中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (7): 1078-1083.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0120
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
新型固定重建与关节镜下固定修复膝关节后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折:非随机对照试验方案和预试验结果
陈广栋1,张 洋2,倪永健1,杜红梅1,曹同军1,单忠林1
- 1沧州市中心医院骨三科,河北省沧州市 061000;2解放军新疆军区总医院关节外科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000
A new fixation and reconstruction method versus arthroscopic reconstruction for treating avulsion fracture at the tibial insertion of the knee posterior cruciate ligament: study protocol for a non-randomized controlled trial and preliminary results
Chen Guang-dong1, Zhang Yang2, Ni Yong-jian1, Du Hong-mei1, Cao Tong-jun1, Shan Zhong-lin1
- 1Third Department of Orthopedics, Cangzhou Central Hospital, Cangzhou 061000, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Joint Surgery, Xinjiang Military General Hospital, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
膝交叉韧带:又称十字韧带,位于膝关节中央稍后方,非常强韧,由滑膜衬覆,可分为前、后2条。2条韧带协同可限制膝关节过度运动。
关节镜:是一种观察关节内部结构的直径约5 mm的棒状光学器械,是用于诊治关节疾患的内窥镜。
摘要
背景:关节镜下手术治疗膝关节交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折可最大程度地减少手术创伤,但因其植入的固定物牢靠性相对较差,术后早期不能进行功能锻炼,不利于膝关节功能恢复。传统切开复位内固定修复膝关节后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折常不能牢靠固定,也影响修复效果。
目的:文章设计并提出腘窝倒“L”形切口入路新型接骨板骨折固定及韧带张力重建,牢固固定骨块,并保持良好的韧带张力,有利于膝关节功能恢复,对比观察此方法和关节镜下固定治疗膝关节后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折效果的差异。
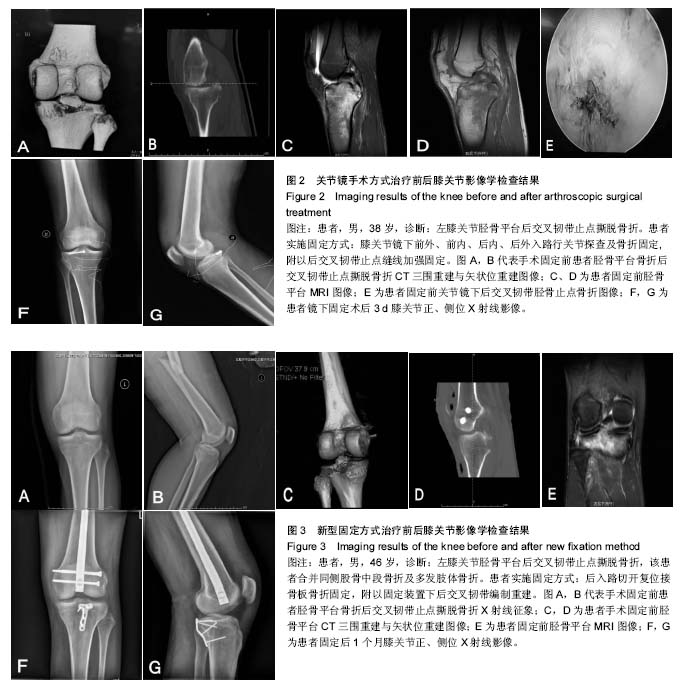
方法:研究为前瞻性、单中心、非随机对照临床试验。将180例(膝)后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折患者按治疗方式不同分为2组,关节镜组采用关节镜下固定修复,新型固定重建组采用腘窝倒“L”形切口入路新型接骨板骨折固定并韧带张力重建修复,每组90例(膝),术后随访6周,6,12个月。
结果与讨论:研究的主要结局指标为术后12个月以Lysholm评分优良率以评估膝关节功能恢复情况;次要结局指标为术前、术后6周,6个月以Lysholm评分评价膝关节功能恢复优良率,术前、术后6周,6,12个月膝关节Lysholm评分、HSS评分、目测类比评分、后抽屉试验阴性率及膝关节X射线形态;术后6周,6,12个月的不良反应发生率。稿件提交时作者已获得62例(膝)的预试验结果显示,术后3个月,与关节镜组比较,新型固定重建组的后抽屉试验阴性率及Lysholm评分均升高(P < 0.05)。试验的目的在于和关节镜下内固定相比,评价腘窝倒“L”形切口入路新型接骨板骨折固定并韧带张力重建修复膝关节后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折效果的差异,在骨折牢靠固定,更有利于患者膝关节功能恢复方面更有优势。试验经沧州市中心医院医学伦理委员会批准(审批单位:沧州市中心医院,审批号:2017-120-01)。研究符合世界医学会制定的《赫尔辛基宣言》的要求。参与者本人对试验方案和过程均知情同意,并签署知情同意书。试验设计时间为2017年1月,试验于2018年4月至开始进行患者招募及数据收集,2019年6月招募结束,2020年8月进行结果指标分析,2020年10月试验完成。文章结果将以科学会议报告,或在同行评议的期刊上发表传播。试验已在中国临床试验注册中心注册(注册号:ChiCTR1800015026),注册方案版本号1.0。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-0257-6719(陈广栋)
中图分类号:

.jpg)