| [1] Hallberg I,Rosenqvist AM,Kartous L,et al.Health-related quality of life after osteoporotic fuactures.Osteoporos Int. 2004;15(10): 834-841.[2] Johnell O,Kanis JA,Odén A,et al.Mortality after osteoporotic fractures.Osteoporos Int.2004;15(1):35-42.[3] Eck JC,Nachtigall D,Humphreys SC,et al.Comparison of vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for treatment of vertebral compression fractures:a meta-analysis of the literature. Spine J.2008; 8(3): 488-497.[4] Korovessis P,Vardakastanis K,Vitsas V,et al.Is Kiva implant advantageous to balloon kyphoplasty in treating osteolytic metastasis to the spine? Comparison of 2 percutaneous minimal invasive spine techniques: a prospective randomized controlled short-term study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(4): E231-239.[5] 王凯,李春亮,朱海勇,等.不同治疗方法减轻老年退行性骨质疏松性胸腰椎体压缩性骨折腰背部疼痛的差异:2年随访的非随机,对照临床试验方案及预试验结果[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(19):3000-3004.[6] McGirt MJ,Parker SL,Wolinsky JP,et al.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures:an evidenced-based review of the literature.Spine J. 2009;9(6):501-508.[7] Tan HY, Wang LM,Zhao L,et al.A prospective study of percutaneous vertebroplasty for chronic painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture.Pain Res Manag. 2015;20(1): e8-11.[8] 杨丰建,林伟龙,朱炯,等.经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2011, 21(1):50-54.[9] 杨惠林.科学认识椎体成形术与椎体后凸成形术的临床价值[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(6):441-443. [10] 徐宝山,胡永成,闫广辉,等.经皮椎体成形术和后凸成形术的相关问题探讨[J].中华骨科杂志,2009, 29(5):430-436.[11] Bouza C,López-Cuadrado T,Almendro N,et al.Safety of balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in Europe: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Eur Spine J.2015;24(4):715-723. [12] Schlaich C,Minne HW,Bruckner T,et al.Reduced pulmonary function in patients with spinal osteoporo tic fractures. Osteoporos Int.1998;8(3):261-267.[13] 赵丽,关继奎,杨欢.老年COPD合并胸腰椎骨折PVP术对肺功能的改善研究[J].中外医疗,2011,30(8): 22-23.[14] 黄荷,吴培玉,谢春亮.椎体强化术治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折前后 肺功能变化及相关因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016,24(2): 128-132.[15] Yang HL, Zhao L, Liu J,et al.Changes of pulmonary function for patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures after kyphoplasty.J Spinal Disord Tech.2007;20(3):221-225.[16] Seybold EA,Sweeney CA,Fredrickson BE,et al.Functional outcome of low lumbar burst fractures. A multicenter review of operative and nonoperative treatment of L3-L5.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1999;24(20): 2154-2161.[17] 干旻峰,钮俊杰,朱若夫,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性下腰椎骨折疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015,23(12): 1068-1071.[18] 王兆红,吴德慧,马超,等.双侧经椎弓根入路与单侧经椎弓根外极外侧入路在椎体成形术中的应用比较[J].中国骨伤, 2012,25(12): 975-978.[19] Ge Z, Ma R, Chen Z, et al. Uniextrapedicular kyphoplasty for the treatment of thoracic osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Orthopedics.2013;36(8):e1020-e1024.[20] Huang Z,Wan S,Ning L,et al.Is unilateral kyphoplasty as effective and safe as bilateral kyphoplasties for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures? A Meta-analysis.Clin Orthop Related Res.2014;472(9):2833-2842.[21] 刘磊,刘光旺,马超.单侧椎弓根旁入路椎体成形术治疗下胸椎压缩性骨折的疗效观察[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2015,17(9): 780-785.[22] Chen C,Chen L,Gu Y,et al.Kyphoplasty for chronic painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures via unipedicular versus bipedicular approachment:a comparative study in early stage. Injury.2010;41(4):356-359. [23] 杨惠林,牛国旗,梁道臣,等.单球囊与双球囊后凸成形术对椎体复位作用的研究[J].中华外科杂志,2004,40(21):1299-1302.[24] Liebschner MA,Rosenberg WS,Keaveny TM.Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1547-1554.[25] 王想福,范有福,石瑞芳,等.单侧穿刺椎体后凸成形术骨水泥分布与穿刺角度的关系[J].中国骨伤,2015,8(28):704-707.[26] 申勇,刘法敬,张英泽.单、双侧经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2011,21(3): 202-206. [27] Chen L, Yang H, Tang T. Unilateral versus bilateral balloon kyphoplasty for multilevel osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a prospective study. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2011; 36(7):534-540.[28] Molloy S, Mathis JM, Belkoff SM.The effect of vertebral body percentage fill on mechanical behavior during percutaneous vertebroplasty.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2003;28(14):1549-1554.[29] 崔维,刘宝戈,王磊,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术中球囊扩张体积与骨水泥注射量的相关性分析[J].中华外科杂志, 2015,53(4): 289-293.[30] Kaufmann TJ,Trout AT,Kallmes DF.The effects of cement volume on clinical outcomes of percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27(9):1933-193[31] 徐磊,杨惠林,姜为民,等.单侧经皮聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥椎体成形治疗中骨水泥注入位置、注入量与疗效的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,16(21):3833-3837.[32] 杨惠林,Hansen A Yuan,陈亮.椎体后凸成形术治疗老年骨质疏松脊柱压缩骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2003,23(5):262-265.[33] 邹德威,马华松,邵水霖,等.球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术治疗老年骨质疏松脊柱压缩骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2003,23(5):257-261.[34] Chen L,Dong R,Gu Y,et al.Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kümmell's Disease.Pain Physician.2015;18(4): 373-381.[35] Hadjipavlou AG,Tzermiadianos MN,Katonis PG,et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures and osteolytic tumours. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(12): 1595-1604.[36] Hulme PA,Krebs J,Ferguson SJ,et al.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty:a systematic review of 69 clinical studies.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2006,31(17):1983-2001.[37] Georgy BA.Clinical experience with High-Viscosity cements for percutaneous vertebral body augmentation: occurrence, degree, and location of cement leakage compared with kyphoplasty.Am J Neuroradiol.2010;31(3):504-508. [38] 杨森,徐韬,盛伟斌,等.单双侧球囊灌注骨水泥椎体成形修复骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的系统评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(8):1306-1312.[39] Xie W,Jin D,Ma H,et al. Cement leakage in percutaneous vertebral augmentation for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: analysis of risk factors.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2016; 29(4):E171-176. |
.jpg)
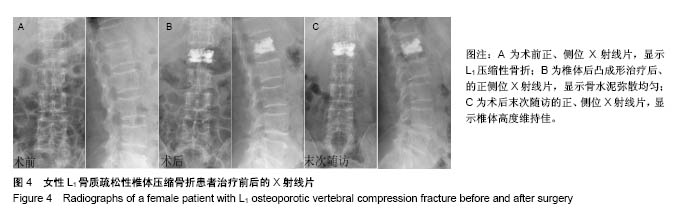
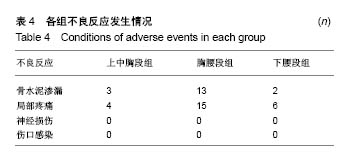
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)