| [1]Sims JB,Roberts WC.Comparison of findings in patients with versus without atrial fibrillation just before isolated mitral valve replacement for rheumatic mitral stenosis(with or without associated mitral regurgitation).Am J Cardiol. 2006;97(7): 1035-1038.[2]邬晓臣,张近宝,欧阳辉,等.二尖瓣置换同期行双极射频消融术治疗风湿性二尖瓣病变合并心房颤动的疗效分析[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2014;21(6):827-829.[3]Chugh SS,Havmoeller R,Narayanan K,et al.Worldwide epidemiologyof atrial fibrillation:a Global burden of Disease 2010 Study.Circulation.2014;129(8):837-847.[4]Stulak JM,Dearani JA,Sundt TM,et al.Superiority of cut-and -sew technique for the Cox maze procedure: Comparison with radiofrequency ablation.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;133(4):1023-1027.[5]韩劲松,王辉山,汪曾炜,等.人工瓣环置入和迷宫Ⅲ型手术治疗退行性二尖瓣环扩张伴发心房颤动[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(52):8522-8528.[6]Stulak JM,Dearani JA,Sundt TM,et al.Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: Comparison of Catheter-Based Techniques and the Cox-Maze III Operation.Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;91(6): 1882-1889.[7]Funatsu T,Kobavashi J,Nakajima H,et al.Long-term results and reliability of cryothermic ablation based maze procedure for atrial fibrillation concomitant with mitral valve surgery.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.2009;36(2):267-271.[8]崔永强,孟旭,李岩,等.心脏直视手术中双极射频消融治疗心房颤动91例分析[J].中华外科杂志,2009,47(7):533-536.[9]王辉山,汪曾炜,李新民,等.141例心脏手术同期施行双极射频迷宫手术治疗心房颤动[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志, 2009,25(6): 371-374.[10]Garcia-Villarreal OA.Cox-maze III procedure for atrial fibrillation. A preliminary study.Arch Cardiol Mex. 2016;86(3):208-213.[11]Garcia-Villarreal OA.Cox maze III procedure: the best alternative in surgery for atrial fibrillation.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2014;148(1):368-369.[12]Stulak JM,Suri RM,Burkhart HM,et al.Surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation for two decades: Are the results of new Techniques equivalent to the Cox maze III procedure?J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2014;147(5):1478-1487.[13]Doty JR,Doty DB,Jones KW,et al.Comparison of standard Maze III and radiofrequency Maze operations for treatment of atrial fibrillation.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;133(4): 1037-1044.[14]韩劲松,王辉山,汪曾炜,等.Cox迷宫III型手术治疗风湿性二尖瓣病变伴发心房颤动的安全性和有效性[J].中华医学杂志, 2016, 96(13):1011-1015.[15]Wang H,Han J,Wang Z,et al.A prospective randomized trial of the cut-and-sew Maze procedure in patients undergoing Surgey for rheumatic mitral valve disease.J Thorac Cardiovasc surg.2018;155(2):608-617.[16]Di Eusanio G,Gregorini R,Mazzola A,et al.Giant left atrium and mitral valve replacement:risk factor analysis.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.1988;2(3):151-159.[17]Rajagopal S,Rajagopal L,Nair M,et al.Radiofrequency catheter ablation in a patient with giant left atrium and permanent atrial fibrillation: maintenance of sinus rhythm at 1 year.Indian Heart J.2008;60(3):257-259.[18]Gillinov AM,Gelijns AC,Parides MK,et al.Surgical Ablation of atrial fibrillation during mitral-valve surgery.N Engl J Med. 2015;372(15):1399-1409.[19]Ad N,Henry L,Hunt S,et al.Should surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation be performed in patients with a significantly enlarged left atrium?J Thorac Cardiovasc surg. 2014;147(1):236-241.[20]Kim HJ,Kim JB,Jung SH,et al.Surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with a giant left atrium undergoingmitral valve surgery.Heart.2016;102(15):1206-1214.[21]Marui A,Tambara K,Tadamura E,et al.A novel approach to restore atrial function after the maze procedure in patiens with an enlarged left atrium.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2007;32(2): 308-312.[22]Sunderland N,Nagendran M,Maruthappu M,et al.In patients with an enlarged left atrium does left atrial size reduction improve maze surgery success?Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg.2011;13(6):635-641. [23]Kim YG,Shim J,Oh SK,et al.Different responses of left atrium and left atrial appendage to radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation:a follow up MRI study. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):7871.[24]Burstein B,Nattel S.Atrial Fibrosis: Mechanisms and Clinical Relevance in Atrial Fibrillation.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51(8): 802-809.[25]Iwasaki YK,Nishida K,Kato T,et al.Atrial fibrillation pathophysiology:implications for management. Circulation. 2011;124(20):2264-2274.[26]Kosakai Y.Treatment of atrial fibrillation using the Maze procedure:the Japanese experience.Semin Thorac Cardiova Surg.2000;12(1):44-52.[27]Pande S,Agarwal SK,Mohanty S,et al.Effect of mitral valve replacement on reduction of left atrial size.Asian Cardiovas Thorac Ann.2013;21(3):288-292.[28]Ad N,Henry L,Hunt S,et al.DO we increase the operative risk by adding the Cox Maze III procedure to aortic valve replacement and coronary artery bypass surgery?J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2012;143(4):936-944.[29]Louagie Y,Buche M,Eucher P,et al.Improved patient survival with concomitant Cox Maze III procedure compared with heart surgery alone.Ann Thorac Surg.2009;87(2):440-446.[30]王辉山,汪曾炜,尹宗涛,等.Cox迷宫III手术治疗心脏瓣膜病合并持续性房颤[J].中国胸心血管外科杂志,2015,31(12):743-747.[31]Park JH,Shin SH,Lee MJ.Clinical and Echocardiographic Factors Affecting Tricuspid Regurgitation Severity in the Patients with Lone Atrial Fibrillation.J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2015;23(3):136-142. |
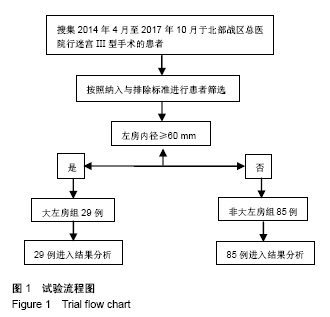
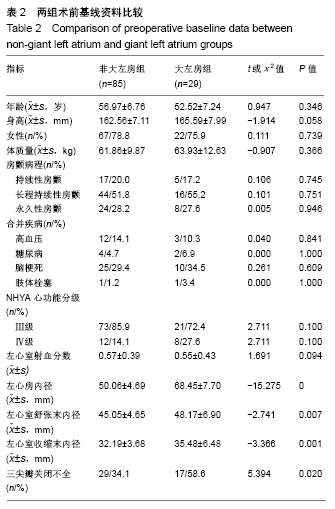
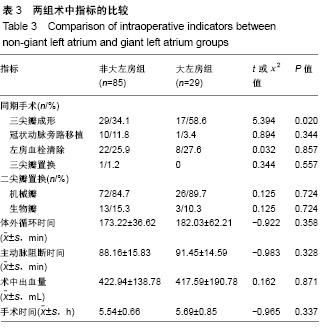
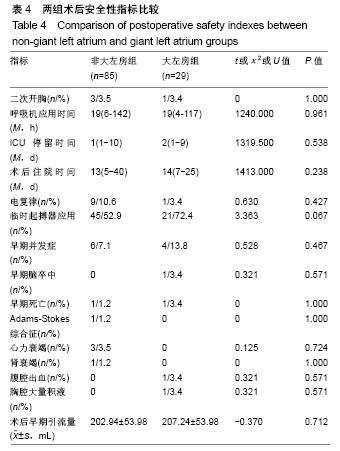
.jpg)
.jpg)