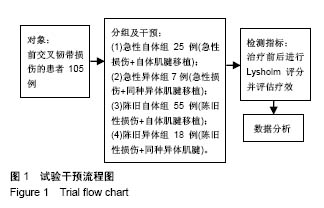
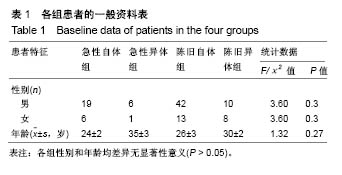
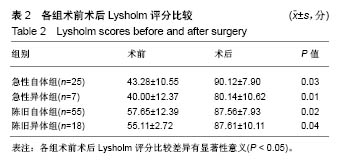
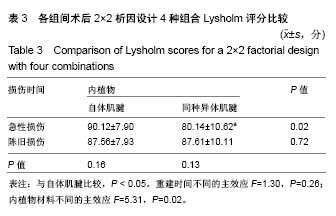
| [1] Hurd WJ, Axe MJ, Snyder-Mackler L. Influence of age, gender, and injury mechanism on the development of dynamic knee stability after acute ACL rupture. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2008;38(2):36-41. [2] Renstrom P, Ljungqvist A, Arendt E, et al. Non-contact ACL injuries in female athletes: an International Olympic Committee current concepts statement. Br J Sports Med. 2008;42(6):394-412.[3] Anderson AF, Anderson CN. Correlation of meniscal and articular cartilage injuries in children and adolescents with timing of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(2):275-281.[4] Anstey DE, Heyworth BE, Price MD, et al. Effect of timing of ACL reconstruction in surgery and development of meniscal and chondral lesions. Phys Sports Med. 2012;40(1):36-40.[5] Li B, Bai L, Fu Y, et al. Effect of timing of surgery in partially injured ACLs. Orthopedics. 2012;35(5):408-412.[6] Herbst E, Hoser C, Gfoller P, et al. Impact of surgical timing on the outcome of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(2):569-577.[7] Mook WR, Miller MD, Diduch DR, et al. Multiple-ligament knee injuries: a systematic review of the timing of operative intervention and postoperative rehabilitation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(12):2946-2957.[8] Brambilla L, Pulici L, Carimati, et al. Prevalence of associated lesions in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: correlation with surgical timing and with patient age, sex, and body mass index. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(12):2966-2973.[9] Kwok CS, Harrison T, Servant C. The optimal timing for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with respect to the risk of postoperative stiffness. Arthroscopy. 2013;29(3): 556-565.[10] Krutsch W, Zellner J, Baumann F, et al. Timing of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction within the first year after trauma and its influence on treatment of cartilage and meniscus pathology. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(2):418-425.[11] Camp CL, Lebaschi A, Cong GT, et al. Timing of postoperative mechanical loading affects healing following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: analysis in a murine model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(16):1382-1391.[12] Kennedy J, Jackson MP, O'Kelly P, et al. Timing of reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament in athletes and the incidence of secondary pathology within the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(3):362-366.[13] Andernord D, Karlsson J, Musahl V, et al. Timing of surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament. Arthroscopy. 2013;29(11): 1863-1871.[14] Chong RW, Tan JL. Rising trend of anterior cruciate ligament injuries in females in a regional hospital. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2004;33(3):298-301.[15] Kaeding CC, Aros B, Pedroza A, et al. Allograft versus autograft anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: predictors of failure from a moon prospective longitudinal cohort. Sports Health. 2011;3(1):73-81.[16] Rice RS, Waterman BR, Lubowitz JH. Allograft versus autograft decision for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: an expected-value decision analysis evaluating hypothetical patients. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(4):539-547.[17] Hu J, Qu J, Xu D et al. Allograft versus autograft for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: an up-to-date meta-analysis of prospective studies. Int Orthop. 2013;37(2):311-320.[18] Aslan A, Ozer O, Baydar ML, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries: does surgical treatment with autograft versus allograft option affect the clinical results? Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2012;18(2):153-161.[19] Paschos NK, Howell SM. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: principles of treatment. EFORT Open Reviews. 2016;1(11):398-408.[20] Kane PW, Wascher J, Dodson CC, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with bone-patellar tendon-bone autograft versus allograft in skeletally mature patients aged 25 years or younger. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016; 24(11):3627-3633.[21] Sun K, Zhang J, Wang Y, et al. Arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with at least 2.5 years’ follow-up comparing hamstring tendon autograft and irradiated allograft. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(9):1195-1202.[22] Islam MZ, Rahman M, Ali ME, et al. Arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with triplet autograft of semitendinosus tendon. Mymensingh Med J. 2017;26(3): 545-550.[23] Wasserstein D, Sheth U, Cabrera A, et al. A systematic review of failed anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with autograft compared with allograft in young patients. Sports Health. 2015;7(3):207-216.[24] Barrera Oro F, Sikka R, Wolters B, et al. Autograft versus allograft: an economic cost comparison of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(9):1219-1225.[25] Bottoni CR, Smith EL, Shaha J, et al. Autograft versus allograft anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a prospective, randomized clinical study with a minimum 10-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(10):2501-2509.[26] Zeng C, Gao S, Li H, et al. Autograft versus allograft in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and systematic review of overlapping systematic reviews. Arthroscopy. 2016;32(1): 153-163.[27] Mariscalco MW, Magnussen RA, Mehta D, et al. Autograft versus nonirradiated allograft tissue for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(2):492-499.[28] Engelman GH, Carry PM, Hitt KG, et al. Comparison of allograft versus autograft anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction graft survival in an active adolescent cohort. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(10):2311-2318.[29] Jia YH, Sun PF. Comparison of Clinical Outcome of Autograft and Allograft Reconstruction for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears. Chin Med J. 2015;128(23):3163-3166.[30] Yang R, Deng H, Hou J, et al. Comparison of Knee Stability and Synovial Fluid Alterations in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction With a Hamstring Autograft or an Allograft. Orthopedics. 2017;40(15):e892-e897.[31] Cooper MT, Kaeding C. Comparison of the hospital cost of autograft versus allograft soft-tissue anterior cruciate ligament reconstructions. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(11):1478–1482.[32] Cvetanovich GL, Mascarenhas R, Saccomanno MF, et al. Hamstring autograft versus soft-tissue allograft in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthroscopy. 2014;30(12):1616-1624.[33] Mascarenhas R, Erickson BJ, Sayegh ET, et al. Is there a higher failure rate of allografts compared with autografts in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review of overlapping meta-analyses. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(2): 364-372.[34] Noyes FR, Barber-Westin SD. Posterior cruciate ligament allograft reconstruction with and without a ligament augmentation device. Arthroscopy. 1994;10(4):371-382.[35] 冯华,洪雷,耿向苏,等.前十字韧带损伤合并内侧半月板ramp损伤[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(11):651-655.[36] Mccarthy M, Mallett K, Abola M, et al. Hospital for special surgery ACL registry: 2-year outcomes suggest low revision and return to OR rates. HSS J. 2017;13(2):119-127.[37] Sklenský J, Vališ P, Repko M, et al. The Use of BTB Allograft in Revision Reconstruction of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament and Its Success Rate in Terms of Subjective Patient Satisfaction. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2017;84(2): 106-113.[38] Catterall JB, Stabler TV, Flannery CR, et al. Changes in serum and synovial fluid biomarkers after acute injury (NCT00332254). Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(6):R229.[39] 林子洪,傅明,康焱,等.前交叉韧带切除后股骨关节软骨变化的初步实验研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2008,2(5):554-565.[40] Jackson DW, Corsetti J, Simon T M. Biologic incorporation of allograft anterior cruciate ligament replacements. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(324):126-133.[41] Malinin TI, Levitt RL, Bashore C. A study of retrieved allografts used to replace anterior cruciate ligaments. Arthroscopy. 2002;18(2):163-170.[42] Jaureguito JW, Paulos LE. Why grafts fail. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(325):25-41. |
.jpg)
.jpg)