中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (6): 882-887.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2450
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
计算机辅助2枚空心钉置入内固定治疗股骨颈骨折的生物力学分析
申洪全,陆 慧,张孝华,郭金伟,杨博文,余路鑫,朱 明
- 重庆市江津区中心医院,重庆市 402260
Biomechanical analysis of computer assisted-two cannulated screw fixation for treating femoral neck fracture
Shen Hongquan, Lu Hui, Zhang Xiaohua, Guo Jinwei, Yang Bowen, Yu Luxin, Zhu Ming
- Jiangjin Central Hospital of Chongqing, Chongqing 402260, China
摘要:
文题释义:
股骨颈骨折最佳治疗方案:目前仍然存在争议,治疗方法众多,包括股骨颈加压螺钉经2枚或3枚平行螺钉固定或者关节置换,或者在少数情况下采用非手术治疗。但目前在临床上广泛应用的主流选择仍然是国际内固定学会(AO/ASIF)推荐的纯钛空心螺钉治疗股骨颈骨折,具有手术操作简单、局部解剖分离较少、手术时间较短等优点,已被大多数学者认可。
股骨颈骨折内固定的条件:①抵抗施予骨折线上的剪应力;②抵抗弯应力;③容许轴心上的压应力。
背景:临床上常用的空心钉有单头及双头2类,普通(单头)空心加压螺钉固定容易出现股骨颈短缩,骨质疏松时容易出现退钉现象,因此治疗股骨颈骨折选择普通空心加压螺钉还是双头空心加压螺钉目前存在争议。
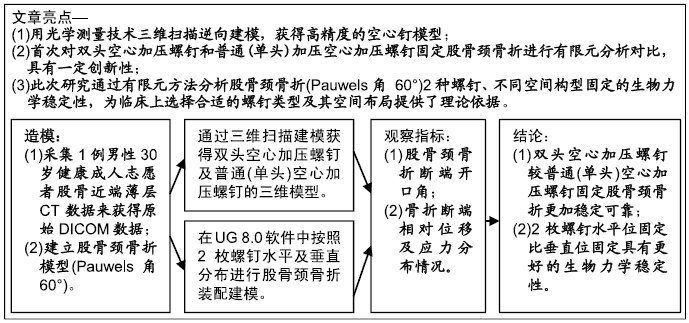
目的:通过有限元分析探讨2枚双头空心加压螺钉与2枚普通(单头)空心加压螺钉的不同空间构型在治疗股骨颈骨折中的生物力学作用。
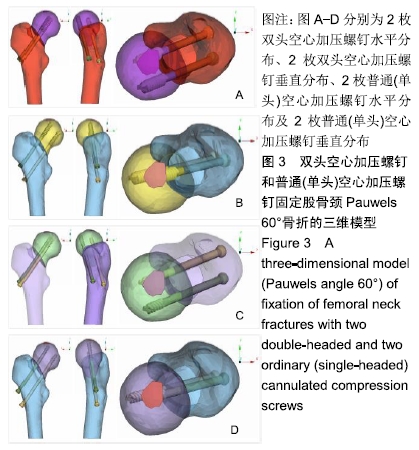
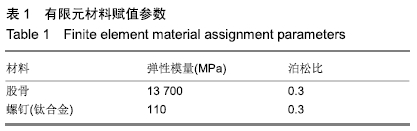
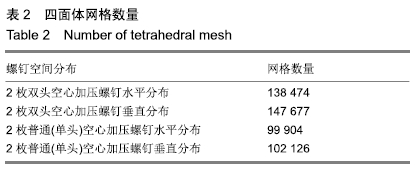
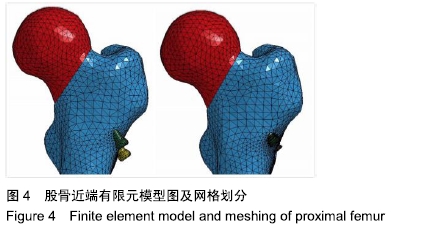
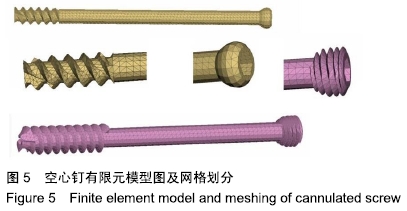
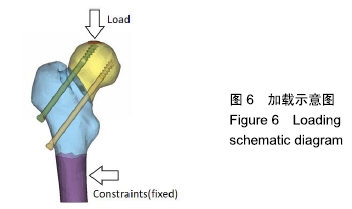
方法:通过采集1名男性30岁健康成人志愿者股骨近端薄层CT扫描来获得原始DICOM数据,在Mimics 10.01软件中建立股骨近端模型,将该模型导入UG 8.0软件中建立股骨颈骨折模型(Pauwels角 60°)。再通过三维扫描建模获得双头空心加压螺钉及普通(单头)空心加压螺钉的三维模型。在UG 8.0软件中按照2枚螺钉水平及垂直分布进行股骨颈骨折装配建模,再将建立的模型导入ANSYS 14.5软件中赋值运算后,测量股骨颈骨折断端开口角、骨折断端相对位移及应力分布情况。
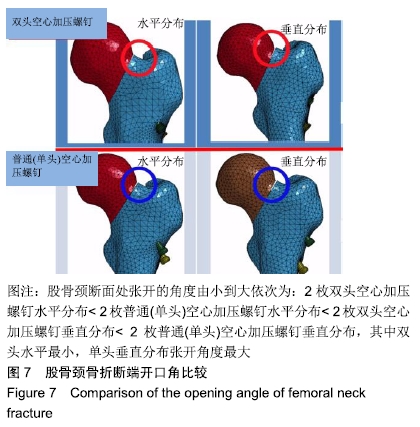
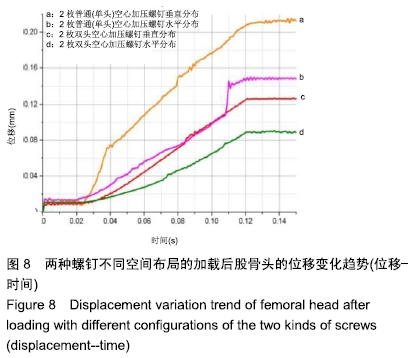
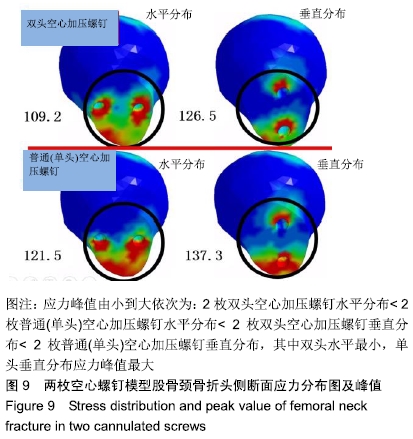
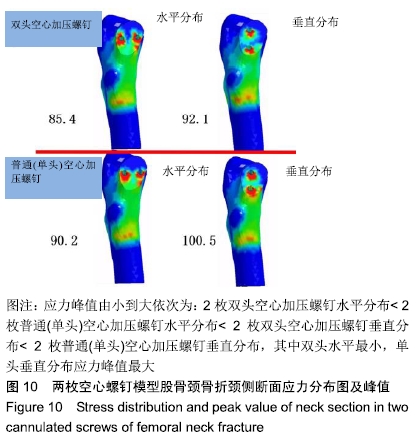
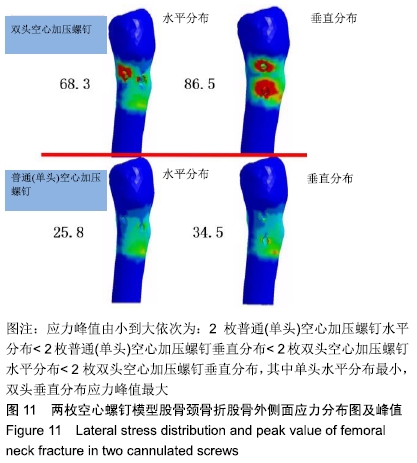
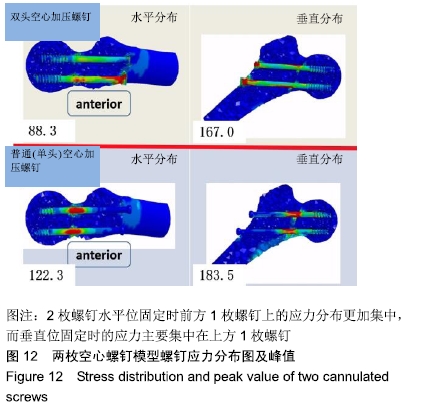
结果与结论:①在生物力学稳定性方面:2枚螺钉水平位固定骨折断端的开口角及位移小于垂直位固定,双头空心加压螺钉的开口角及位移小于普通(单头)空心加压螺钉;②应力分布:2种螺钉固定的应力分布不同,双头空心加压螺钉的螺钉上应力分布较普通(单头)空心加压螺钉更加分散,部分应力传递至螺钉尾部;而在普通(单头)空心加压螺钉中,螺钉上的应力主要集中在骨折断端处;水平和垂直布局的应力分布亦有差别,2枚螺钉水平位固定时前方1枚螺钉上的应力分布更加集中,而垂直位固定时的应力主要集中在上方1枚螺钉;③结果表明,双头空心加压螺钉较普通(单头)空心加压螺钉固定股骨颈骨折更加稳定可靠;2枚螺钉水平位固定比垂直位固定具有更好的生物力学稳定性。因此临床可应用双头加压螺钉治疗股骨颈骨折,当选择2枚螺钉时宜采用水平位固定。ORCID: 0000-0001-7084-2826(申洪全)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: