| [1] Zanotti B,Zingaretti N,Verlicchi A,et al.Cranioplasty: review of materials.J Craniofac Surg.2016; 27(8):2061-2072.[2] Ban SP,Son YJ,Yang HJ,et al.Analysis of complications following decompressive craniectomy for traumatic brain injury.J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2010;48(3):244-250.[3] Honeybul S,Janzen C,Kruger K,et al.The incidence of neurologic susceptibility to a skull defect. World Neurosurg. 2016;86:147-152.[4] Wiggins A,Austerberry R,Morrison D,et al.Cranioplasty with custom-made titanium plates—14 years experience. Neurosurgery. 2012;72(2):248-256.[5] Shah AM,Jung H,Skirboll S.Materials used in cranioplasty: a history and analysis.Neurosurg Focus.2014;36(4):1-7.[6] Tanodekaew S,Channasanon S,Kaewkong P,et al.PLA-HA scaffolds: preparation and bioactivity. Procedia Eng.2013;59: 144-149.[7] Persson M,Lorite GS,Kokkonen HE,et al.Effect of bioactive extruded PLA/HA composite films on focal adhesion formation of preosteoblastic cells.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2014;121: 409-416.[8] 张海峰,杜子婧,毛曦媛,等.3D打印PLA-HA复合材料构建组织工程骨的实验研究[J].国际骨科学杂志,2016,37(1):57-63.[9] 王鑫,周建平,张文祥,等.气动挤出沉积成型材料对人工牙槽骨结构与性能的影响[J].机床与液压, 2014,42(9):84-86.[10] Dadsetan M,Guda T,Runge MB,et al.Effect of calciumphosphate coating and rhBMP-2 on bonere-generation in rabbit calvaria using poly (propylenefumarate) scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2015;18:9-20.[11] Hokugo A,Sorice S,Parhami F,et al.A novel oxysterol promotes bone regeneration in rabbit cranial bone defects.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(7):591-599.[12] Ren X,Bischoff D,Weisgerber DW.Osteogenesis on nanoparticulate mineralized collagen scaffolds via autogenous activation of the canonical BMP receptor signaling pathway.Biomaterials.2015; 50:107-114.[13] Aydin S,Kucukyuruk B,Abuzayed B,et al.Cranioplasty: review of materials and techniques.J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2011;2(2):162.[14] Khader BA,Towler MR.Materials and techniques used in cranioplasty fixation: A review.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;66:315-322. [15] Song T,Qiu ZY,Cui FZ.Biomaterials for reconstruction of cranial defects. Front Mater Sci.2015;9(4):291-295.[16] Goldstein JA,Paliga JT,Bartlett SP.Cranioplasty: indications and advances.Curr Opin Otolaryngo. 2013;21(4):400-409.[17] Junior ACA,Hamamoto Filho PT,Neto AAP,et al.Biomaterials for Reconstruction of Cranial Defects. Arq Bras Neurocir. 2016;35(4): 291-295.[18] Kwarcinski J,Boughton P,Ruys A,et al.Cranioplasty and Craniofacial Reconstruction: A Review of Implant Material, Manufacturing Method and Infection Risk.Appl Sci. 2017;7(3):1-17.[19] Staffa G,Barbanera A,Faiola A,et al.Custom made bioceramic implants in complex and large cranial reconstruction: a two-year follow-up.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012;40(3):e65-e70.[20] Moreiragonzalez A,Jackson IT,Miyawaki T,et al.Clinical outcome in cranioplasty: critical review in long-term follow-up. J Craniofac Surg.2003;14(2):144.[21] 李建华,闫玉华,李世普,等.可降解聚乳酸与羟基磷灰石复合材料的研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2007,4(2):37-39,42.[22] Bhaskar B,Owen R,Bahmaee H,et al.Composite porous scaffold of PEG/PLA support improved bone matrix deposition in vitro compared to PLA-only scaffolds.J Biomed Mater Res A.2018; 106(5):1334-1340. [23] Gupta B,Revagade N,Hilborn J.Poly(lactic acid) fiber: An overview. Prog Polym Sci.2007; 32(4):455-482.[24] Mao D,Li Q,Bai N,et al.Porous stable poly (lactic acid)/ethyl cellulose/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds prepared by a combined method for bone regeneration.Carbohydr Polym. 2018; 180:104-111.[25] 党丽,王鹏程,吴昊,等.PLA/HA多孔生物支架的制备及性能研究[J].塑料科技, 2014,42(10):87-91.[26] 杨翰搏,大木顺司,王苓.PLA/HA复合材料蠕变行为研究[J].西华大学学报(自然科学版),2015,34(1):22-26.[27] 吴景泉,刘俊,谢爱国,等.自体骨粉移植修复兔下颌骨部分缺损的骨组织形态计量学检测[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2012,6(6):1612-1614.[28] Hurvitz KA,Kobayashi M,Evans GRD.Current options in head and neck reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;118(5):122e-133e.[29] Movassaghi K,Ver HJ,Ganchi P,et al.Cranioplasty with subcutaneously preserved autologous bone grafts.Plast Reconstr Surg.2006;117(1):202.[30] Sundseth J,Sundseth A,Berg-Johnsen J,et al.Cranioplasty with autologous cryopreserved bone after decompressive craniectomy. Complications and risk factors for developing surgical site infection. Acta Neurochir.2014;156(4):805-811. |
.jpg)
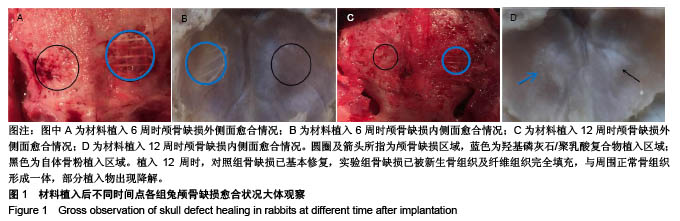
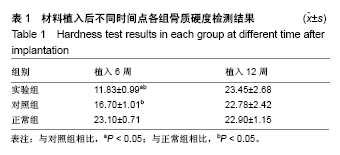
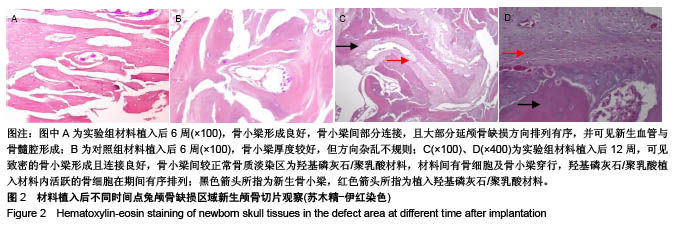
.jpg)