中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (6): 888-892.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1189
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
桥接系统混棒与双棒结构治疗股骨及胫骨骨折的生物力学特点
汪 亮1,黄朝朝2,于娇娜2,顾卫东1,王 忍1,钱志艺1
- 1常州市第七人民医院骨科,江苏省常州市 213011;2天津市威曼生物材料有限公司牛顿实验室,天津市 301600
Biomechanical characteristics of bridge-link type combined internal fixation system with mixed-rod versus double-rod in the treatment of femoral and tibial fractures
Wang Liang1, Huang Zhaozhao2, Yu Jiaona2, Gu Weidong1, Wang Ren1, Qian Zhiyi1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the Seventh People's Hospital of Changzhou, Changzhou 213011, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Newton Laboratory, Tianjin Weiman Biomaterials Co., Ltd., Tianjin 301600, China
摘要:
文题释义:
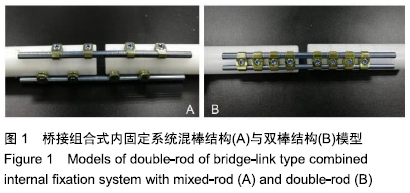
桥接系统双棒与混棒结构:桥接系统双棒结构类似于锁定钢板,固定骨折方式为平行一侧骨面的偏心固定,但偏心固定可能导致纵向上固定减弱及横向上抗扭转降低,骨折端固定不牢靠而使骨折不易愈合,甚至内固定疲劳失效。桥接系统混棒结构为一根单棒固定骨折后,在其径向90°或135°处固定另一根单棒,实现非平面整体、立体固定,骨折端纵向上坚强固定,横向上抗疲劳性能强。
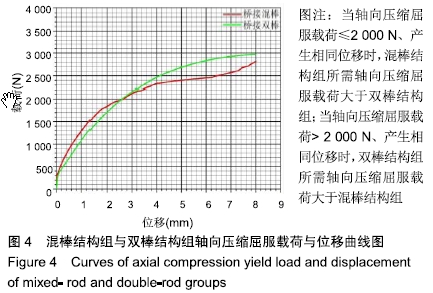
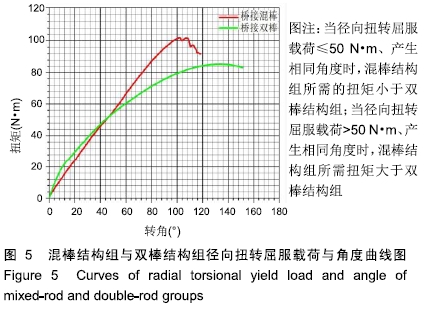
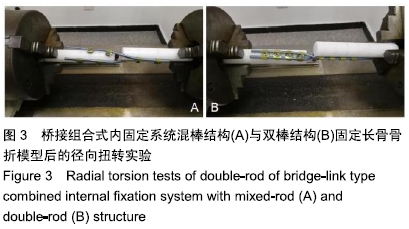
轴向压缩与径向扭转实验:轴向压缩实验是以3 mm/min的速度向模型两端施加轴向压力,观察轴向压缩屈曲载荷与骨折端位移的变化;径向扭转实验是以2 r/min的速度径向旋转,观察横向扭矩与角度变化。轴向压缩实验主要观察纵向上骨折端稳定程度,径向扭转实验主要观察横向上抗疲劳性能。
背景:桥接系统双棒结构为偏心固定,术后可能导致纵向上固定减弱及横向上抗扭转降低。
目的:比较桥接组合式内固定系统混棒与双棒结构治疗股骨及胫骨骨折的生物力学特性。
方法:以40根短聚甲醛材料配对模拟人体长骨骨干模型20个,其中10个以桥接组合式内固定系统混棒结构固定(混棒结构组),另10个以桥接组合式内固定系统双棒结构固定(双棒结构组),对2组分别进行轴向压缩实验和径向扭转实验(每种实验各选择每组5个模型),观察2组的轴向压缩力与位移情况,以及横向扭转力与角度变化,记录各组曲线出现折点或趋于水平状态时的载荷即最大载荷,并计算屈服载荷。
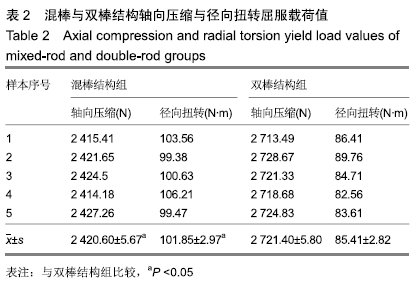
结果与结论:①当轴向压缩屈服载荷≤2 000 N、产生相同位移时,混棒结构组所需轴向压缩屈服载荷大于双棒结构组;当轴向压缩屈服载荷>2 000 N、产生相同位移时,双棒结构组所需轴向压缩屈服载荷大于混棒结构组,并且双棒结构组最大轴向压缩屈服载荷大于混棒结构组[(2 420.60±5.67),(2 721.40±5.80)N,t=-82.885,P=0];②当径向扭转屈服载荷≤50 N•m、产生相同角度时,混棒结构组所需的扭矩小于双棒结构组;当径向扭转屈服载荷>50 N•m、产生相同角度时,混棒结构组所需扭矩大于双棒结构组,并且混棒结构组最大径向扭转屈服载荷大于双棒结构组 [(101.85±2.97),(85.41±2.82)N•m,t=8.985,P=0];③结果说明,桥接系统混棒与双棒结构纵向上均可坚强固定骨折,但混棒结构固定骨折更稳定、牢靠,更容易促使骨折愈合;混棒结构横向上固定骨折后,骨折端容易产生微动,符合弹性固定,并且最大抗扭转力及抗疲劳性能优于双棒结构,可防止因横向不稳定造成的桥接系统断裂。ORCID: 0000-0002-0608-5303(汪亮)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: