| [1]Beck EC,Barragan M,Tadros MH,et al.Detoamore. Approaching the compressive modulus of articular cartilage with decellularized cartilage-based hydrogel.Acta Biomater. 2016;38:9-105.[2]孙凯,年争好,徐成,等.丝素蛋白复合胶原蛋白支架的制备及性能研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014,28(7):903-908.[3]Curl WW,Krome J,Gordon ES,et al.Cartilage injuries: A review of 31, 516 knee arthroscopies. Arthroscopy. 1997;13(4): 456-460.[4]Sun K,Li R,Jiang W,et al.Comparison of three-dimensional printing and vacuum freeze-dried techniques for fabricating composite scaffolds.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016; 477(4):1085-1091.[5]Sun K,Li R,Li H,et al.Comparison of three- dimensional printing for fabricating silk fibroin-blended scaffolds.Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater.2018;8(67):480-486.[6]Chen YN,Peng L,Liu T,et al.Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Tannic Acid Hydrogels with Excellent Mechanical Properties and Shape Memory Behaviors.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(40): 27199-27206.[7]Sheu SY,Chen WS,Sun JS,et al.Biological characterization of oxidized hyaluronic acid/resveratrol hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(12): 3457-3466. [8]Fenn SL, Oldinski RA.Visible light crosslinking of methacrylated hyaluronan hydrogels for injectable tissue repair.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016;104(6): 1229-1236. [9]Zhou Y,Liang K,Zhao S,et al.Photopolymerized maleilated chitosan/methacrylated silk fibroin micro/nanocomposite hydrogels as potential scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;108:383-390. [10]年争好,李晖,李瑞欣,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原蛋白/丝素蛋白复合骨组织工程支架材料的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(8):1149-1154.[11]年争好,孙凯,徐成,等.大鼠BMSCs成骨诱导及复合支架材料构建组织工程骨组织的研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2015, 12(1):1-5.[12]Reyes R, Delgado A, Solis R,et al.Cartilage repair by local delivery of transforming growth factor-β 1 or bone morphogenetic protein-2 from a novel, segmented polyurethane/polylacticco-glycolic bilayered scaffold.J Biomed Mater Res A.2014;102(4):1110-1120.[13]Paul A,Manoharan V,Krafft D,et al.Nanoengineered biomimetic hydrogels for guiding human stem cell osteogenesis in three dimensional microenvironments.J Mater Chem B. 2016;4(20):3544-3554.[14]Kotecha M,Klatt D,Magin RL.Monitoring cartilage tissue engineering using magnetic resonance spectroscopy, imaging, and elastography.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2013(19):470-484.[15]Aroni MAT,Spolidório LC,Andersen OZ,et al.Loading deproteinized bovine bone with strontium enhances bone regeneration in rat calvarial critical size defects.Clin Oral Investig.2018. doi: 10.1007/s00784-018-2588-6.[Epub ahead of print][16]Zheng G,Qiu G,Ge M,et al.Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate obliterative bronchiolitis in a murine model via IDO.Respir Res.2017;18(1):119.[17]Trohatou O,Roubelakis MG. Mesenchymal stem /stromal cells in regenerative medicine: past,present,and future.Cell Reprogram.2017;19(4):217-224.[18]Shimomura K,Ando W,Moriguchi Y,et al. Next generation mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)- based cartilage repair using scaffold-free tissue engineered constructs generated with synovial mesenchymal stem cells.Cartilage.2015;6(2 Suppl): 13-29.[19]Holt BD,Wright ZM,Arnold AM,et al. Graphene oxide as a scaffold for bone regeneration.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol.2017;9(3):e1437.[20]Wang K,Xu J,Cai J,et al. Serum levels of resistin and interleukin-17 are associated with increased cartilage defects and bone marrow lesions in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2017;27(2):339-344. [21]Li F,Yao J,Tian H,et al.Correlations between traditional chinese medicine syndromes and IL-1,MMP and TIMP-1 in knee osteoarthritis.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2017;10(10): 14660-14666.[22]Duro-Castano A,Lim NH,Tranchant I,et al.In vivo imaging of MMP-13 activity using a specific polymer-FRET peptide conjugate detects early osteoarthritis and inhibitor efficacy. Adv Funct Mater.2018:1802738.[23]李乐,寇久社.三种质量浓度医用臭氧局部注射对兔膝OA行为 学及滑膜匀浆中IL-1?TNF-α水平的影响[J]. 解放军预防医学杂志,2018,36(1):77-79.[24]Yamasaki K,Nakasa T,Miyaki S,et al.Expression of microRNA- 146a in osteoarthritis cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(4):1035-1041.[25]Jones KJ,Sheppard WL,Arshi A,et al. Articular cartilage lesion characteristic reporting is highly variable in clinical outcomes studies of the knee. Cartilage. 2018:1947603518756464.doi: 10.1177/1947603518756464.[Epub ahead of print].[26]Zhang X,Wu S,Naccarato T,et al. Regeneration of hyaline-like cartilage in situ with SOX9 stimulation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.PLoS One. 2017;12(6):e0180138.[27]Sasaki T,Akagi R,Akatsu Y,et al.The effect of systemic administration of G-CSF on a full-thickness cartilage defect in a rabbit model MSC proliferation as presumed mechanism:G-CSF for cartilage repair.Bone Joint Res. 2017;6(3):123-131. [28]Chang YH,Liu HW,Wu KC,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells and their clinical applications in osteoarthritis.Cell Transplant. 2016;25:937-950.[29]Yoshimura H,Muneta T,Nimura A,et al.Comparison of rat mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow,synovium,periosteum,adipose tissue,and muscle. Cell Tissue Res.2007;327(3):449-462.[30]Tao SC,Yuan T,Zhang YL,et al.Exosomes derived from miR-140 - 5p-overexpressing human synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model. Theranostics. 2017; 7(1):180-195.[31]Zhang S,Chuah SJ,Lai RC,et al.MSC exosomes mediate cartilage repair by enhancing proliferation,attenuating apoptosis and modulating immune reactivity. Biomaterials. 2017;156:16-27.[32]Toh WS,Lai RC,Hui JHP,et al.MSC exosome as a cell-free MSC therapy for cartilage regeneration:implications for osteoarthritis treatment.Semin Cell Dev Biol.2017;67:56-64.[33]Yubo M,Yanyan L,Li L,et al.Clinical efficacy and safety of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for osteoarthritis treatment: A meta-analysis.PLoS One.2017;12(4):e0175449. [34]Paek HJ,Kim C,Tuan RS. Stem cell-based repair and regeneration of articular cartilage. J Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;2(6):177-182. |
.jpg)
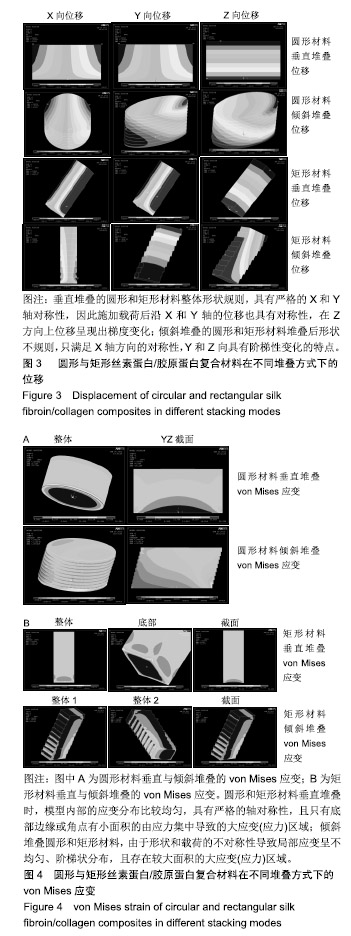
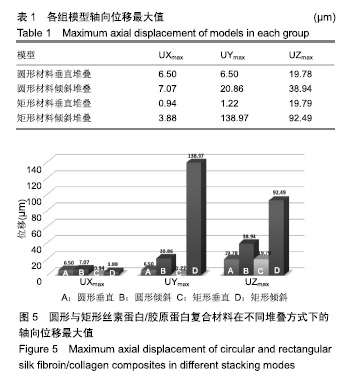
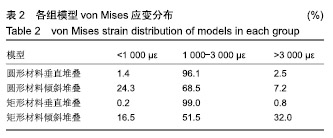
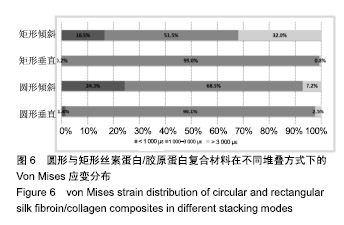
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)