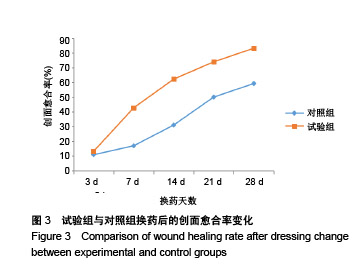
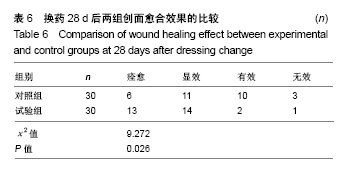
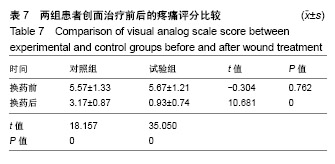
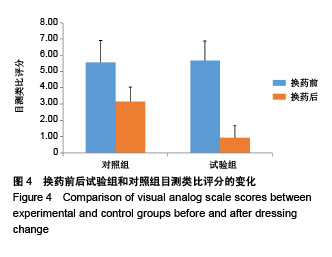
| [1]Lin YN,Hsieh TY,Huang SH,et al.Management of venous ulcers according to their anatomical relationship with varicose veins.Phlebology.2018;33(1):44-52.[2]Pascarella L,Shortell CK.Medical management of venous ulcers. Semin Vasc Surg.2015;28(1):21-28.[3]Finlayson KJ, Parker CN, Miller C,et al.Predicting the likelihood of venous leg ulcer recurrence: The diagnostic accuracy of a newly developed risk assessment tool.Int Wound J. 2018;15(5):686-694.[4]Branisteanu DE, Feodor T, Baila S,et al.Impact of chronic venous disease on quality of life: Results of vein alarm study. Exp Ther Med.2019;17(2):1091-1096.[5]Xie T,Ye J,Rerkasem K,et al.The venous ulcer continues to be a clinical challenge: an update. Burns Trauma.2018;6:18.[6]Todd M.Assessment and management of older people with venous leg ulcers.Nurs Older People. 2018;30(5):39-48.[7]Cowan T.Strategies for improving outcomes in venous leg ulcer care.J Wound Care.2018;27(7):456-457.[8]Applewhite A,Chowdhry SA,Desvigne M,et al.Inpatient and Outpatient Wound Treatment Recommendations: Assessing Use of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Systems or Oxidized Regenerated Cellulose (ORC)/ Collagen/Silver-ORC Dressings.Wounds.2018;30(8 supp): S19-S35.[9]Murray RZ,West ZE,Cowin AJ,et al.Development and use of biomaterials as wound healing therapies. Burns Trauma. 2019;7:2.[10]García-Lizarribar A, Fernández-Garibay X, Velasco-Mallorquí F,et al.Composite Biomaterials as Long-Lasting Scaffolds for 3D Bioprinting of Highly Aligned Muscle Tissue. Macromol Biosci. 2018;18(10):e1800167.[11]Wang J,Wang Y,Liu D,et al.Preparation and cytological study of collagen/nano-hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide composites. Acta Bioeng Biomech.2018;20(4):65-74.[12]Zhang Z,Guo W,Gao S,et al. Native tissue-based strategies for meniscus repair and regeneration. Cell Tissue Res. 2018; 373(2):337-350.[13]Sun H, Lv H, Qiu F,et al. Clinical application of a 3D-printed scaffold in chronic wound treatment: a case series J Wound Care.2018;27(5):262-271.[14]Ming L,Zhipeng Y,Fei Y,et al.Microfluidic-based screening of resveratrol and drug-loading PLA/Gelatine nano-scaffold for the repair of cartilage defect. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup1):336-346.[15]Yu F,Li M,Yuan Z,et al.Mechanism research on a bioactive resveratrol- PLA-gelatin porous nano-scaffold in promoting the repair of cartilage defect.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13: 7845-7858.[16]陈洪让,张海涛,李永生,等.手持静电纺丝可降解纳米纤维原位组织修复的实验研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(2):257-264.[17]柳芳芹.压力治疗系统管理在下肢静脉溃疡湿性愈合中的应用效果观察[J].齐鲁护理杂志,2012,18 (23):31-32.[18]Harries RL,Bosanquet DC, Harding KG. Wound bed preparation: TIME for an update. Int Wound J. 2016;13 Suppl 3:8-14.[19]Cazzell S.A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing a Human Acellular Dermal Matrix Versus Conventional Care for the Treatment of Venous Leg Ulcers. Wounds. 2019;31(3): 68-74.[20]Briggs M, Ferris FD, Glynn C,et al.World Union of Wound Healing Societies EXPERT WORKING GROUP. Assessing pain at wound dressing-related procedures. Nurs Times. 2004;100(41):56-57.[21]中华人民共和国卫生部.中药新药临床研巧指导原则.北京:中国医药科技出版社,2002:68-73.[22]Finlay V,Burrows S,Kendell R,et al.Modified Vancouver Scar Scale score is linked with quality of life after burn. Burns. 2017;43(4):741-746.[23]Dash BC,Xu Z,Lin L,et al.Stem Cells and Engineered Scaffolds for Regenerative Wound Healing. Bioengineering (Basel).2018;5(1).pii: E23.doi: 10.3390/bioengineering5010023. [24]Lien SM,Ko LY,Huang TJ.Effect of pore size on ECM secretion and cell growth in gelatin scaffold for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2009;5(2): 670-679. [25]Hoveizi E,Ebrahimi-Barough S,Tavakol S,et al. In Vitro Differentiation of Human iPS Cells into Neural like Cells on a Biomimetic Polyurea.Mol Neurobiol.2017;54(1):601-607. [26]Kim HW, Yu HS, Lee HH. Nanofibrous matrices of poly(lactic acid) and gelatin polymeric blends for the improvement of cellular responses. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;87(1):25-32. [27]Wang S,Zhang Y,Wang H,et al.Fabrication and properties of the electrospun polylactide/silk fibroin-gelatin composite tubular scaffold. Biomacromolecules. 2009;10(8): 2240-2244. [28]Chiou BS,Jafri H,Avena-Bustillos R,et al.Properties of electrospun pollock gelatin/poly(vinyl alcohol) and pollock gelatin/poly(lactic acid) fibers.Int J Biol Macromol. 2013;55: 214-220.[29]Paschoalin RT,Traldi B,Aydin G,et al. Solution blow spinning fibres: New immunologically inert substrates for the analysis of cell adhesion and motility.Acta Biomater.2017;51:161-174. [30]Aldana AA,Abraham GA.Current advances in electrospun gelatin-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications.Int J Pharm.2017;523(2):441-453.[31]Ye K, Liu D, Kuang H,et al.Three-dimensional electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds displaying bone morphogenetic protein-2-derived peptides for the promotion of osteogenic differentiation of stem cells and bone regeneration.J Colloid Interface Sci.2019;534:625-636.[32]Deng K,Yang Y,Ke Y,et al.A novel biomimetic composite substitute of PLLA/gelatin nanofiber membrane for dura repairing.Neurol Res.2017;39(9):819-829.[33]Liu Y,Cui H,Zhuang X,et al.Electrospinning of aniline pentamer-graft-gelatin/PLLA nanofibers for bone tissue engineering.Acta Biomater.2014;10(12):5074-5080.[34]Zhang C,Cao M,Lan J,et al.Regulating proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts on poly(l-lactide)/gelatin composite nanofibers via timed biomineralization. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(8):1968-1980.[35]Piran M,Shiri M,Soufi Zomorrod M,et al.Electrospun triple-layered PLLA/gelatin. PRGF/PLLA scaffold induces fibroblast migration.J Cell Biochem.2019.doi: 10.1002/jcb. 28422. [Epub ahead of print][36]Amjadian S,Seyedjafari E,Zeynali B,et al. The synergistic effect of nano-hydroxyapatite and dexamethasone in the fibrous delivery system of gelatin and poly(l-lactide) on the osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Pharm. 2016;507(1-2):1-11.[37]Nair HKR. Microcurrent as an adjunct therapy to accelerate chronic wound healing and reduce patient pain.J Wound Care. 2018;27(5):296-306.[38]Frescos N.Assessment of pain in chronic wounds: A survey of Australian health care practitioners. Int Wound J. 2018;15(6): 943-949.[39]Upton D,Solowiej K,Hender C,et al. Stress and pain associated with dressing change in patients with chronic wounds.J Wound Care.2012;21(2):53-54,56,58 passim.[40]Höglund A,Hakkarainen M,Edlund U,et al.Surface modification changes the degradation process and degradation product pattern of polylactide. Langmuir. 2010;26(1):378-383.[41]Echave MC,Saenz del Burgo L,Pedraz JL,et al.Gelatin as Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering. Curr Pharm Des. 2017; 23(24):3567-3584. |
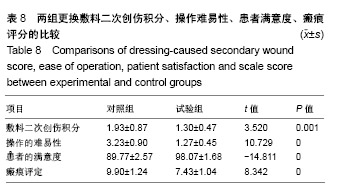
.jpg)
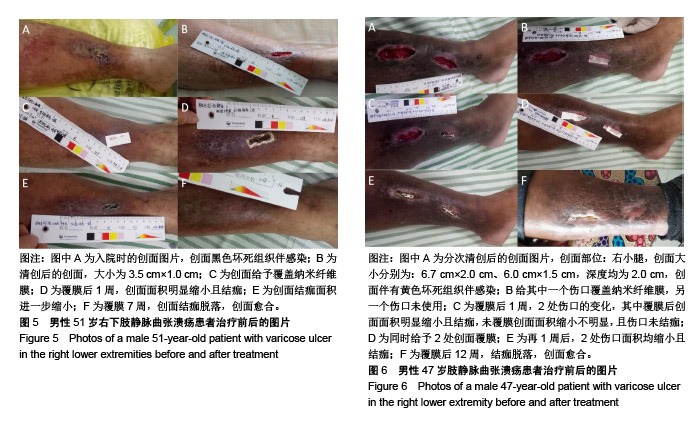



.jpg)