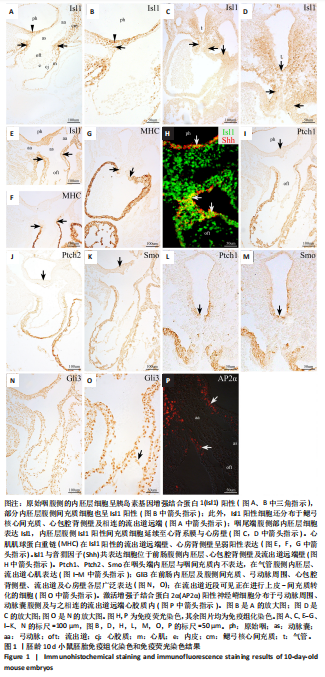
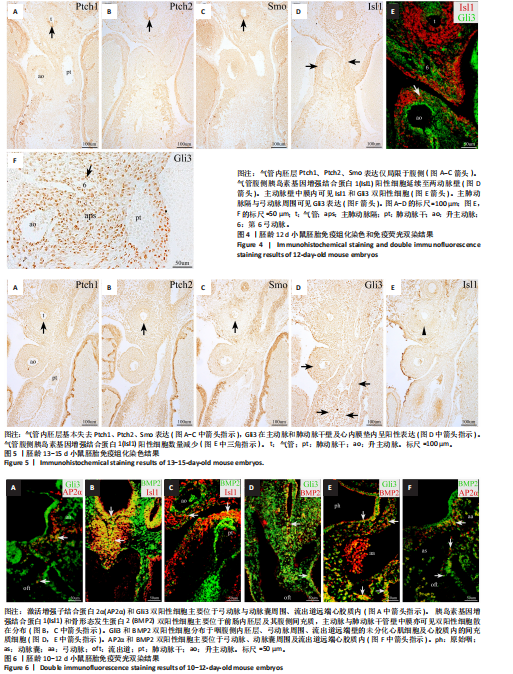
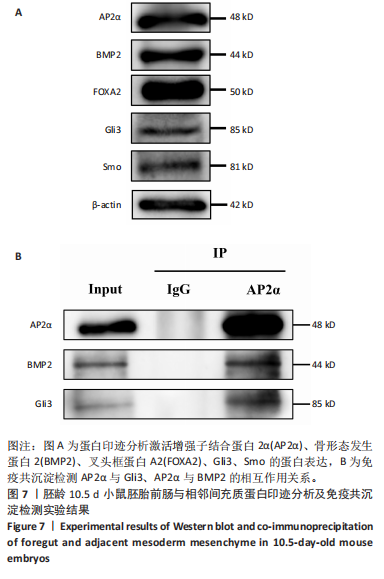
[1] ZHAO K, YANG Z. The second heart field: the first 20 years. Mamm Genome. 2023;34(2):216-228.
[2] Zaffran S, Kelly RG. New developments in the second heart field. Differentiation. 2012;84(1):17-24.
[3] ALKOBTAWI M, RAY H, BARRIGA EH, et al. Characterization of Pax3 and Sox10 transgenic Xenopus laevis embryos as tools to study neural crest development. Dev Biol. 2018;444 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S202-s208.
[4] DE BONO C, LIU Y, FERRENA A, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics uncovers a non-autonomous Tbx1-dependent genetic program controlling cardiac neural crest cell development. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):1551.
[5] KIBALNYK Y, AFANASIEV E, NOBLE RMN, et al. The chromatin regulator Ankrd11 controls cardiac neural crest cell-mediated outflow tract remodeling and heart function. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):4632.
[6] ZHANG KK, XIANG M, ZHOU L, et al. Gene network and familial analyses uncover a gene network involving Tbx5/Osr1/Pcsk6 interaction in the second heart field for atrial septation. Hum Mol Genet. 2016; 25(6):1140-1151.
[7] LI MR, LUO XJ, PENG J. Role of sonic hedgehog signaling pathway in the regulation of ion channels: focus on its association with cardio-cerebrovascular diseases. J Physiol Biochem. 2023;79(4):719-730.
[8] YIN W, LIONTOS A, KOEPKE J, et al. An essential function for autocrine hedgehog signaling in epithelial proliferation and differentiation in the trachea. Development. 2022;149(3):dev199804.
[9] GUZZETTA A, KOSKA M, ROWTON M, et al. Hedgehog-FGF signaling axis patterns anterior mesoderm during gastrulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(27):15712-15723.
[10] LIM TB, FOO SYR, CHEN CK. The Role of Epigenetics in Congenital Heart Disease. Genes (Basel). 2021;12(3):390.
[11] GILL E, BAMFORTH SD. Molecular Pathways and Animal Models of Truncus Arteriosus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1441:853-865.
[12] WASHINGTON SMOAK I, BYRD NA, ABU-ISSA R, et al. Sonic hedgehog is required for cardiac outflow tract and neural crest cell development. Dev Biol. 2005;283(2):357-372.
[13] CHRIST A, MARCZENKE M, WILLNOW TE. LRP2 controls sonic hedgehog-dependent differentiation of cardiac progenitor cells during outflow tract formation. Hum Mol Genet. 2020;29(19): 3183-3196.
[14] CORTES C, FRANCOU A, DE BONO C, et al. Epithelial Properties of the Second Heart Field. Circ Res. 2018;122(1):142-154.
[15] SCHUSSLER O, GHARIBEH L, MOOTOOSAMY P, et al. Cardiac Neural Crest Cells: Their Rhombomeric Specification, Migration, and Association with Heart and Great Vessel Anomalies . Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021;41(3):403-429.
[16] KODO K, UCHIDA K, YAMAGISHI H. Genetic and Cellular Interaction During Cardiovascular Development Implicated in Congenital Heart Diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:653244.
[17] TANG W, LI Y, LI A, et al. Clonal analysis and dynamic imaging identify multipotency of individual Gallus gallus caudal hindbrain neural crest cells toward cardiac and enteric fates. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1894.
[18] ZHANG C, LI Y, CAO J, et al. Hedgehog signalling controls sinoatrial node development and atrioventricular cushion formation. Open Biol. 2021;11(6):210020.
[19] SHEEHAN-ROONEY K, SWARTZ ME, LOVELY CB, et al. Bmp and Shh signaling mediate the expression of satb2 in the pharyngeal arches. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59533.
[20] LIU C, GUO H, SHI C, et al. BMP signaling in the development and regeneration of tooth roots: from mechanisms to applications. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1272201.
[21] HE K, JIANG H, LI W, et al. Primary cilia mediate skeletogenic BMP and Hedgehog signaling in heterotopic ossification. Sci Transl Med. 2024;16(757):eabn3486.
[22] MANZARI-TAVAKOLI A, BABAJANI A, FARJOO MH, et al. The Cross-Talks Among Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) Signaling and Other Prominent Pathways Involved in Neural Differentiation. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022;15:827275.
[23] LIANG S, LI HC, WANG YX, et al. Pulmonary endoderm, second heart field and the morphogenesis of distal outflow tract in mouse embryonic heart. Dev Growth Differ. 2014;56(4):276-292.
[24] TAKIGAWA-IMAMURA H, FUMOTO K, TAKESUE H, et al. Exploiting mechanisms for hierarchical branching structure of lung airway. PLoS One. 2024;19(8):e0309464.
[25] CARBALLO GB, HONORATO JR, DE LOPES GPF, et al. A highlight on Sonic hedgehog pathway. Cell Commun Signal. 2018;16(1):11.
[26] CALLEJAS-MARIN A, MORENO-BRAVO JA, COMPANY V, et al. Gli2-Mediated Shh Signaling Is Required for Thalamocortical Projection Guidance. Front Neuroanat. 2022;16:830758.
[27] NIEWIADOMSKI P, NIEDZIÓŁKA SM, MARKIEWICZ Ł, et al. Gli Proteins: Regulation in Development and Cancer. Cells. 2019;8(2):147.
[28] PENG T, TIAN Y, BOOGERD CJ, et al. Coordination of heart and lung co-development by a multipotent cardiopulmonary progenitor. Nature. 2013;500(7464):589-592.
[29] YOSHIDA S, YOSHIDA K. Regulatory mechanisms governing GLI proteins in hedgehog signaling. Anat Sci Int. 2025;100(2):143-154.
[30] HILGENDORF KI, MYERS BR, REITER JF. Emerging mechanistic understanding of cilia function in cellular signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25(7):555-573.
[31] HASENPUSCH-THEIL K, WEST S, KELMAN A, et al. Gli3 controls the onset of cortical neurogenesis by regulating the radial glial cell cycle through Cdk6 expression. Development. 2018;145(17):dev163147.
[32] YANG Z. The Principle of Cortical Development and Evolution. Neurosci Bull. 2025;41(3): 461-485.
[33] PALMQUIST-GOMES P, MEILHAC SM. Shaping the mouse heart tube from the second heart field epithelium. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2022; 73:101896.
[34] MOTOYAMA J, MILENKOVIC L, IWAMA M, et al. Differential requirement for Gli2 and Gli3 in ventral neural cell fate specification. Dev Biol. 2003;259(1):150-161.
[35] ROWTON M, PEREZ-CERVANTES C, HUR S, et al. Hedgehog signaling activates a mammalian heterochronic gene regulatory network controlling differentiation timing across lineages. Dev Cell. 2022;57(18):2181-2203.e2189.
[36] ERHARDT S, ZHENG M, ZHAO X, et al. The Cardiac Neural Crest Cells in Heart Development and Congenital Heart Defects. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2021;8(8):89.
|