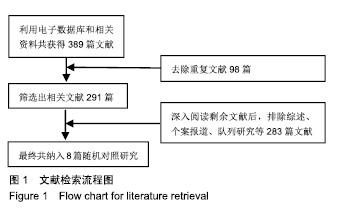
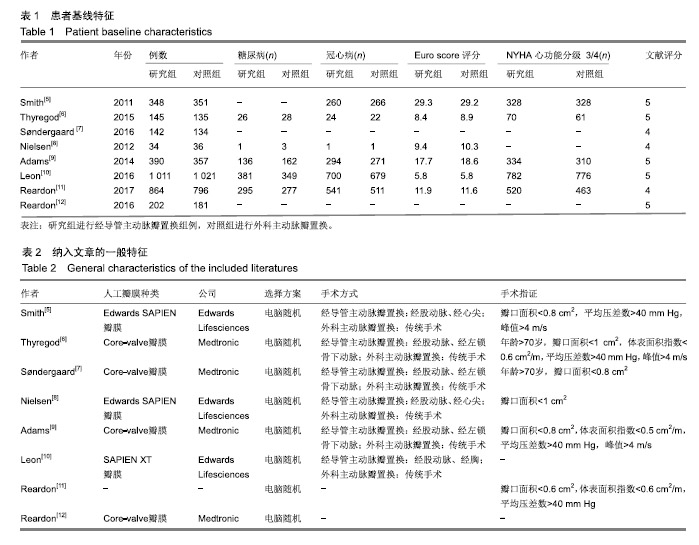
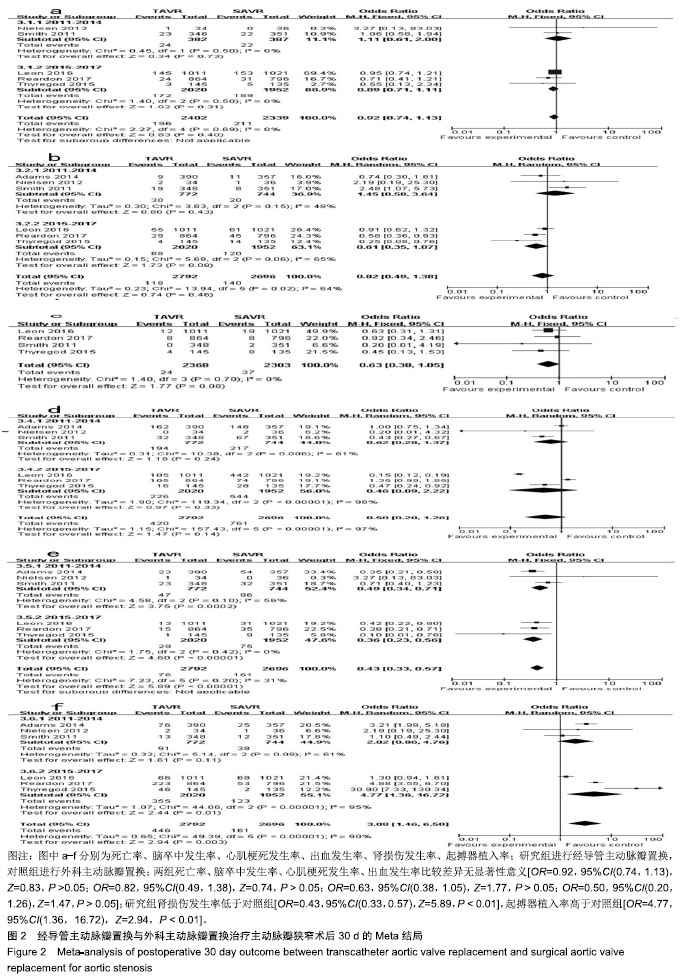
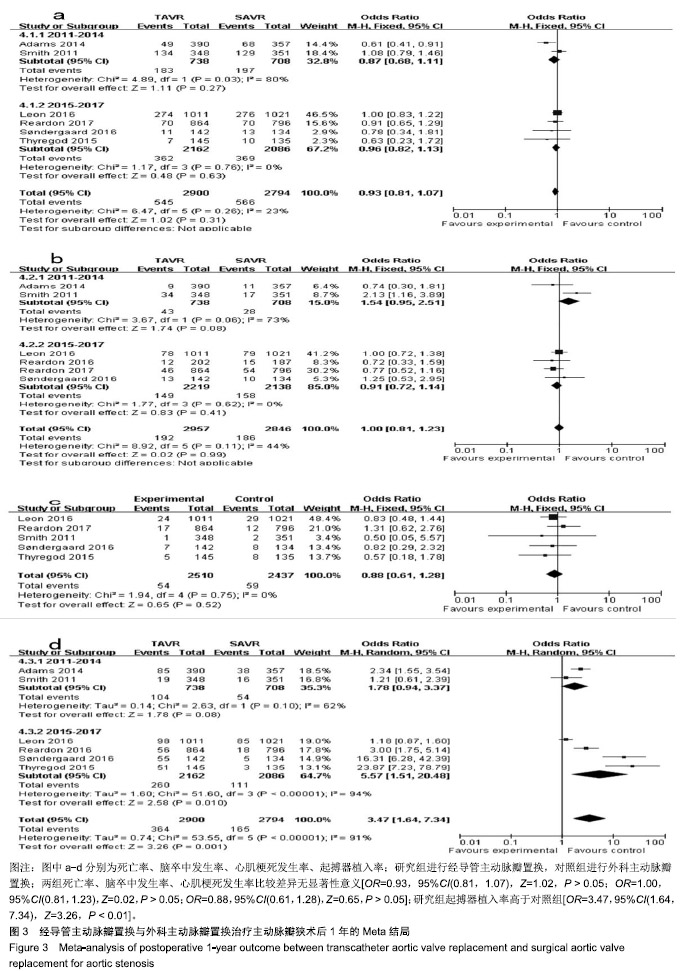
| [1]Strike E,Arklina B,Stradins P,et al.Postoperative pain management strategies and delirium after transapical aortic valve replacement: a randomized controlled trial.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2018;1-5.[2]Liu Z,Kidney E,Bem D,et al.Transcatheter aortic valve implantation for aortic stenosis in high surgical risk patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2018;13(5):e0196877.[3]Wang Y,Zhou Y,Zhang L,et al.Midterm outcome of transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement in low to intermediate risk patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Cardiol. 2018;71(6):534-539.[4]Svenssin LG,Blackstone EH,Rajeswaran J,et al.Comprehensive analysis of mortality among patients undergoing TAVR results of the PARTNER Trial.J Am Coll Cardiol.2014;64(2):158-168.[5]Smith CR,Leon MB,Mack MJ,et al.Transcatheter versus surgical aortic-valve replacement in high-risk patient.N Engl J Med. 2011; 364(23):2187-2198.[6]Thyregod HG,Steinbruchel DA,Ihlemann N,et al.Transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients with severe aortic valve stenosis 1-year results from the all-comers notion randomized clinical trial J Am Coll Cardiol.2015;57(5):276-280.[7]Søndergaard L,Steinbrüchel DA,Ihlemann N,et al.Two-year outcomes in patients with severe aortic valve stenosis randomized to transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement the all-comers nordic aortic valve intervention randomized clinical trial.Circ Cardiovasc Interv.2016;9(6):e003665.[8]Nielsen HH,Klaaborg KE,Nissen H,et al.A prospective, randomised trial of transapical transcatheter aortic valve implantation vs. surgical aortic valve replacement in operable elderly patients with aortic stenosis: the STACCATO trial. EuroIntervention. 2012;8(3): 383-389.[9]Adams DH,Popma JJ,Reardon MJ,et al.Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Replacement with a Self-Expanding Prosthesis.N Engl J Med. 2014; 371(10):967-968.[10]Leon ML,Smith CR,Mack MJ,et al.Transcatheter or surgical aortic-valve replacement in intermediate-risk patients.N Engl J Med. 2016;374(17):1609-1620.[11]Reardon MJ,Van NM,Popma J,et al.Transcatheter or surgical aortic-valve replacement in intermediate-risk patients.N Engl J Med. 2017;376(14):1321-1331.[12]Reardon MJ,Kleiman NS,Adams DH,et al.Outcomes in the randomized corevalve US pivotal high-risk trial in patients with a society of thoracic surgeons risk score of 7% or less.JAMA Cardiol. 2016;1(8):945-949.[13]Gargiulo G,Sannino A,Capodanno D,et al.Transcatheter aortic valve implantation versus surgical aortic valve replacement a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Intern Med. 2016;165(5):334-344.[14]Siemieniuk RA,Agoritsas T,Manja V,et al.Transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients with severe aortic stenosis at low and intermediate risk: systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ.2016;354:i5130.[15]郭丽娜,施仲伟.经导管Edwards-Sapien主动脉瓣植入术临床应用[J].国际心血管病杂志, 2011,38(4):209-212.[16]李昕,刘世栋,朱鹏冲,等.经导管主动脉瓣置入术的研究进展[J].国际心血管病杂志,2018,45(1):8-11.[17]Arora S, Misenheimer JA,Ramaraj R.Transcatheter aortic valve replacement: comprehensive review and present status.Tex Heart Inst J.2017;44(1):29-38.[18]Fischer-Rasokat U,Renker M,Liebetrau C,et al. 1-yearsurvival after TAVR of patients with low-flow, low-gradient and high-gradient aortic valve stenosis in matched study populations.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12(8):752-763.[19]Elmaraezy A,Ismail A,Abushouk AI.Efficacy and safety of transcatheter aortic valve replacement in aortic stenosis patients at low to moderate surgical risk: a comprehensive meta-analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord.2017;17(1):234.[20]Mack MJ,Leon MB,Thourani VH,et al.Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement with a balloon-expandable valve in low-risk patients.N Engl J Med.2019;380(18):1695-1705.[21]Guedeney P,Tchétché D,Petronio AS,et al.Impact of coronary artery disease and percutaneous coronary intervention in women undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement: From the WIN-TAVI registry.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;93(6): 1124-1131.[22]Solomonica A,Choudhury T,Bagur R.Newer-generation of Edwards transcatheter aortic valve systems: SAPIEN 3, Centera, and SAPIEN 3 Ultra.Expert Rev Med Devices.2019;16(2):81-87.[23]Goodall G,Lamotte M,Ramos M,et al.Cost-effectiveness analysis of the SAPIEN 3 TAVI valve compared with surgery in intermediate-risk patients.J Med Econ.2019;22(4):289-296.[24]Baron SJ,Wang K,House JA,et al.Cost-effectiveness of transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients with severe aortic stenosis at intermediate risk. Circulation. 2019; 139(7):877-888.[25]Kapadia SR,Huded CP,Kodali SK,et al.Stroke after surgical versus transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve replacement in the PARTNER Trial.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(20):2415-2426.[26]Chen S,Redfors B,Ben-Yehuda O,et al.Transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients with prior cardiac surgery in the Randomized PARTNER 2A Trial.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;11(21):2207-2216.[27]Abdelghani M,Allali A,Kaur J,et al.Impact of prosthesis-iteration evolution and sizing practice on the incidence of prosthesis-patient mismatch after transcatheter aortic valve replacement.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;93(5):971-979.[28]Still S,Szerlip M,Mack M.TAVR Vs. SAVR in intermediate-risk patients: what influences our choice of therapy.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018;20(10):82.[29]Stähli BE,Reinthaler M,Leistner DM,et al.Transcatheter aortic vavle replacement and concomitant mitral regulation.Front Cardiovasc Med.2018;5:74.[30]Indolfi C,Bartorelli AL,Berti S,et al.Updated clinical indications for transcatheter aortic valve implantation in patients with severe aortic stenosis: expert opinion of the Italian Society of Cardiology and GISE.J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown).2018,19(5):197-210. |
.jpg)
.jpg)