中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (28): 4463-4468.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0389
• 血管组织构建 vascular tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
家兔静脉冲压拉伸实验:动静脉的力学参数差异
张雨豪1,2,牛 培1,张志敏2,牛小龙1,申文增1,周玉娟1,刘福林2
- 1河北大学医学院,河北省保定市 071000;2河北大学附属医院心脏外科,河北省保定市 071030
Stamping tensile test in rabbits: differences in mechanical parameters between veins and arteries
Zhang Yu-hao1, 2, Niu Pei1, Zhang Zhi-min2, Niu Xiao-long1, Shen Wen-zeng1, Zhou Yu-juan1, Liu Fu-lin2
- 1Medical School of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Cardiac Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071030, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
.jpg)
文题释义:
杨氏模量(Young's modulus):是描述固体材料抵抗形变能力的物理量。当一条长度为L、截面积为S的金属丝在力F作用下伸长?L时,F/S叫应力,其物理意义是金属丝单位截面积所受到的力;?L/L叫应变,其物理意义是金属丝单位长度所对应的伸长量。应力与应变的比叫弹性模量。?L是微小变化量。
滞后环:在弹性变形范围内,骤然加载和卸载的开始阶段,应变总要落后于应力,不同步。因此,其结果必然会使得加载线和卸载线不重合,而形成一个封闭的滞后回线,这个回线称为弹性滞后环。这个环说明加载时消耗在变形上的功大于卸载时金属恢复变形所做的功。
摘要
背景:目前国内冠状动脉旁路移植术后血管桥通畅性与生物力学相关的研究较少。
目的:从血管生物力学的角度出发,对比分析静脉和动脉的力学参数差异。
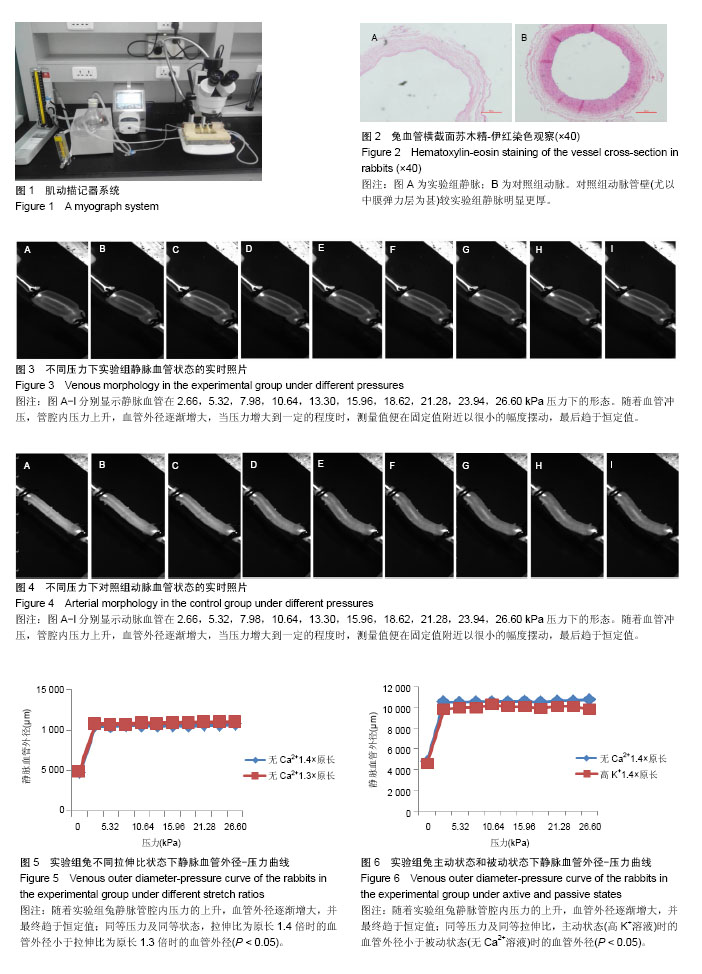
方法:家兔20只,对照组10只,实验组10只。游离实验组家兔一侧颈外静脉,对照组家兔一侧颈总动脉置入保存液,随后立即将血管标本进行冲压拉伸实验,测量不同压力(0-26.6 kPa)、主动状态(高K+溶液)和被动状态(无Ca2+溶液)下兔动静脉血管外径变化,行苏木精-伊红染色观察血管形态学特点,并对冲压拉伸力学实验数据进行分析。
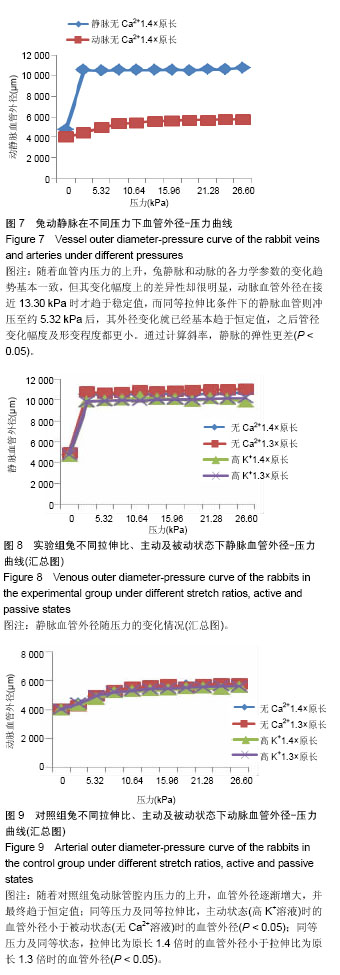
结果与结论:①不论在主动力学或是被动力学的实验中,血管外径(内径)-压力曲线,血管壁厚度-压力曲线,周向拉伸比-压力曲线均呈现先变化后趋于稳定值的规律;②对比静脉和动脉的力学参数发现:静脉的弹性明显不如动脉(P < 0.05),开始冲压后,静脉的外径迅速增大,最终趋于恒定值时接近动脉的外径的2倍,体式显微镜下看到的静脉管壁明显更薄,随着血管内压力的上升,动脉血管外径在接近13.3 kPa时才趋于稳定值,而同等拉伸比条件下的静脉血管则冲压至约5.32 kPa后,其外径变化就已经基本趋于恒定值;③血管组织形态学显示:对于横截面下的静脉和动脉,静脉管壁厚度明显小于动脉;④结果说明,随着管腔内压力的上升,静脉更早地达到弹性极值,顺应性更差,在高压的环境中更容易受到损伤,符合静脉管壁弹力层较薄这一组织学特性。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-0601-3104(张雨豪)
中图分类号:
.jpg)