中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (3): 368-373.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0032
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
人工全踝关节置换与踝关节融合治疗创伤性踝关节炎:疗效和安全性比较
许 骏,谢 林
- 南京中医药大学附属省中西结合医院骨伤科,江苏省南京市 210000
Artificial ankle arthroplasty versus ankle joint fusion for traumatic ankle arthritis: efficacy and safety
Xu Jun, Xie Lin
- Department of Orthopedics, Nanjing Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
踝关节融合:是一种造成关节强直的手术,其具有终止病情、解除疼痛、纠正畸形、稳定关节的作用,费用较低,术后效果尚可,因此患者容易接受。虽然其也存在一定的弊端,如切口感染、融合不良、融合畸形等会影响手术的效果和患者术后踝关节的功能,但其仍是严重踝关节炎的标准治疗方式。微创踝关节融合是指在关节镜下进行关节融合术,由于术中不需剥离骨膜,因此对局部血运影响较小,可减少术中出血量,加速骨融合的速度。
人工全踝关节置换:早期由于假体材料、软组织处理技术不成熟、松动以及适应证不明确等原因,造成术后疗效不佳、手术失败率较高,限制了其在临床中的应用。近年来,随着假体材料、固定方式、手术入路方式的改善,人工全踝关节置换的手术成功率也逐渐提高,并且取得了满意的术后疗效,5年生存率高达90%以上。目前多项研究结果显示,人工全踝关节置换具有快速解除疼痛、改善关节活动障碍、提高患者预后生活质量等优点。
摘要
背景:目前人工全踝关节置换和关节镜踝关节融合均可用于治疗严重的创伤性关节炎,但是何种治疗方式可使患者获益更多尚无定论。
目的:探究人工全踝关节置换与踝关节融合在创伤性踝关节炎治疗中的临床疗效和安全性。
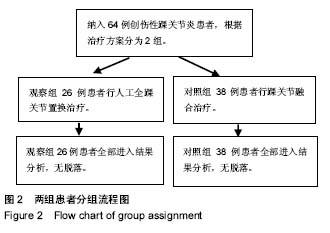
方法:回顾分析2012年1月至2015年12月南京中医药大学附属省中西结合医院收治的经保守治疗无效的创伤性踝关节炎患者64例64踝的病例资料,根据患者所接受的治疗方式将其分为观察组和对照组,其中观察组患者26例26踝行人工全踝关节置换,对照组患者38例38踝行踝关节融合。记录并比较2组患者手术情况、住院时间、术后并发症、翻修率、跛行率以及出院后随访情况,同时评估和比较2组患者的术前、术后踝关节Kofoed评分、目测类比评分以及美国矫形足踝协会踝-后足评分(AOFAS)情况。
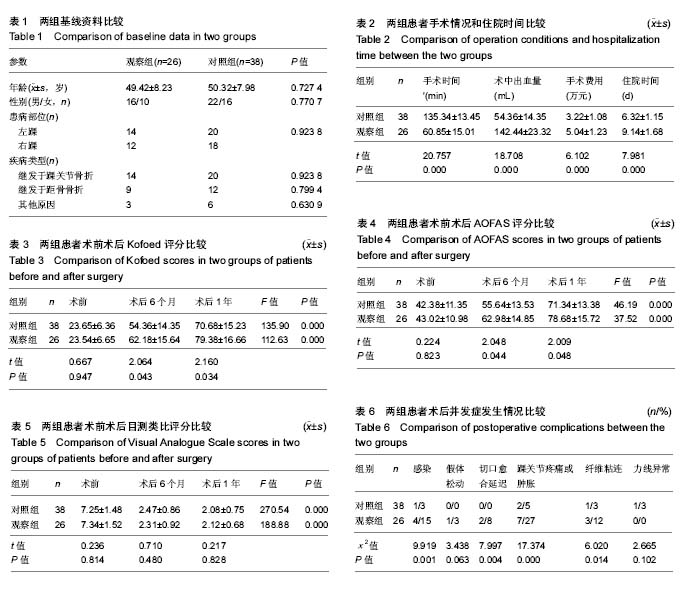
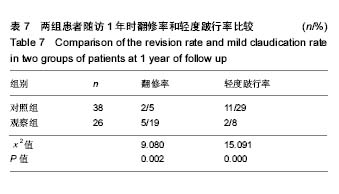
结果与结论:①对照组患者的手术时间明显长于观察组(P < 0.05)。而观察组患者的术中出血量、手术费用和术后住院时间明显高于对照组(P < 0.05);②组内比较,2组患者术后6个月、1年Kofoed评分、目测类比评分、AOFAS评分均高于术前(P < 0.05);组间比较,2组患者术前Kofoed评分、目测类比评分、AOFAS评分差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);观察组患者术后6个月、1年的Kofoed评分和AOFAS评分均明显优于对照组(P < 0.05);2组患者术后6个月、1年的目测类比评分差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③对照组患者的术后感染率、切口愈合延迟率、纤维粘连和踝关节疼痛或肿胀率均明显低于观察组(P < 0.05);④对照组患者随访1年时的翻修率明显低于观察组,但轻度跛行率明显高于观察组,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);⑤综上,关节镜下踝关节融合具有创伤小、费用低、术后住院时间短等优势,但其术后跛行率较高;人工全踝关节置换则在改善踝关节功能和活动度方面具有明显优势,但其术后翻修率和部分并发症发病率相对较高。因此,在实际应用过程中,应充分考虑患者病情、年龄以及经济情况等因素,选择最优的治疗方案,积极避免各种术后并发症,提高患者术后生活质量。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-3822-642X(许骏)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)