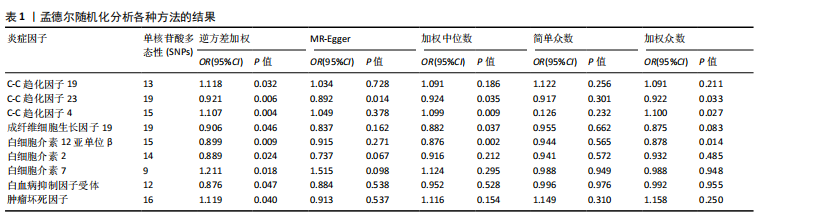
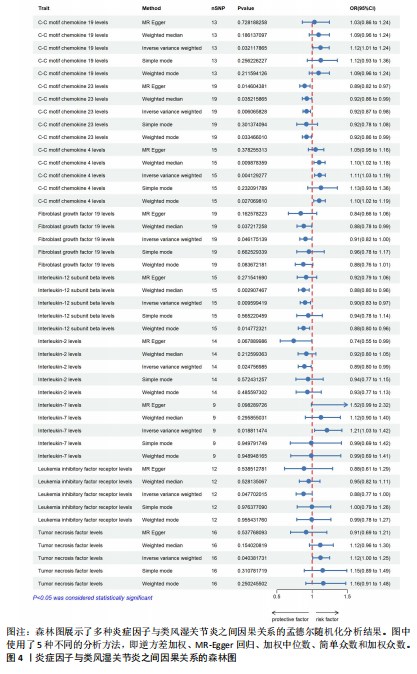
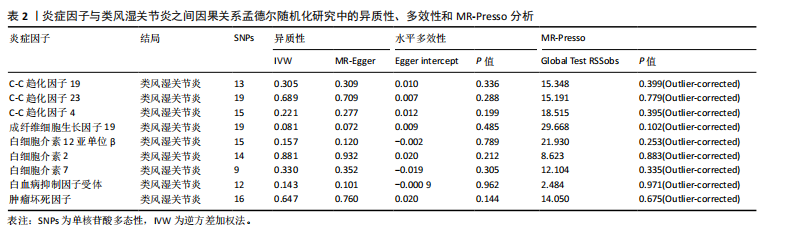
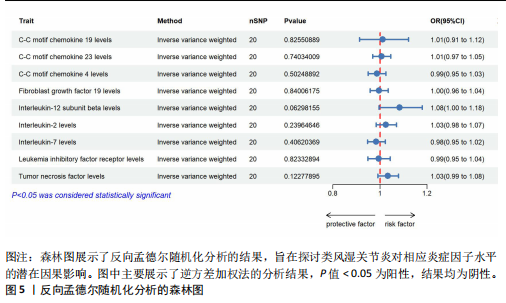
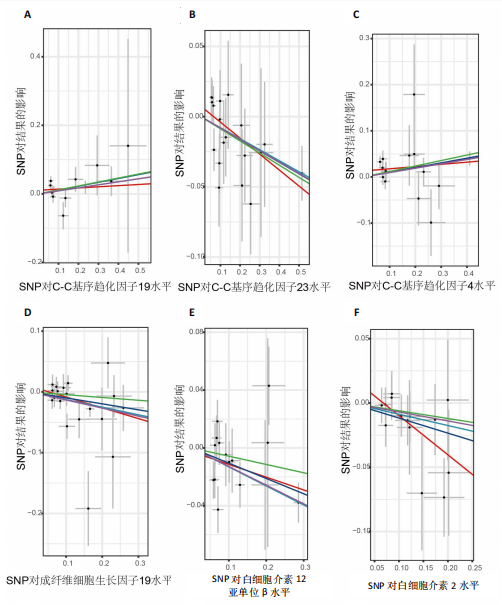
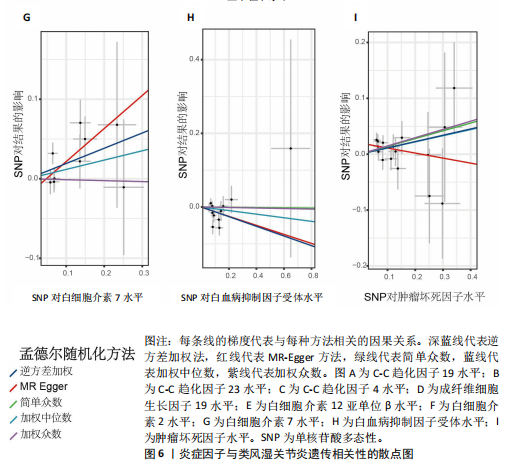
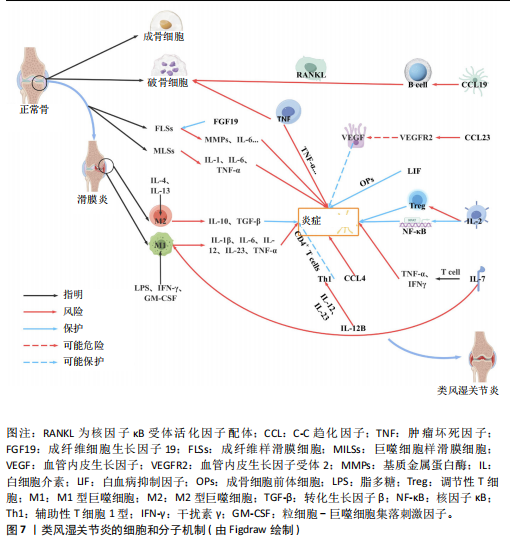
[1] NEUMANN E, FROMMER K, DILLER M, et al. [Rheumatoid arthritis]. Z Rheumatol, 2018;77(9):769-775.
[2] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, MCINNES IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016; 388(10055):2023-2038.
[3] WU YY, LI XF, WU S, et al. Role of the S100 protein family in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):35.
[4] ZHOU Q, LI T, FANG G, et al. Bioactive Molecules against Rheumatoid Arthritis by Suppressing Pyroptosis. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023;16(7):952.
[5] KOLARZ G. Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Acta Med Austriaca. 1988;15(5): 128-130.
[6] LOTTENBURGER T, JUNKER P, HORSLEV-PETERSEN K. Diurnal Variation of Connective Tissue Metabolites in Early and Long-Standing Rheumatoid Arthritis and in Healthy Individuals. Scand J Rheumatol. 2011;40(2):88-94.
[7] MORALES AJ. Study Design for the Evaluation of Treatment. Semin Reprod Endocrinol. 1996;14(2):111-118.
[8] MURPHY SW. Longitudinal Studies 1: Determinants of Risk. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2249:83-101.
[9] BOEHM FJ, ZHOU X. Statistical Methods for Mendelian Randomization in Genome-Wide Association Studies: A Review. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022;20:2338-2351.
[10] BURGESS S, SMALL DS, THOMPSON SG. A Review of Instrumental Variable Estimators for Mendelian Randomization. Stat Methods Med Res. 2017;26(5):2333-2355.
[11] LI J, TANG M, GAO X, et al. Mendelian Randomization Analyses Explore the Relationship between Cathepsins and Lung Cancer. Commun Biol. 2023;6(1):1019.
[12] YUAN S, MICHAELSSON K, WAN Z, et al. Associations of Smoking and Alcohol and Coffee Intake with Fracture and Bone Mineral Density: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Calcif Tissue Int. 2019;105(6):582-588.
[13] PENG H, WANG S, WANG M, et al. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Metabolism. 2022; 133:155220.
[14] ZHAO R, ZHANG YW, YAO JY, et al. Genetic Association between Interleukin-17 and Susceptibility to Rheumatoid Arthritis. BMC Med Genomics, 2023;16(1):277.
[15] SMITH GD, EBRAHIM S. ‘Mendelian Randomization’: Can Genetic Epidemiology Contribute to Understanding Environmental Determinants of Disease? Int J Epidemiol. 2003;32(1):1-22.
[16] DAVEY SG, HEMANI G. Mendelian Randomization: Genetic Anchors for Causal Inference in Epidemiological Studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89-R98.
[17] CHEN Z, BOEHNKE M, WEN X, et al. Revisiting the Genome-Wide Significance Threshold for Common Variant GWAS. G3 (Bethesda). 2021;11(2):jkaa056.
[18] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Avoiding Bias from Weak Instruments in Mendelian Randomization Studies. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40(3):755-764.
[19] YAO X, HUANG J, ZHONG H, et al. Targeting Interleukin-6 in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases and Cancers. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;141(2):125-139.
[20] KUWABARA T, ISHIKAWA F, KONDO M, et al. The Role of IL-17 and Related Cytokines in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases. Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:3908061.
[21] RODRIGUEZ-ELIAS AK, MALDONADO-MURILLO K, LOPEZ-MENDOZA LF, et al. Genetics and Genomics in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An Update. Gac Med Mex. 2016;152(2):218-227.
[22] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, BARTON A, et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18001.
[23] BARTOK B, FIRESTEIN GS. Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes: Key Effector Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010; 233(1):233-255.
[24] KERKMAN PF, ROMBOUTS Y, VAN DER VOORT EI, et al. Circulating Plasmablasts/Plasmacells as a Source of Anticitrullinated Protein Antibodies in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(7):1259-1263.
[25] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage Plasticity, Polarization, and Function in Health and Disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440.
[26] MOADAB F, KHORRAMDELAZAD H, ABBASIFARD M. Role of CCL2/CCR2 Axis in the Immunopathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Latest Evidence and Therapeutic Approaches. Life Sci. 2021;269:119034.
[27] HAN KY, KIM CW, LEE TH, et al. CCL23 Up-Regulates Expression of KDR/Flk-1 and Potentiates VEGF-Induced Proliferation and Migration of Human Endothelial Cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;382(1):124-128.
[28] ARRUDA-SILVA F, BIANCHETTO-AGUILERA F, GASPERINI S, et al. Human Neutrophils Produce CCL23 in Response to Various TLR-Agonists and TNFalpha. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017;7:176.
[29] CHEN H, LI J, PI C, et al. FGF19 Induces the Cell Cycle Arrest at G2-Phase in Chondrocytes. Cell Death Discov. 2023; 9(1):250.
[30] KUROSE A, YOSHIDA W, YOSHIDA M, et al. Effects of Paclitaxel on Cultured Synovial Cells from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cytometry. 2001;44(4):349-354.
[31] GUO A, LI K, XIAO Q. Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 Alleviates Palmitic Acid-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress via the AMPK/PGC-1alpha Pathway in Skeletal Muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;526(4):1069-1076.
[32] QUINONEZ-FLORES CM, LOPEZ-LOEZA SM, PACHECO-TENA C, et al. Stability of Housekeeping Genes in Inflamed Joints of Spontaneous and Collagen-Induced Arthritis in DBA/1 Mice. Inflamm Res. 2021; 70(5):619-632.
[33] FUKUDA K, MIURA Y, MAEDA T, et al. Interleukin-12B is Upregulated by Decoy Receptor 3 in Rheumatoid Synovial Fibroblasts. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(4): 3647-3652.
[34] WANG MJ, XU XL, MI YY, et al. Association of IL12B Gene Polymorphisms with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Arch Med Res. 2016;47(2):126-133.
[35] NGIOW SF, TENG MW, SMYTH MJ. A Balance of Interleukin-12 and -23 in Cancer. Trends Immunol. 2013;34(11):548-555.
[36] WATFORD WT, HISSONG BD, BREAM JH, et al. Signaling by IL-12 and IL-23 and the Immunoregulatory Roles of STAT4. Immunol Rev. 2004;202:139-156.
[37] HUNTER CA. New IL-12-Family Members: IL-23 and IL-27, Cytokines with Divergent Functions. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(7): 521-531.
[38] SINIGAGLIA F, D’AMBROSIO D, PANINA-BORDIGNON P, et al. Regulation of the IL-12/IL-12R Axis: A Critical Step in T-Helper Cell Differentiation and Effector Function. Immunol Rev. 1999;170:65-72.
[39] POPE RM, SHAHRARA S. Possible Roles of IL-12-Family Cytokines in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013;9(4):252-256.
[40] YUAN N, YU G, LIU D, et al. An Emerging Role of Interleukin-23 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2019; 41(2):185-191.
[41] ZHANG SX, WANG J, WANG CH, et al. Low-Dose IL-2 Therapy Limits the Reduction in Absolute Numbers of Circulating Regulatory T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021;13: 1759720X211011370.
[42] LI N, LI X, SU R, et al. Low-Dose Interleukin-2 Altered Gut Microbiota and Ameliorated Collagen-Induced Arthritis. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:1365-1379.
[43] SUN H, ZHAO Y, WANG K, et al. Low Dose IL-2 Suppresses Osteoclastogenesis in Collagen-Induced Arthritis via JNK-Dependent Pathway. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2020;8(4):727-735.
[44] KOSMACZEWSKA A, CISZAK L, SWIERKOT J, et al. Exogenous IL-2 Controls the Balance in Th1, Th17, and Treg Cell Distribution in Patients with Progressive Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with TNF-Alpha Inhibitors. Inflammation. 2015;38(2):765-774.
[45] MITRA S, LEONARD WJ. Biology of IL-2 and Its Therapeutic Modulation: Mechanisms and Strategies. J Leukoc Biol. 2018;103(4):643-655.
[46] ZHANG SX, CHEN HR, WANG J, et al. The Efficacy and Safety of Short-Term and Low-Dose IL-2 Combined with Tocilizumab to Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1359041.
[47] ZHANG C, LIU J, WANG J, et al. The Emerging Role of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor in Cancer and Therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;221:107754.
[48] WANG J, CHANG CY, YANG X, et al. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor, a Double-Edged Sword with Therapeutic Implications in Human Diseases. Mol Ther. 2023;31(2):331-343.
[49] DECHANET J, TAUPIN JL, CHOMARAT P, et al. Interleukin-4 but Not Interleukin-10 Inhibits the Production of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor by Rheumatoid Synovium and Synoviocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1994;24(12):3222-3228.
[50] RODAN SB, WESOLOWSKI G, HILTON DJ, et al. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Binds with High Affinity to Preosteoblastic RCT-1 Cells and Potentiates the Retinoic Acid Induction of Alkaline Phosphatase. Endocrinology. 1990;127(4):1602-1608.
[51] NICOLA NA, BABON JJ. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF). Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2015;26(5):533-544.
[52] LEE J, PARK C, KIM HJ, et al. Stimulation of Osteoclast Migration and Bone Resorption by C-C Chemokine Ligands 19 and 21. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(7):e358.
[53] BRUHL H, MACK M, NIEDERMEIER M, et al. Functional Expression of the Chemokine Receptor CCR7 on Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(12):1771-1774.
[54] GUO X, XU T, ZHENG J, et al. Accumulation of Synovial Fluid CD19+CD24hiCD27+ B Cells Was Associated with Bone Destruction in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):14386.
[55] SHI LJ, LI JH, HU FL, et al. [Clinical Significance of Serum C-C Chemokine Ligand 19 Levels in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis]. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016;48(1):667-671.
[56] CHANG TT, LIN LY, CHEN C, et al. CCL4 Contributes to Aging-Related Angiogenic Insufficiency through Activating Oxidative Stress and Endothelial Inflammation. Angiogenesis. 2024;27(3):475-499.
[57] SUCUR A, JAJIC Z, ARTUKOVIC M, et al. Chemokine Signals Are Crucial for Enhanced Homing and Differentiation of Circulating Osteoclast Progenitor Cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):142.
[58] ZHANG L, YU M, DENG J, et al. Chemokine Signaling Pathway Involved in CCL2 Expression in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Yonsei Med J. 2015;56(4):1134-1142.
[59] AHMAD R, KOCHUMON S, CHANDY B, et al. TNF-α Drives the CCL4 Expression in Human Monocytic Cells: Involvement of the SAPK/JNK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(4):908-921.
[60] PICKENS SR, CHAMBERLAIN ND, VOLIN MV, et al. Characterization of Interleukin-7 and Interleukin-7 Receptor in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(10):2884-2893.
[61] CHURCHMAN SM, PONCHEL F. Interleukin-7 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(6):753-759.
[62] TORALDO G, ROGGIA C, QIAN WP, et al. IL-7 Induces Bone Loss In Vivo by Induction of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha from T Cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(1):125-130.
[63] VAN ROON JA, GLAUDEMANNS KA, BIJLSMA JW, et al. Interleukin 7 Stimulates Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha and Th1 Cytokine Production in Joints of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62(2):113-119.
[64] MEYER A, PARMAR PJ, SHAHRARA S. Significance of IL-7 and IL-7R in RA and Autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2022; 21(7):103120.
[65] HARTGRING SA, VAN ROON JA, WENTING-VAN WM, et al. Elevated Expression of Interleukin-7 Receptor in Inflamed Joints Mediates Interleukin-7-Induced Immune Activation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(9):2595-2605.
[66] CAI L, XU H, ZHANG H, et al. Blockade of IL-7Ralpha Alleviates Collagen-Induced Arthritis via Inhibiting Th1 Cell Differentiation and CD4+ T Cell Migration. Mol Immunol. 2016;79:83-91.
[67] XU H, CAI L, LI Z, et al. Dual Effect of IL-7/IL-7R Signalling on the Osteoimmunological System: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunology. 2021;164(1):161-172.
[68] PETROVIC-RACKOV L, PEJNOVIC N. Clinical Significance of IL-18, IL-15, IL-12 and TNF-Alpha Measurement in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2006;25(4):448-452.
[69] INAM IM, AMJAD S, ALAM SM, et al. Serum Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha as a Competent Biomarker for Evaluation of Disease Activity in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cureus. 2021;13(5):e15314.
[70] AKATSUKA H, OKUBO M, ISHIDA H, et al. Synovial Mononuclear Cells Consist with T Cells Which Produce High Levels of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha. Microbiol Immunol. 1997;41(4):367-370.
[71] HAWORTH C, BRENNAN FM, CHANTRY D, et al. Expression of Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Regulation by Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha. Eur J Immunol. 1991;21(10):2575-2579.
[72] CHOPIN F, GARNERO P, LE HENANFF A, et al. Long-Term Effects of Infliximab on Bone and Cartilage Turnover Markers in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(3):353-357.
[73] GINTING AR, HIDAYAT R, SUMARIYONO S, et al. Role of Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein 1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-Alpha) in Bone Loss of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int J Rheumatol. 2020;2020:9149762.
[74] OKAZAKI H, LIN Q, NISHIKAWA K, et al. TNFalpha but Not IL-17 Is Critical in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Spontaneously Occurring in a Unique FcgammaRIIB-Deficient Mouse Model. Mod Rheumatol. 2014;24(6):931-938.
[75] FENG X. Regulatory Roles and Molecular Signaling of TNF Family Members in Osteoclasts. Gene. 2005;350(1):1-13.
[76] MABILLEAU G, PASCARETTI-GRIZON F, BASLE MF, et al. Depth and Volume of Resorption Induced by Osteoclasts Generated in the Presence of RANKL, TNF-Alpha/IL-1 or LIGHT. Cytokine. 2012;57(2):294-299.
[77] WU Y, YANG Y, WANG L, et al. Effect of Bifidobacterium on Osteoclasts: TNF-Alpha/NF-kappaB Inflammatory Signal Pathway-Mediated Mechanism. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1109296.
[78] ADAMI G, ORSOLINI G, ADAMI S, et al. Effects of TNF Inhibitors on Parathyroid Hormone and Wnt Signaling Antagonists in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2016;99(4):360-364.
[79] POLLARD LC, CHOY EH, GONZALEZ J, et al. Fatigue in Rheumatoid Arthritis Reflects Pain, Not Disease Activity. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45(7):885-889.
|