中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (5): 703-709.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1563
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
脂多糖干预ob/ob小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化
刘大勇1,周伟伟1,2,肖 蕊1,王梅蕊1,赵梦明1,贾 智1
- 1天津医科大学口腔医院牙体牙髓科,天津市 300070;2首都医科大学附属北京口腔医院急诊综合诊疗中心,北京市 100069
Lipopolysaccharides affect osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells derived from ob/ob mice
Liu Dayong1, Zhou Weiwei1, 2, Xiao Rui1, Wang Meirui1, Zhao Mengming1, Jia Zhi1
- 1Department of Dental Endodontics, Tianjin Medical University School & Hospital of Stomatology, Tianjin 300070, China; 2Emergency Comprehensive Medical Center, Beijing Stomatological Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 脂多糖:是革兰阴性菌的表面抗原物质,是许多噬菌体吸附的受体,其毒性成分主要为类脂质A。脂多糖只有当细菌死亡溶解或用人工方法破坏菌细胞后才释放出来,所以叫做内毒素,其位于细胞壁的最外层,覆盖于细胞壁的黏肽上。 Ob/ob小鼠:是瘦素基因(ob)纯合突变的小鼠,1950年由Ingalls成功繁育,其特征为肥胖、多食、高血糖和胰岛素抵抗,近年来发现瘦素与肥胖密切相关。
摘要
背景:肥胖是牙周炎及机体其他疾病的易感因素,因肥胖与瘦素密切相关,目前尚无通过瘦素基因突变小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的分化情况探索相关机制的研究。
目的:通过研究ob/ob遗传性肥胖小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞在脂多糖刺激下的成骨能力及成骨相关分子的表达,从分子及细胞水平探讨肥胖与成骨能力的相关机制。
方法:选用8周龄雄性肥胖ob/ob小鼠、8周龄雄性C57小鼠(由中国医学科学院实验动物研究所提供)各8只,取两组小鼠双侧股骨,采用全骨髓法分离培养纯化得到ob/ob小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞及C57小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞,加入含有100 μg/L脂多糖的成骨诱导液进行成骨诱导分化,通过碱性磷酸酶染色、茜素红染色和碱性磷酸酶活性检测观察比较两组小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨能力。采用RT-PCR检测两组小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中Alp、Runx2、Ocn、Nf-κb mRNA表达水平。
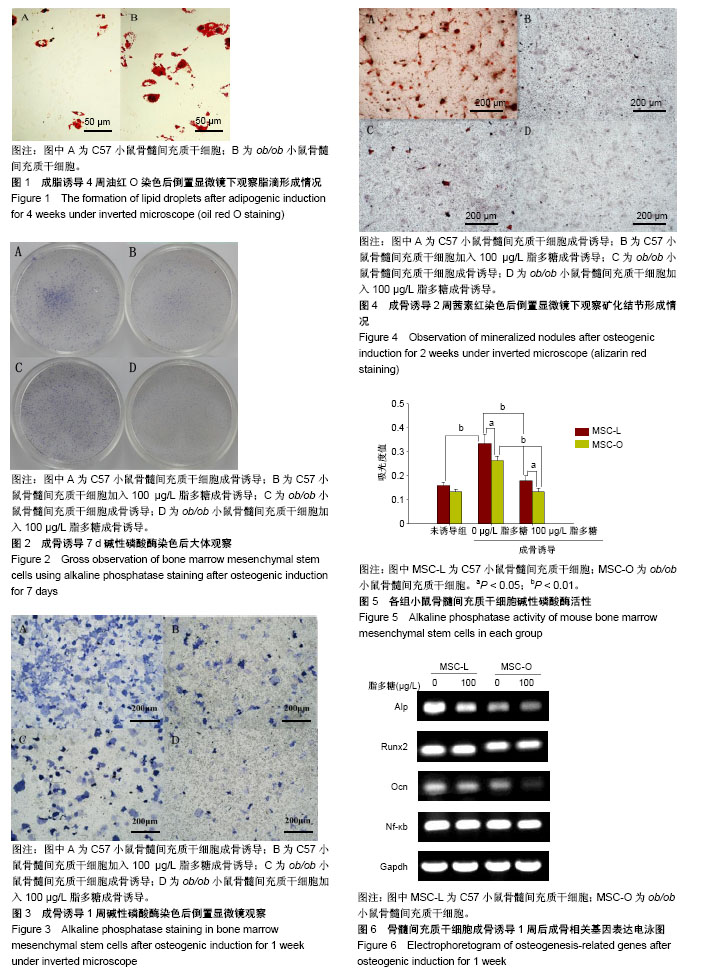
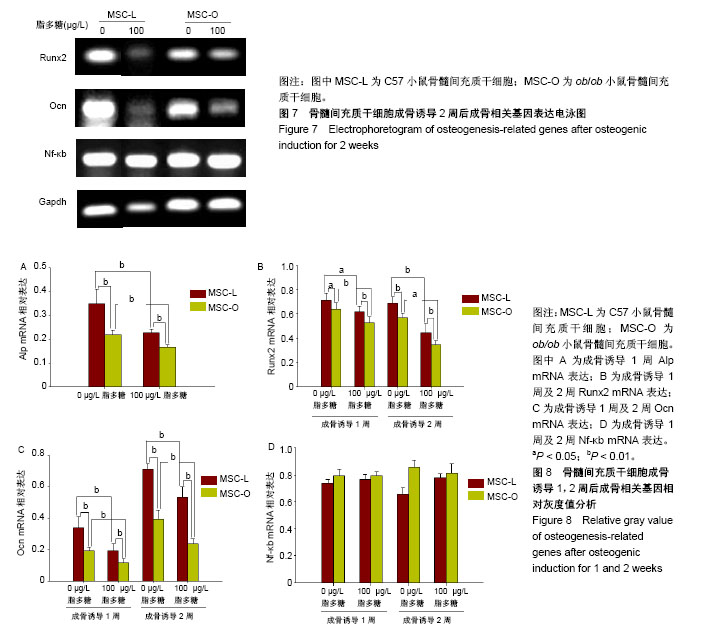
结果与结论:①成骨诱导1周后,与C57小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞比较,ob/ob小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞碱性磷酸酶染色减弱,碱性磷酸酶活性显著降低(P < 0.01);成骨诱导液中添加脂多糖后,碱性磷酸酶活性较未添加脂多糖组显著下降(P < 0.01),ob/ob小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞碱性磷酸酶活性亦较C57小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞显著降低(P < 0.05);②成骨诱导2周后,与C57小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞比较,ob/ob小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞茜素红染成橘红色的矿化结节减少,而成骨诱导液中添加脂多糖后,两组骨髓间充质干细胞均未见矿化结节形成;③成骨诱导后,与C57小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞比较,ob/ob小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中Alp、Runx2、Ocn mRNA表达降低(P < 0.05);诱导液中加入脂多糖后,Alp、Runx2、Ocn表达较未添加脂多糖组均显著减少(P < 0.05),且在ob/ob小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中Ocn、Runx2表达较C57小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞明显降低(P < 0.05);④结果表明,瘦素缺乏的肥胖小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨向分化发生障碍。在低浓度脂多糖刺激下,ob/ob小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力较C57小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞下降更明显。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-8511-2658(刘大勇)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)