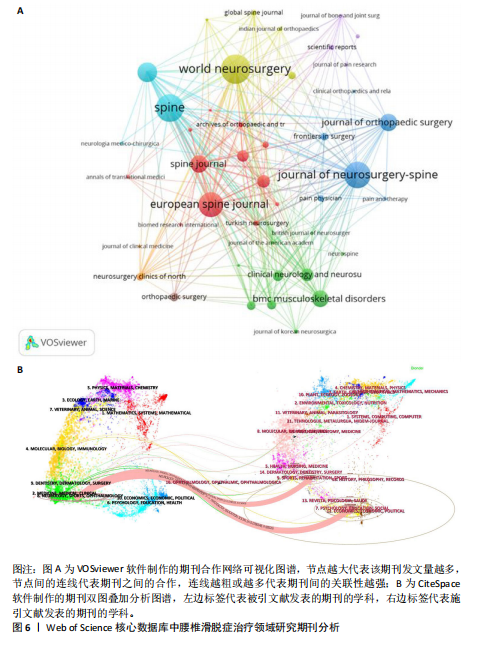
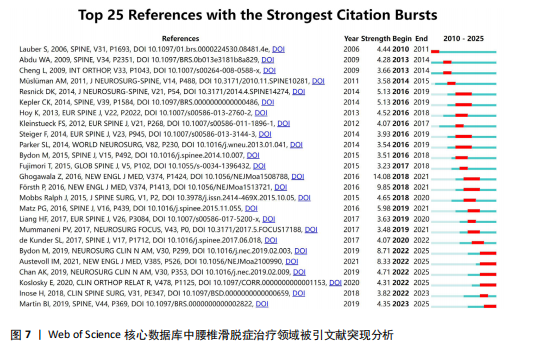
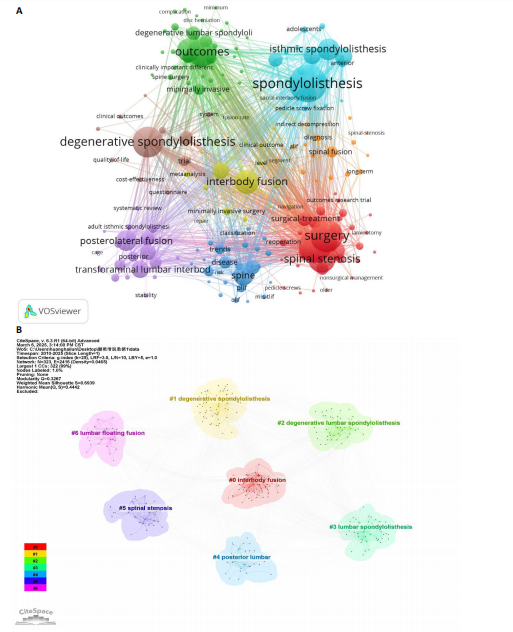
[1] CHAN AK, SHARMA V, ROBINSON LC, et al. Summary of Guidelines for the Treatment of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2019;30(3):353-364.
[2] SAREMI A, GOYAL KK, BENZEL EC, et al. Evolution of lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis with key radiographic features. Spine J. 2024;24(6):989-1000.
[3] BHALLA A, BONO CM. Isthmic Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2019;30(3):283-290.
[4] MOHILE NV, KUCZMARSKI AS, LEE D, et al. Spondylolysis and Isthmic Spondylolisthesis: A Guide to Diagnosis and Management. J Am Board Fam Med. 2022;35(6):1204-1216.
[5] CHUNG CC, SHIMER AL. Lumbosacral Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis. Clin Sports Med. 2021;40(3):471-490.
[6] RATHBONE J, RACKHAM M, NIELSEN D, et al. A systematic review of anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF), transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF), posterolateral lumbar fusion (PLF). Eur Spine J. 2023;32(6):1911-1926.
[7] HAN XG, TANG GQ, HAN X, et al. Comparison of Outcomes between Robot-Assisted Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Single-Level Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(7):2093-2101.
[8] WANG C, ZHANG H, ZHANG L, et al. Accuracy and deviation analysis of robot-assisted spinal implants: A retrospective overview of 105 cases and preliminary comparison to open freehand surgery in lumbar spondylolisthesis. Int J Med Robot. 2021;17(4):e2273.
[9] VICKERS AJ, VERTOSICK EA, LEWITH G, et al. Acupuncture for Chronic Pain: Update of an Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis. J Pain. 2018;19(5):455-474.
[10] GENG Y, ZHU R, MAIMAITUERXUN M. Bibliometric review of carbon neutrality with CiteSpace: evolution, trends, and framework. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022; 29(51):76668-76686.
[11] BUKAR UA, SAYEED MS, RAZAK SFA, et al. A method for analyzing text using VOSviewer. MethodsX. 2023;11:102339.
[12] CHEN C, HU Z, LIU S, et al. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(5):593-608.
[13] VAN ECK NJ, WALTMAN L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84(2):523-538.
[14] CUI GY, HAN XG, WEI Y, et al. Robot-Assisted Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion in the Treatment of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(7):1960-1968.
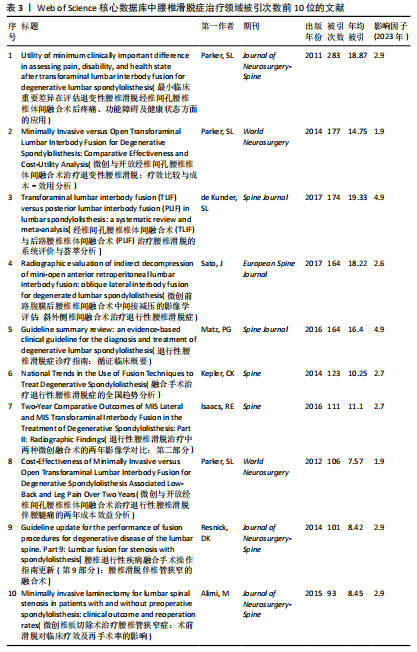
[15] PARKER SL, MENDENHALL SK, SHAU DN, et al. Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis: comparative effectiveness and cost-utility analysis. World neurosurgery. 2014;82(1-2):230-238.
[16] CARREON LY, GLASSMAN SD, GHOGAWALA Z, et al. Modeled cost-effectiveness of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion compared with posterolateral fusion for spondylolisthesis using N(2)QOD data. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(6):916-921.
[17] MATZ PG, MEAGHER RJ, LAMER T, et al. Guideline summary review: An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine J. 2016;16(3):439-448.
[18] PARKER SL, ADOGWA O, PAUL AR, et al. Utility of minimum clinically important difference in assessing pain, disability, and health state after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011; 14(5):598-604.
[19] DE KUNDER SL, VAN KUIJK SMJ, RIJKERS K, et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) in lumbar spondylolisthesis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2017;17(11): 1712-1721.
[20] DROSSOPOULOS PN, ONONOGBU-UCHE FC, TABARESTANI TQ, et al. Evolution of the Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF): From Open to Percutaneous to Patient-Specific. J Clin Med. 2024;13(8): 2271.
[21] QIN R, LIU B, ZHOU P, et al. Minimally Invasive Versus Traditional Open Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for the Treatment of Single-Level Spondylolisthesis Grades 1 and 2: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:180-189.
[22] HAIK NV, BURGESS AE, TALBOT NC, et al. Robotic Systems in Spinal Surgery: A Review of Accuracy, Radiation Exposure, Hospital Readmission Rate, Cost, and Adverse Events. World Neurosurg. 2025;195:123721.
[23] YANG JS, HE B, TIAN F, et al. Accuracy of Robot-Assisted Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Placement for Treatment of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: A Comparative Cohort Study. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:2479-2487.
[24] STURGILL D, HOW J, BLAJDA T, et al. Are the Clinical Outcomes and Cost-Effectiveness of Robot-Assisted Pedicle Screw Placement in Lumbar Fusion Surgery Superior to Computed Tomography Navigation and Freehand Fluoroscopy-Guided Techniques? A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2024;191:81-90.
[25] VERMUE H, TACK P, GRYSON T, et al. Can robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty be a cost-effective procedure? A Markov decision analysis. Knee. 2021;29:345-352.
[26] KIA C, ANTONACCI CL, WELLINGTON I, et al. Spinal Implant Osseointegration and the Role of 3D Printing: An Analysis and Review of the Literature. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022;9(3):108.
[27] LI GQ, TONG T, WANG LF. Comparative analysis of the effects of OLIF and TLIF on adjacent segments after treatment of L4 degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):203.
[28] SINGHATANADGIGE W, TANGDAMRONGTHAM T, LIMTHONGKUL W, et al. Incidence and Risk Factors for Lumbar Sympathetic Chain Injury After Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Neurospine. 2024;21(3):820-832.
[29] JI XK, LI J. Effect of three-volt moxibustion with helium-neon laser irradiation on quality of care in patients with lumbar radiculopathy spondylosis. World J Clin Cases. 2024; 12(15):2522-2528.
[30] VARPAEI HA, FARHADI K, MOHAMMADI M, et al. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction: a concept analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024; 36(1):133.
[31] KöHLI P, SCHöNNAGEL L, HAMBRECHT J, et al. The relationship between paraspinal muscle atrophy and degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis at the L4/5 level. Spine J. 2024;24(8):1396-1406.
[32] LENG Y, TANG C, HE B, et al. Correlation between the spinopelvic type and morphological characteristics of lumbar facet joints in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2023; 38(4):425-435.
|