| [1] Abudu A, Carter SR, Grimer RJ. The outcome and functional results of diaphyseal endoprostheses after tumour excision. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]. 1996;78B: 652-657.[2] Rougraff BT, Simon MA, Kneisl JS, et al. Limb salvage compared with amputation for osteosarcoma of the distal end of the femur. A long-term oncological, functional, and quality-of-life study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(5): 649-656.[3] Muscolo DL, Petracchi LJ, Ayerza MA, et al. Massive femoral allografts followed for 22 to 36 years. Report of six cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992;74(6): 887-892.[4] Benevenia J, Kirchner R, Patterson F, et al. Outcomes of a modular intercalary endoprosthesis as treatment for segmental defects of the femur, tibia, and humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(2): 539-548.[5] Palumbo BT, Henderson ER, Groundland JS, et al. Advances in segmental endoprosthetic reconstruction for extremity tumors: a review of contemporary designs and techniques. Cancer Control. 2011;18(3): 160-170.[6] 刘安庆,张银光,王春生,等. 人股骨生物力学特性的三维有限元分析[J]. 西安医科大学学报, 2001, 22(3):242-244.[7] Taylor ME, Tanner KE, Freeman MA, et al. Stress and strain distribution within the intact femur: compression or bending. Med Eng Phys.1996;18(2):122-131.[8] Sakai R, Itoman M, Mabuehi K. Assessments of different kinds of stems by experiments and FEM analysis:appropriate stress distribution on a hip prosthesis. Clin Biomech. 2006;21(8): 826-833.[9] 李红梅,雷霆,方树铭,等.生物医用钛合金的研究进展[J].金属功能材料, 2011,4(18): 70-73.[10] Mousa WF, Kobayashi M, Shinzato S, et al. Biological and mechanical properties of PMMA-based bioactive bone cements. Biomaterials. 2000;21(21): 2137-2146.[11] Keyak JH,Rossi SA. Prediction of femoral fracture load using finite element models: an examination of stress and strain based failure theories. J Biomech.2000;33(2):209-214. [12] Pedersen DR, Brand RA, Davy DT. Pelvic muscle and acetabular contact forces during gait. J Biomech. 1997;30(9):959-965.[13] Reilly DT, Burstein AH. The mechanical properties of cortical bone. J Bone Joint Surg. 1974;56(9):1001-1022.[14] Greene N, Holtom PD, Warren CA, et al. In vitroelution of tobranmycin and vancomycin polymethylmethacrylate beads and spacers form simplex and palacos. Am J Orthop. 1998;27(3): 201-205.[15] 张国宝,彭楚峰,刘昌奎,等. Ti6Al4V合金精铸件疲劳性能试验研究[J].铸造技术,2008,29(1):54-58.[16] Sewell H. Femoral diaphyseal endoprosthetic reconstruction after segmental resection ofprimary bone tumours. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(6): 867-874.[17] Damron TA, Leerapun T, Hugate RR, et al. Does the second -generation intercalary humeral spacer improve on the first? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(6):1309-1317.[18] 李建民,杨强,杨志平,等. 骨肉瘤髓腔内侵袭范围MRI测量与确定合理截骨平面的相关研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(23):1792-1794.[19] 俞树荣,宋伟. Ti-6Al-4V燕尾榫结构微动疲劳裂纹萌生及扩展行为研究[J].中国机械工程,2015,26(24): 3386-3390.[20] 赵雪瑞.木楔在松木家具贯穿榫结构中增强作用的研究[D]. 株洲:中南林业科技大学, 2013.[21] 田东牧,胡永成,冀勇,等.骨水泥用于股骨近端组配式假体柄固定的有限元分析[J]. 天津理工大学学报,2017,33(3):26-29.[22] Mousa WF, Kobayashi M, Shinzato S, et al. Biological and mechanical properties of PMMA-based bioactive bone cements. Biomaterials. 2000;21(21): 2137-2146.[23] 曹勇,朱建炜,施红光. 股骨的三维有限元重建及初步力学分析[J]. 黑龙江医药, 2010, 23(6): 932-935.[24] Huiskes R. A survey of finite element analysis in orthopedic: the first decade. Biomechanics. 1983;16(6): 385-409.[25] Iula A, Vazquez F, Pappalardo M, et al. Finite element three-dimensional analysis of the vibrational behaviour of the Langevin-type transducer. Ultrasonics. 2002;40(1-8): 513-517.[26] Trabelsi N, Yosibash Z. Patient-specific finite-element analyses of the proximal femur with orthotropic material properties validated by experiments. J Biomech Eng. 2011;133(6): 061001-061011.[27] 程光凯,魏相博,侯永威,等. 加载方式对股骨头近端应力分布影响的研究[C]. 天津市生物医学工程学会.生物医学工程与临床:天津市生物医学工程学会第三十四届学术年会论文集, 2014.[28] Dimaio FR. The science of bone cement: a historical review. Orthopedics. 2002;25(12):1399-1407.[29] Chao EY, Conventry MB. Fracture of the femoral component after total hip replacement. J Bone Jt Surg. 1981;63(7):1078-1094.[30] 范洪辉,李冬松,周振平,等. 不同骨质密度下生物型及骨水泥型股骨假体置入后的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2007, 22(6): 207-210.[31] 胡永成. 膝关节周围恶性肿瘤的人工假体重建技术[J].中华骨科杂志,2011, 31(6): 717-722.[32] Sewell MD, Spiegelberg BG, Hanna SA, et al. Total femoral endoprosthetic replacement following excision of bone tumours. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]. 2009;91B:1513-1520.[33] Rehlmann A, Mosser V, Bergmann G, et al. Effects of stem designand material properties on stress in hip endoprosthesis. J Biomed Eng. 1987; 9(3):77-83.[34] Huiskes R, Weinans H, van Rietbergen B. The relationship between stress shieding and bone resorption around total hip stems and the effects of flexible materials. Clin Orthop. 1992;274: 124-134.[35] Uhthoff HK, Bardos DI, Liskova-Kiar M. The advantages of titanium alloy over stainless steel titanium plate for the internal fixation of fractures. An experimental study in dogs. J Bone Joint Surg. 1981;63(3):427-434. |
.jpg)
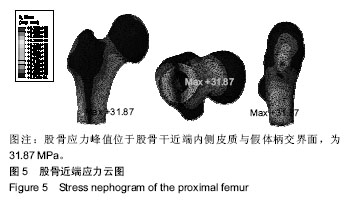

.jpg)
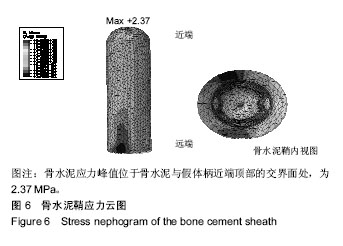
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
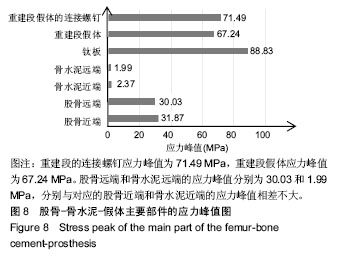
.jpg)
.jpg)