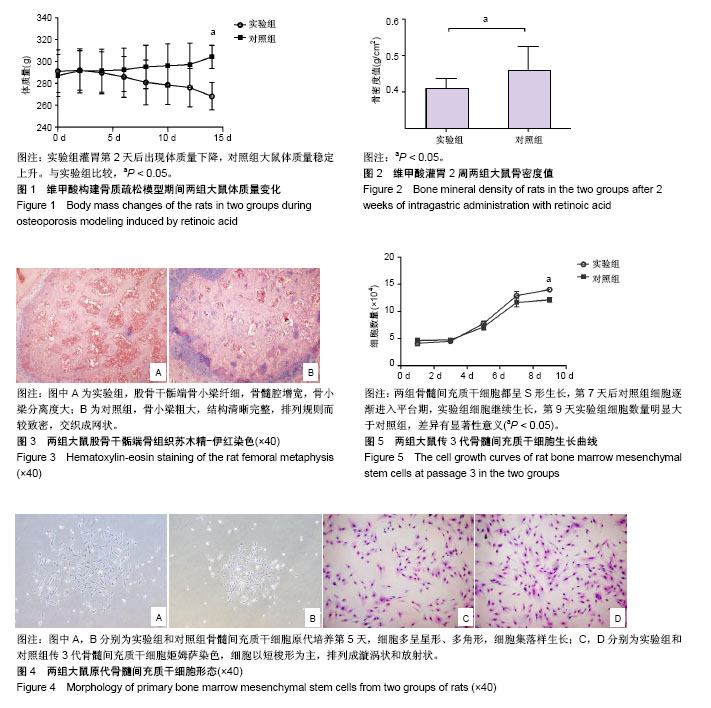
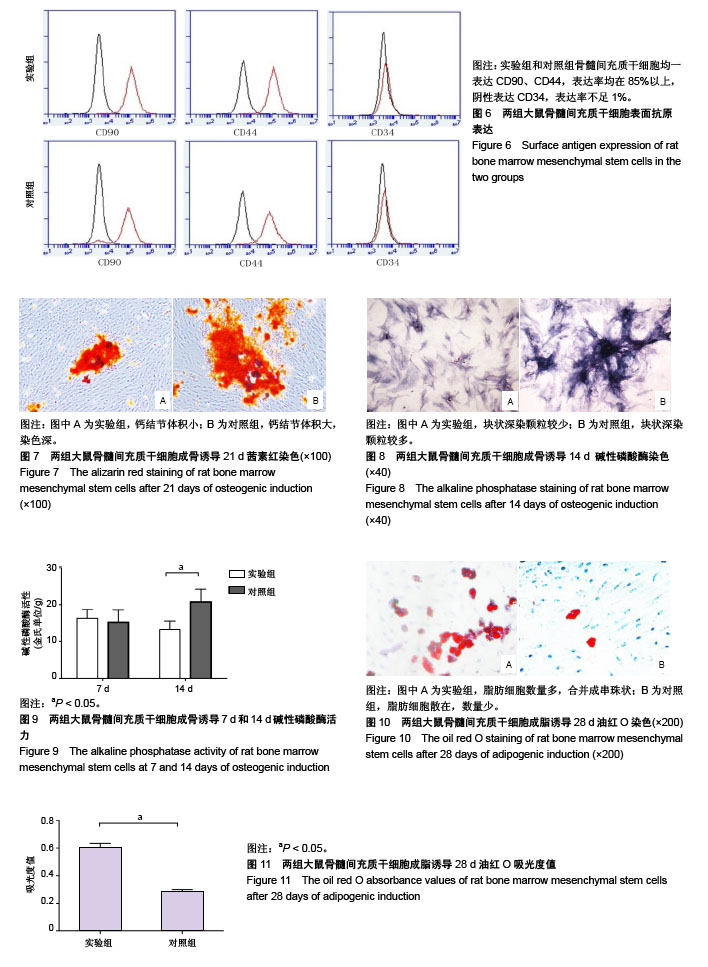
.jpg)
.jpg)