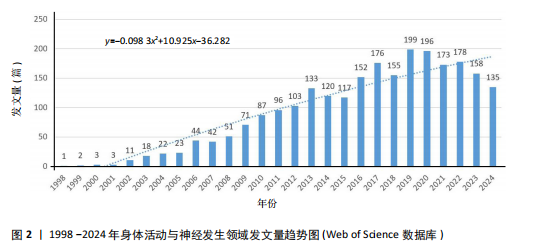
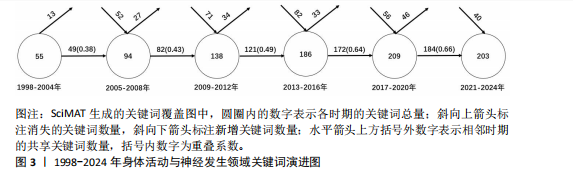
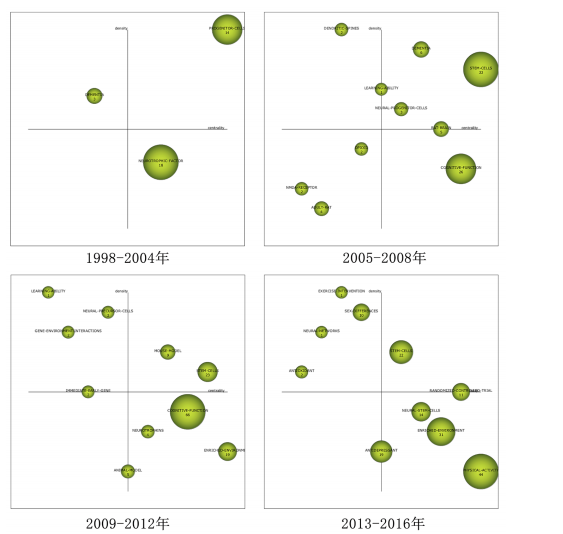
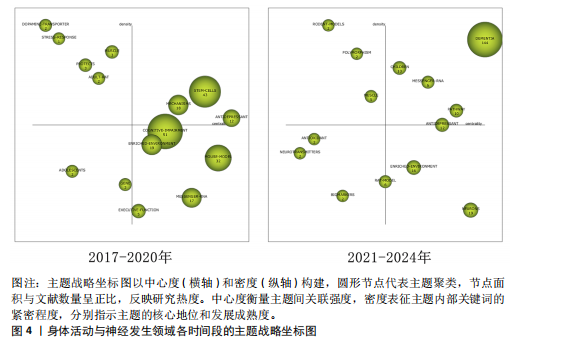
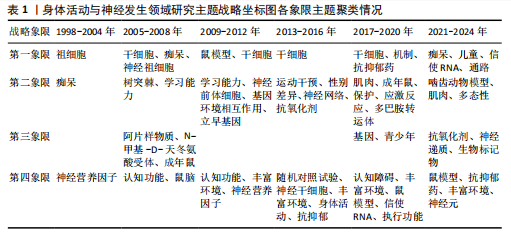
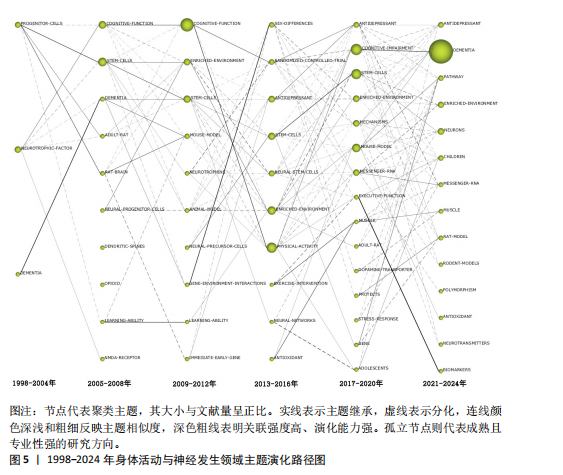
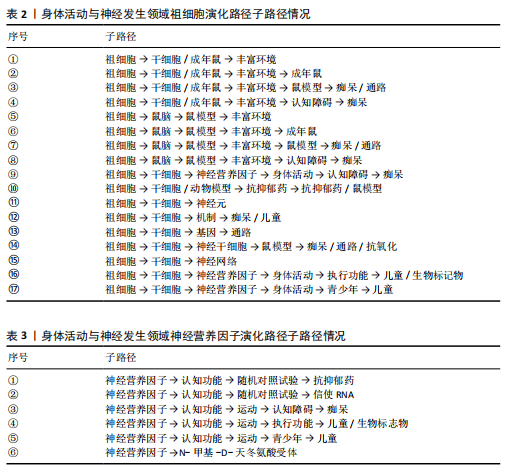
[1] PIERRET C, MORRISON J, RATH P, et al. Developmental cues and persistent neurogenic potential within an in vitro neural niche. BMC Dev Biol. 2010;10:5.
[2] TIWARI V, MISHRA A, SINGH S, et al. Crosstalk between Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Its Role in Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023;14(12): 2271-2281.
[3] ALMULLA A, MOGULKOC R, BALTACI A, et al. Learning, Neurogenesis and Effects of Flavonoids on Learning. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2022;22(2):355-364.
[4] SAHAY A, SCOBIE K, HILL A, et al. Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to improve pattern separation. Nature. 2011;472(7344):466-470.
[5] YAU SY, GIL-MOHAPEL J, CHRISTIE BR, et al. Physical exercise-induced adult neurogenesis: a good strategy to prevent cognitive decline in neurodegenerative diseases? Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:403120.
[6] BAEK SS. Role of exercise on the brain. J Exerc Rehabil. 2016;12(5):380-385.
[7] AUGUSTO-OLIVEIRA M, ARRIFANO GP, LEAL-NAZARÉ CG, et al. Exercise Reshapes the Brain: Molecular, Cellular, and Structural Changes Associated with Cognitive Improvements. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(12): 6950-6974.
[8] VAN PRAAG H, KEMPERMANN G, GAGE FH. Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2(3):266-270.
[9] ZHAI K, MA W, HUANG T. Hot spots and trends in knee revision research since the 21st century: a bibliometric analysis. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(5):388.
[10] KIM Y, DELEN D. Medical informatics research trend analysis: A text mining approach. Health Informatics J. 2018;24(4): 432-452.
[11] ZHONG D, LI Y, HUANG Y, et al. viaMolecular Mechanisms of Exercise on Cancer: A Bibliometrics Study and Visualization Analysis CiteSpace. Front Mol Biosci. 2021; 8:797902.
[12] COBO MJ, LóPEZ-HERRERA AG, HERRERA-VIEDMA E, et al. SciMAT: A new science mapping analysis software tool. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol. 2012;63(8):1609-1630.
[13] 陈晓鹏, 严晓燕, 孙洋, 等. 基于SciMAT的防护服装研究动态演进分析[J]. 服装学报,2023,8(6):521-528.
[14] 夏洋, 李文梅. 近20年国际学业情绪研究主题动态演化路径分析[J]. 当代外语研究,2023,23(5):94-102+132.
[15] 李丽霞, 任卓明, 张子柯. 基于关键词的知识图谱挖掘信息技术学科演化趋势[J]. 电子科技大学学报,2020,49(5):780-787.
[16] 陶文兵, 金海. 一种新的基于图谱理论的图像阈值分割方法[J]. 计算机学报, 2007,30(1): 110-119.
[17] 董雪季, 王晓慧. 国际科学计量学研究主题动态演化路径分析[J]. 数字图书馆论坛,2018(10):9-17.
[18] CARRASCO-GARRIDO C, DE-PABLOS-HEREDERO C, RODRíGUEZ-SáNCHEZ J. Exploring hybrid telework: A bibliometric analysis. Heliyon. 2023;9(12):e22472.
[19] ISO-MARKKU P, KUJALA UM, KNITTLE K, et al. Physical activity as a protective factor for dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review, meta-analysis and quality assessment of cohort and case-control studies. Br J Sports Med. 2022;56(12):701-709.
[20] DOMINGUEZ LJ, VERONESE N, VERNUCCIO L, et al. Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Other Lifestyle Factors in the Prevention of Cognitive Decline and Dementia. Nutrients. 2021;13(11):4080.
[21] LATINO F, TAFURI F. Physical Activity and Cognitive Functioning. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60(2):216.
[22] SINGH AS, SALIASI E, VAN DEN BERG V, et al. Effects of physical activity interventions on cognitive and academic performance in children and adolescents: a novel combination of a systematic review and recommendations from an expert panel. Br J Sports Med. 2019;53(10):640-647.
[23] FERREIRA RN, DE MIRANDA AS, ROCHA NP, et al. Neurotrophic Factors in Parkinson’s Disease: What Have we Learned from Pre-Clinical and Clinical Studies? Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(31):3682-3702.
[24] DE LA ROSA A, OLASO-GONZALEZ G, ARC-CHAGNAUD C, et al. Physical exercise in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9(5):394-404.
[25] VALENZUELA PL, CASTILLO-GARCíA A, MORALES JS, et al. Exercise benefits on Alzheimer’s disease: State-of-the-science. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;62:101108.
[26] BASSO MA, BATISTA AP, CHANG SWC, et al. The Future of Nonhuman Primate Neuroscience: Peril or Possibilities? J Neurosci. 2024;44(37):e1458242024.
[27] GUO JJ, CAO YZ, ZHANG T, et al. Multisensory Fusion Training and 7, 8-Dihydroxyflavone Improve Amyloid-β-Induced Cognitive Impairment, Anxiety, and Depression-Like Behavior in Mice Through Multiple Mechanisms. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2024;20:1247-1270.
[28] YOKOYAMA R, AGO Y, IGARASHI H, et al. (R)-ketamine restores anterior insular cortex activity and cognitive deficits in social isolation-reared mice. Mol Psychiatry. 2024;29(5):1406-1416.
[29] ZHU JW, GE FF, ZENG Y, et al. Physical and Mental Activity, Disease Susceptibility, and Risk of Dementia A Prospective Cohort Study Based on UK Biobank. Neurology. 2022;99(8):E799-E813.
[30] SIMS SK, WILKEN-RESMAN B, SMITH CJ, et al. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Nerve Growth Factor Therapeutics for Brain Injury: The Current Translational Challenges in Preclinical and Clinical Research. Neural Plast. 2022;2022:3889300.
[31] VOGT C, FLOEGEL M, KASPER J, et al. Oxytocinergic modulation of speech production-a double-blind placebo-controlled fMRI study. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2023;18(1):nsad035.
[32] ZHU XQ, CHEN WJ, THIRUPATHI A. Sprint Interval Training Improves Brain-Derived Neurotropic Factor-Induced Benefits in Brain Health-A Possible Molecular Signaling Intervention. Biology (Basel). 2024;13(8):562.
[33] HAMILTON GF, RHODES JS. Exercise Regulation of Cognitive Function and Neuroplasticity in the Healthy and Diseased Brain. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;135:381-406.
[34] LU Y, BU FQ, WANG F, et al. Recent advances on the molecular mechanisms of exercise-induced improvements of cognitive dysfunction. Transl Neurodegener. 2023;12(1):9.
[35] PEKDEMIR B, RAPOSO A, SARAIVA A, et al. Mechanisms and Potential Benefits of Neuroprotective Agents in Neurological Health. Nutrients. 2024;16(24):4368.
[36] TRISAL A, SINGH I, GARG G, et al. Gut-brain axis and brain health: modulating neuroinflammation, cognitive decline, and neurodegeneration. 3 Biotech. 2025;15(1):25.
[37] MA C, LIN M, GAO J, et al. The impact of physical activity on blood inflammatory cytokines and neuroprotective factors in individuals with mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022;34(7):1471-1484.
[38] HUANG T, GONG XK, LIANG Z, et al. Exercised-enriched blood plasma rescues hippocampal impairments and cognitive deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease model. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024; 1870(5): 167197.
[39] HANSON ND, OWENS MJ, NEMEROFF CB. Depression, antidepressants, and neurogenesis: a critical reappraisal. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36(13): 2589-2602.
[40] VAQUERO-RODRÍGUEZ A, ORTUZAR N, LAFUENTE JV, et al. Enriched environment as a nonpharmacological neuroprotective strategy. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023; 248(7):553-560.
[41] TERREROS-RONCAL J, MORENO-JIMéNEZ EP, FLOR-GARCíA M, et al. Impact of neurodegenerative diseases on human adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Science. 2021;374(6571):1106-1113.
[42] HAN Y, YUAN M, GUO YS, et al. The role of enriched environment in neural development and repair. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:890666.
[43] HOSSEINY S, PIETRI M, PETIT-PAITEL A, et al. Differential neuronal plasticity in mouse hippocampus associated with various periods of enriched environment during postnatal development. Brain Struct Funct, 2015;220(6):3435-3448.
[44] CHEN C, NAKAGAWA S. Physical activity for cognitive health promotion: An overview of the underlying neurobiological mechanisms. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;86:101868.
[45] XIONG LL, CHEN L, DENG IB, et al. P75 neurotrophin receptor as a therapeutic target for drug development to treat neurological diseases. Eur J Neurosci. 2022;56(8):5299-5318.
[46] DIAMOND A, LEE K. Interventions shown to aid executive function development in children 4 to 12 years old. Science. 2011;333(6045):959-964.
[47] MIGLIORE L, COPPEDÈ F. Gene-environment interactions in Alzheimer disease: the emerging role of epigenetics. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022;18(11):643-660.
[48] SULTANA OF, BANDARU M, ISLAM MA, et al. Unraveling the complexity of human brain: Structure, function in healthy and disease states. Ageing Res Rev. 2024;100:102414.
[49] THYFAULT JP, BERGOUIGNAN A. Exercise and metabolic health: beyond skeletal muscle. Diabetologia. 2020;63(8):1464-1474.
[50] POWERS SK, GOLDSTEIN E, SCHRAGER M, et al. Exercise Training and Skeletal Muscle Antioxidant Enzymes: An Update. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;12(1):39.
[51] PEDERSEN BK. Physical activity and muscle-brain crosstalk. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019; 15(7): 383-392. |