| [1] 马雄.原发性胆汁性肝硬化诊治进展[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2016, 32(4):21-22.[2] 田耀洲.难治性原发性胆汁性肝硬化治疗进展[C]. 重庆:中华中医药学会脾胃病分会第二十七届全国脾胃病学术交流会,2015.[3] 张静雯,时永全,韩英.肝硬化的治疗进展[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2015,31(3):465-468.[4] O'Grady JG. Liver transplantation. Jama. 2015; 43(11): 686-688.[5] Pangeni R, Sahni JK, Ali J, et al. Resveratrol: review on therapeutic potential and recent advances in drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014;11(8):1285-1298.[6] Faghihzadeh F, Hekmatdoost A, Adibi P. Resveratrol and liver: A systematic review. J Res Med Sci. 2015;20(8):797-810.[7] 罗德兰,杨丹,舒梅铃,等.白藜芦醇抗肝癌作用机制的研究进展[J].世界华人消化杂志,2014, 22(31):4769-4773.[8] Chan CC, Lee KC, Huang YH, et al. Regulation by resveratrol of the cellular factors mediating liver damage and regeneration after acute toxic liver injury. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29(3):603-613.[9] Tang Y, Gan X, Cheheltani R, et al. Targeted delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor improves stem cell therapy in a rat myocardial infarction model. Nanomedicine. 2014; 10(8):1711-1718.[10] Atashi F, Modarressi A, Pepper MS. The role of reactive oxygen species in mesenchymal stem cell adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation: a review. Stem Cells Dev. 2015; 24(10):1150-1163.[11] Jeong H, Yim HW, Cho YS, et al. Efficacy and safety of stem cell therapies for patients with stroke: a systematic review and single arm meta-analysis. Int J Stem Cells. 2014;7(2):63-69.[12] Bruin JE, Saber N, Braun N, et al. Treating diet-induced diabetes and obesity with human embryonic stem cell-derived pancreatic progenitor cells and antidiabetic drugs. Stem Cell Reports. 2015;4(4):605-620.[13] Morigi M, De Coppi P. Cell therapy for kidney injury: different options and mechanisms--mesenchymal and amniotic fluid stem cells. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2014;126(2):59.[14] 陆炼,于兵,胡以平.肝干细胞研究进展[J].第二军医大学学报, 2017,38(4):493-500.[15] Hardin H, Yu XM, Harrison AD, et al. Generation of Novel Thyroid Cancer Stem-Like Cell Clones: Effects of Resveratrol and Valproic Acid. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(6):1662-1673.[16] 韩海燕,宋文广.脂肪间充质干细胞移植后肝硬化大鼠血生化指标的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(36):5364-5370.[17] Singh A, Ahmad I, Iqbal Z, et al. Resveratrol nanoparticles improve oral delivery and arrests the progression of paracetamol-induced liver cirrhosis:stability assessment, in-vitro and in-vivo studies. National Biotechnology Conference.2015.[18] Habeeb MA, Vishwakarma SK, Bardia A, et al. Hepatic stem cells: A viable approach for the treatment of liver cirrhosis. World J Stem Cells. 2015;7(5):859-865.[19] Ulrich H. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells, Embryonic Stem Cells and Development Section. Stem Cell Rev. 2017;13(1):3.[20] Zhang H, Zhai Z, Wang Y, et al. Resveratrol ameliorates ionizing irradiation-induced long-term hematopoietic stem cell injury in mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;54:40-50.[21] Rimmelé P, Lofek-Czubek S, Ghaffari S. Resveratrol increases the bone marrow hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell capacity. Am J Hematol. 2014;89(12): E235-238.[22] 李静,杨雅娟,李常娟,等.牛磺酸对四氯化碳所致大鼠肝硬化门静脉高压的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2016,23(9):65-69.[23] 陈振宙,张雪丹.熊果酸对四氯化碳所致大鼠肝纤维化及门静脉高压的影响[J].安徽医药,2017,21(4):635-639.[24] 吴志强,王卫东,林杰,等.吲哚菁绿清除试验在肝癌术前评估肝脏储备功能的临床应用[J].岭南现代临床外科, 2015,15(4): 389-393.[25] 杨博,罗庆,康权,等.TNF-α、TGF-β1在胆汁淤积性肝硬化中平衡调控肝脏干细胞分化[J].南方医科大学学报, 2018,38(4): 375-383.[26] El-Youssef M, Mu Y, Huang L, et al. Increased expression of transforming growth factor-beta1 and thrombospondin-1 in congenital hepatic fibrosis: possible role of the hepatic stellate cell. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999;28(4):386-392.[27] Tang LY, Heller M, Meng Z, et al. Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGF-β) Directly Activates the JAK1-STAT3 Axis to Induce Hepatic Fibrosis in Coordination with the SMAD Pathway. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(10):4302-4312.[28] Ji H, Minuk GY, Peng Z, et al. Active immunization against transforming growth factor beta1 prevents hepatic fibrosis in a rat model of liver disease. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017; 95(6):743-749.[29] Wang Y, Zhao L, Jiao FZ, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid alleviates liver fibrosis by suppressing the transforming growth factor-β1 signal pathway. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2018;17(5):423-429.[30] Liu F, Zhang J, Qian J, et al. Emodin alleviates CCl4?induced liver fibrosis by suppressing epithelial?mesenchymal transition and transforming growth factor?β1 in rats. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(3):3262-3270. |
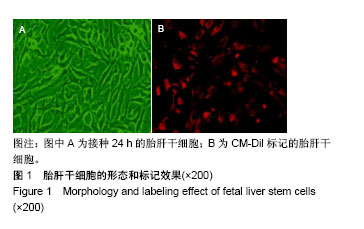
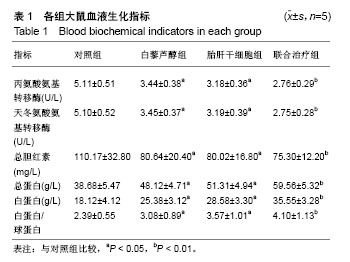
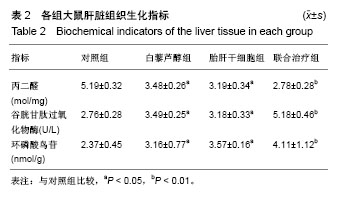
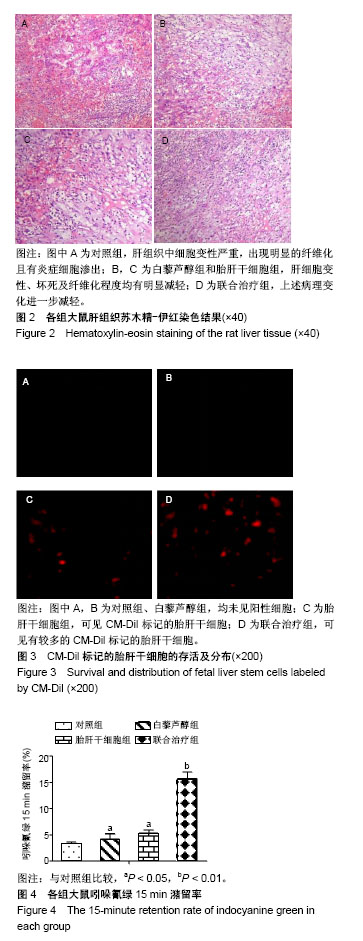
.jpg)
.jpg)