中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 2503-2514.doi: 10.12307/2026.612
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
p53在肌肉骨骼疾病中的作用
杜彦利1,2,汪 屹1,2,王振宇2,王煊晖1,2,李新业1,2,熊喜峰3,缪海雄1,2
- 1广东医科大学第一临床医学院,广东省湛江市 524023;2暨南大学附属广州红十字会医院骨科,广东省广州市 510220;3暨南大学附属广州红十字会医院,广州市创伤外科研究所,广东省广州市 510220
-
收稿日期:2025-02-12接受日期:2025-06-20出版日期:2026-04-08发布日期:2025-08-29 -
通讯作者:缪海雄,博士,主任医师,硕士生导师,广东医科大学第一临床医学院,广东省湛江市 524023;暨南大学附属广州红十字会医院骨科,广东省广州市 510220 共同通讯作者:熊喜峰,博士,副研究员,暨南大学附属广州红十字会医院,广州市创伤外科研究所,广东省广州市 510220 -
作者简介:第一作者:杜彦利,男,1997年生,黑龙江省黑河市人,汉族,2021年牡丹江医学院毕业,主要从事p53在肌肉骨骼疾病中的分子机制及治疗靶点研究。 共同第一作者:汪屹,男,1998年生,四川省广安市人,汉族,2022年成都医学院毕业,主要从事p53在肌肉骨骼疾病中的信号通路调控及病理机制研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(81902802),项目负责人:熊喜峰;广州市科技计划-市校联合项目(2023A03J0571),项目负责人:缪海雄;广州市科技计划项目(202201010020),项目负责人:熊喜峰
The role of p53 in musculoskeletal diseases
Du Yanli1, 2, Wang Yi1, 2, Wang Zhenyu2, Wang Xuanhui1, 2, Li Xinye1, 2, Xiong Xifeng3, Miao Haixiong1, 2
- 1First Clinical Medical College, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510220, Guangdong Province, China; 3Guangzhou Institute of Traumatic Surgery, Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510220, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2025-02-12Accepted:2025-06-20Online:2026-04-08Published:2025-08-29 -
Contact:Miao Haixiong, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, First Clinical Medical College, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510220, Guangdong Province, China Co-corresponding author: Xiong Xifeng, MD, Associate researcher, Guangzhou Institute of Traumatic Surgery, Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510220, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Du Yanli, First Clinical Medical College, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510220, Guangdong Province, China Wang Yi, First Clinical Medical College, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510220, Guangdong Province, China Du Yanli and Wang Yi contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81902802 (to XXF); Guangzhou Science and Technology Program – City and University Joint Project, No. 2023A03J0571 (to MHX); Guangzhou Science and Technology Program, No. 202201010020 (to XXF)
摘要:
文题释义:
p53:是一种重要的肿瘤抑制基因,在维持细胞正常功能和抑制肿瘤发生发展等方面发挥着关键作用,主要功能有细胞周期调控、DNA修复、细胞凋亡诱导等。p53不仅在癌症中发挥着核心作用,而且在肌肉骨骼疾病中的功能也逐渐被揭示。研究表明,p53在肌肉再生、骨骼重塑以及软骨修复等过程中都扮演着重要角色,p53的异常表达与骨质疏松症、骨关节炎等疾病的进展密切相关。
肌肉骨骼疾病:是一类涉及肌肉、骨骼、关节及相关运动系统结构的疾病,主要包括退行性疾病、炎症性疾病、代谢性疾病等,核心策略涵盖了药物调控、物理干预与手术修复。p53蛋白通过调控细胞凋亡通路、DNA损伤反应和代谢过程等影响疾病的进展。
背景:p53基因是一种关键的肿瘤抑制基因,最初因在调控细胞周期、DNA修复及凋亡中的核心作用而被广泛研究。近年来,研究发现p53在肌肉骨骼疾病中同样发挥重要作用,p53的异常表达和功能失调被认为是这些疾病发生和发展的重要因素,但具体作用机制及临床转化潜力尚未系统阐明。
目的:综述p53在肌肉骨骼疾病中的多重作用,分析p53影响疾病进展的分子机制,并评估p53作为跨疾病治疗靶点的潜力。
方法:通过检索PubMed数据库2004年1月至2024年12月的文献,以“P53,Osteoporosis,Post-Menopausal Osteoporosis,Osteoarthritis,Degenerative Arthritis,Rheumatoid Arthritis,Gout,Low Back Pains,Low Back Ache,Back Pain,Scoliosis“为检索词,纳入原始研究、综述及临床试验等文献,排除非英文文献及无关机制研究,最终筛选81篇文献进行综合分析。
结果与结论:p53通过调控成骨-破骨平衡(如p53-Nedd4-Runx2轴)、软骨细胞凋亡(如miR-34a-SIRT1-p53通路)、炎症递质(如肿瘤坏死因子α/白细胞介素6)及氧化应激(如p53-SLC2A9轴)等机制,参与肌肉骨骼疾病的发生发展。p53的双向作用(促凋亡与抗炎)提示需精准调控p53活性。基于基因编辑(如CRISPR/Cas9)、小分子抑制剂(如PFT-α)及天然产物(如柚皮苷)的干预策略展现出治疗潜力,但临床转化仍需进一步验证。未来需结合多学科技术深化p53机制研究与临床实践。
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-8681-1479(杜彦利)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
杜彦利, 汪 屹, 王振宇, 王煊晖, 李新业, 熊喜峰, 缪海雄, . p53在肌肉骨骼疾病中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(10): 2503-2514.
Du Yanli, , Wang Yi, , Wang Zhenyu, Wang Xuanhui, , Li Xinye, , Xiong Xifeng, Miao Haixiong, . The role of p53 in musculoskeletal diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2503-2514.
2.2 p53的生物学功能 作为典型的多功能转录调控因子,p53蛋白的结构由多个功能域组成,包括氨基末端转录激活域、核心DNA结合域、铰链区调控域等关键功能单元[5]。p53的氨基酸序列在脊椎动物中具有高度保守的特征,保证了其结构和功能的相似性。p53蛋白能够特异性识别并靶向结合DNA序列,对其下游基因网络实施精密调控,其作用范围涵盖了细胞周期控制、DNA修复、细胞凋亡、细胞衰老和细胞代谢等多种生物学过程[6]。Mouse Double Minute 2(MDM2)是p53的的核心负调节因子之一,它能够与p53直接结合,促进其泛素化以及随后的降解过程[7]。值得注意的是,p53的功能活性受到多层级修饰调控,包括磷酸化、乙酰化、甲基化和泛素化等共价修饰事件,可动态调节其亚细胞定位、DNA结合能力和转录活性,以此形成复杂的信号整合网络[8]。
2.2.1 p53与细胞周期 在细胞周期的G1/S检查点的调控过程中,p53蛋白可以通过激活p21蛋白(一种细胞周期抑制因子)的表达来阻滞细胞周期,这一机制为细胞修复DNA损伤提供了关键的时间窗。当不可逆的损伤发生时,p53将激活细胞进入衰老或凋亡程序,从而避免损伤细胞的无限制增殖,构成了机体抗肿瘤防御体系中的核心环节[9]。通过这种方式,p53在维护基因组稳定性和防止肿瘤发展中扮演着至关重要的角色。
2.2.2 p53与细胞凋亡 p53蛋白通过激活BAX、PUMA和NOXA等促凋亡分子编码基因的表达,在线粒体的凋亡通路中发挥着核心调控的作用。在特定病理生理条件下,p53可以通过激活死亡受体途径来触发细胞凋亡。p53的活性受到细胞内外环境因素精细调控,这种调控机制确保了凋亡过程能够在适当的时候被激活,在维持组织细胞群体动态平衡中具有重要作用[10]。通过这种方式,p53可以平衡细胞的存活与程序性死亡,这种动态平衡的机制构成了组织稳态维持的核心保障。
2.2.3 p53与DNA修复 作为DNA修复的关键守护者,p53蛋白参与了多种DNA修复途径,其中包括碱基切除修复、核苷酸切除修复和错配修复等路径,这种功能对于维持基因组的稳定性非常重要,有助于阻断突变的累积,可以在源头上遏制基因的损伤和癌变的风险[11]。通过精细调控DNA修复过程,p53蛋白在保护细胞免受遗传损伤方面提供了重要保障。
2.2.4 p53与细胞衰老 细胞衰老是一种不可逆的生长停滞状态,p53在这一过程中展现出了独特的生物学功能。当细胞面对持续的应激或氧化损伤时,p53可以通过促进p21等效应分子,从而驱动细胞进入衰老状态,这种分子监察机制可以有效阻止受损细胞的进一步增殖,降低机体受潜在有害影响的风险[12]。作为分子稳态的调控中枢,p53在细胞生命周期中起到了守护者的作用,确保了细胞的稳定性和整体健康。
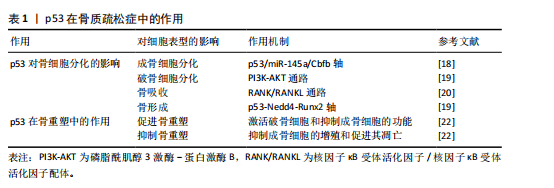
2.3 p53在骨质疏松症中的作用 原发性骨质疏松症作为典型的衰老相关性疾病,患者的数量与人口老龄化进程呈现显著正相关性[13]。人体的衰老首先体现在细胞层面,二者的衰老存在复杂的交互作用。虽然细胞衰老和个体衰老并不完全等同,但是衰老确实限制了细胞的复制寿命,并被认为是衰老过程中的一个关键因素[14]。作为最常见的慢性年龄相关性疾病之一,骨质疏松症当前临床干预手段多局限于症状管理,缺乏针对骨微环境稳态重建的靶向策略[14]。在骨质疏松症发病机制中,p53蛋白通过影响骨细胞的分化和骨代谢等多种方面来对骨质起到形成和维护的作用[15]。
2.3.1 p53对骨细胞分化的影响
(1)成骨细胞分化:p53蛋白显著抑制成骨细胞的分化过程,它通过限制成骨细胞增殖和加速成骨细胞凋亡来降低骨形成。p53通过调节特定的靶基因如p53/miR-145a轴,影响老化骨髓间充质干细胞的衰老和成骨抑制[16],研究显示,在p53过表达的骨髓间充质干细胞中,miR-145a的表达量显著升高,而Cbfb mRNA表达大幅度下降[17]。通过染色质免疫沉淀实验证实,p53直接结合miR-145a的启动子区域,激活其转录。Cbfb的缺失导致成骨分化标志基因(如Runx2、Osterix)的表达下降,同时脂肪分化标志基因(PPARγ、C/EBPα)表达增加。p53基因敲除小鼠骨密度较野生型小鼠明显提高,表明p53/miR-145a/Cbfb轴可能是治疗骨质疏松症的潜在新靶点[18]。
(2)破骨细胞分化:p53显著影响破骨细胞(Osteoclasts)的分化过程,它通过调节与破骨细胞分化密切相关的信号通路,进而影响破骨细胞的形成和活性。贝拉前列素通过激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶-蛋白激酶B通路,促进小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞方向分化。在共培养体系中,经贝拉前列素激活的成骨细胞以核因子κB受体活化因子配体依赖性机制抑制破骨细胞的生成。无论贝前列素如何给药,p53 敲除小鼠的骨量都保持稳定,表明p53在贝前列素的骨量调节中起着至关重要的作用[19]。这些结果揭示了p53在贝前列素影响骨代谢过程中的关键作用,尤其是在调控破骨细胞分化方面的重要性。
(3)骨吸收:p53在促进破骨细胞活性和增加骨吸收方面起到关键作用。研究表明,在某些情况下,p53激活与破骨细胞前体细胞的增殖和分化增强有关,这可能引起骨质流失,特别是在高脂饮食诱导的骨形成抑制中,胰岛素样生长因子1信号通路和p53凋亡通路相关基因的表达发生变化,可能对骨代谢产生影响[20];进一步研究发现,在高脂饮食诱导的骨质疏松模型中,p53激活显著增加破骨细胞前体细胞的分化效率;此外,TGFbR1和白细胞介素17a mRNA表达大幅度上调,而白细胞介素4表达下降。阻断p53后,RANKL诱导的破骨细胞活性降低45%,表明p53可能通过TGFbR1/白细胞介素17a轴增强RANKL信号,进而刺激骨吸收过程[20]。
(4)骨形成:p53在骨形成过程中起到关键的抑制作用,它通过抑制成骨细胞增殖和促进成骨细胞凋亡,减少新骨质的生成。p53与神经元前体细胞表达的Nedd4的启动子区域相互作用,增强Nedd4的转录。而Nedd4作为泛素化酶与Runx2结合,促使Runx2泛素化及降解,这一过程对骨形成具有重要影响。因此,p53-Nedd4-Runx2轴是调控骨形成的一个重要通路,并指出贝前列素治疗绝经后骨质疏松症可能具有潜在的应用价值[19]。
2.3.2 p53在骨重塑中的作用 骨重塑作为持续终身的代谢重构过程,其本质是成骨细胞介导的骨形成和破骨细胞主导的骨吸收的动态平衡,来产生成熟且动态的骨骼结构。p53通过表观遗传调控网络,在骨微环境稳态维持中呈现双向调节特性。
(1)促进骨重塑:p53在促进骨重塑过程中起到了关键的作用,可能通过破骨细胞功能活化与成骨细胞分化抑制的双向调节来实现。研究发现,与野生型同窝小鼠相比,Cyp27b1+/-小鼠模型中呈现显著氧化还原稳态失衡和DNA损伤应答持续激活,抗氧化酶表达水平降低[21],衰老的骨细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞的比例升高,同时衰老相关表型分子异常分泌,并检测到p16、p19和p53蛋白表达水平同步上调[21]。这些证实了p53蛋白在骨代谢稳态维持中的核心调控作用。
(2)抑制骨重塑:p53在抑制骨重塑中扮演着关键角色,主要通过抑制成骨细胞的增殖和促进成骨细胞的凋亡来抑制骨重塑,进而减少骨质的形成。在衰老的骨髓间充质干细胞中[22],
乙酰化修饰的p53水平较年轻细胞明显升高,同时伴随着抑制端粒酶活性和诱导活性氧水平上调 。应用p53抑制剂pifithrin-α后,成骨分化能力大幅度提升,凋亡率明显下降,这些变化均与p53的调控有关。乙酰化p53、p21和p16蛋白表达水平上升,端粒酶活性下降及活性氧水平上升,这些因素均可能对成骨细胞的功能产生抑制作用。此外,地塞米松诱导的成骨细胞损伤可以通过应用p53抑制剂(如pifithrin-α)得到部分逆转,揭示了p53在成骨细胞损伤中的作用。
从分子病理学视角分析,骨质疏松症与骨关节炎虽呈现不同的病理生理学特征(前者以骨量减少为主,后者以软骨退变为核心),但均与p53介导的细胞调控密切相关。在骨质疏松症中,p53通过抑制成骨分化与促进破骨活性破坏骨代谢平衡(表1);而在骨关节炎中,p53则通过诱导软骨细胞凋亡与基质降解加速关节退化。这种机制上的共性与差异,凸显了p53在骨稳态调控中的多面性,也为跨疾病靶向治疗策略的设计提供了理论依据。
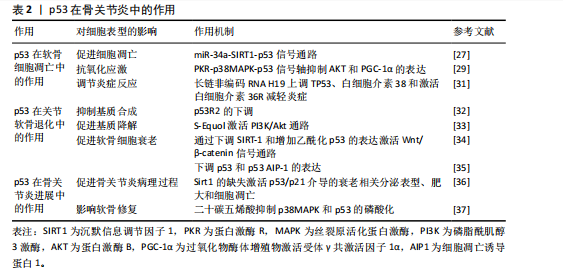
2.4 p53在骨关节炎中的作用 作为全球重大健康挑战的骨关节炎,是一种广泛存在的慢性退行性疾病。据2016年全球疾病负担研究估计,骨关节炎累计影响人群已达2.4亿[23]。骨关节炎可以影响多个关节,包括但不限于膝盖、手、臀部、脚和脚踝[24-25],膝骨关节炎是最常见的骨关节炎类型之一[26]。p53蛋白在骨关节炎中的作用是多方面的,它在软骨细胞凋亡和关节软骨退化中起着关键的作用,并且对骨关节炎的进展产生了重要的影响。研究表明,骨关节炎软骨细胞中p53的表达水平要高于正常的软骨细胞,证实了p53表达水平的下调直接关联软骨细胞凋亡率的降低,进而预防和缓解骨关节炎病变,该现象可能与线粒体凋亡途径存在关联。此外,p53信号通路与骨关节炎的发病机制相关,其激活可以引起某些mRNA的异常表达,通过影响细胞周期等,导致细胞衰老、凋亡。在软骨细胞命运调控中,p53不仅驱动凋亡进程,同时参与自噬活动的精细调节,而软骨细胞衰老、凋亡被认为在骨关节炎的发展中发挥着重要的作用。因此,p53信号通路的激活是衰老调控的重要步骤,可能对骨关节炎具有潜在的治疗作用。
2.4.1 p53在软骨细胞凋亡中的作用
(1)促进细胞凋亡:在骨关节炎的病理过程中,p53通过激活其下游的凋亡效应分子Bax和Puma,发挥促进软骨细胞凋亡的作用,这一过程会引发线粒体功能障碍,进一步促进细胞凋亡,最终导致关节软骨的退化。此外,YAN等[27]发现骨关节炎患者软骨细胞中p53蛋白水平较正常组织升高2倍,同时miR-34a表达上调3倍;体外实验中,miR-34a过表达导致SIRT1 mRNA减少60%(通过双荧光素酶报告基因验证靶向结合),进而激活p53/p21通路,使软骨细胞凋亡率增加;敲低miR-34a后,凋亡率下降至基线水平,表明miR-34a通过直接调节原代人软骨细胞内的SIRT1/p53信号通路来促进细胞凋亡及抑制增殖;另一方面,miR-181a-5p通过直接靶向Sirt1的3’非翻译区,抑制Sirt1的表达,并通过增强p53依赖性信号转导,促进细胞凋亡。因此,应用miR-181a-5p的反义寡核苷酸可能有助于促进软骨细胞的存活[28]。
(2)抗氧化应激:p53通过表观遗传调控网络参与软骨细胞氧化应激防御机制,它通过调节抗氧化基因的表达如超氧化物歧化酶2和过氧化氢酶的提升,来保护软骨细胞免受氧化损伤[29]。研究表明,透明质酸干预的骨关节炎软骨细胞中,磷酸化p53(Ser15)水平下降,同时超氧化物歧化酶2和过氧化氢酶的表达量升高;PKR抑制剂处理可阻断p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶介导的p53磷酸化,使AKT和过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活因子1α的表达提高,显著减少活性氧积累,表明透明质酸能够降低氧化应激水平和磷酸化AKT水平,进而通过调节磷酸化p38和磷酸化p53抑制促炎反应和促凋亡事件,从而对软骨细胞起到保护作用[29]。此外,PKR通过p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶途径介导的p53磷酸化,在肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的人软骨细胞中发挥作用,抑制AKT和PGC-1α的表达,进而影响氧化应激反应[30]。
(3)调节炎症反应:在骨关节炎炎症微环境重塑过程中,p53借助表观遗传调控网络实现双重调控,具体表现为白细胞介素38表达抑制和肿瘤坏死因子α的异常分泌,此类炎症递质级联反应直接触发软骨细胞凋亡,成为病情进展的关键。研究表明,长链非编码RNA H19能够通过上调TP53、白细胞介素38的表达,并激活白细胞介素36受体来减轻炎症,从而改善骨关节炎引起的软骨损伤和软骨细胞凋亡[31]。长链非编码RNA H19通过形成p53-H19分子复合物,增强了白细胞介素38的表达,促使白细胞介素38与白细胞介素36受体特异性结合,构建抗炎信号传导通路,显著抑制了炎症因子生成并且降低了软骨细胞凋亡率[31]。
2.4.2 p53在关节软骨退化中的作用
(1)抑制基质合成:在骨关节炎病理进程中,p53通过负向调控软骨细胞外基质关键组成部分(胶原蛋白和蛋白多糖)的生物合成,加速软骨组织退行性改变,这些基质分子的减少会直接导致软骨磨损和损伤。随着骨关节炎的进展,p53R2的表达水平可能上升,而抑制p53R2的表达可能对人软骨细胞合成代谢产生积极影响,这表明p53R2作为核糖核苷酸还原酶调控亚基,其表达量与病程进展呈正相关性[32]。
(2)促进基质降解:p53在骨关节炎中能够激活基质金属蛋白酶家族成员的转录活性,尤其是基质金属蛋白酶3和基质金属蛋白酶13,这些酶在软骨基质分解中扮演关键角色,加速软骨退化。药理学研究显示,植物雌激素代谢物S-Equol通过激活PI3K/Akt通路,对p53和一氧化氮产生上游调节作用,进而与细胞凋亡和基质降解有关[33],这一通路的激活能够减轻由硝普钠诱导的基质金属蛋白酶13分泌,表明S-Equol可能通过调节p53相关的信号通路,对骨关节炎的进展产生影响[33]。
(3)影响软骨细胞表型:p53在骨关节炎中通过双重机制来影响软骨细胞,一方面促进细胞凋亡,另一方面调节软骨细胞表型,这种双向调控直接干预了软骨细胞的分化成熟时序,最终决定软骨组织的修复再生能力。具体来说,p53可以借助Wnt/β-catenin信号转导轴诱导沉默信息调节因子1表达抑制,并增加乙酰化p53的表达来促进软骨细胞衰老[34]。值得注意的是,p53的效应分子p53AIP-1通过线粒体膜电位去极化机制,在人软骨细胞凋亡中起着重要作用,下调p53表达可防止由剪切应变引起的软骨细胞凋亡[35]。
2.4.3 p53在骨关节炎进展中的影响
(1)促进骨关节炎病理进程:p53在骨关节炎的病理进程中起到关键作用,它通过促进软骨细胞凋亡和基质降解来加速骨关节炎的发展。研究表明,软骨中Sirt1 的缺失会通过异常激活p53/p21介导的衰老相关分泌表型、肥大和细胞凋亡,从而导致骨关节炎发病机制加速[36]。
(2)影响软骨修复:p53对软骨修复机制产生抑制作用,减弱了软骨细胞的再生能力,导致软骨损伤的累积和骨关节炎的进展。二十碳五烯酸作为一种抗氧化剂和n-3多不饱和脂肪酸,干预骨关节炎软骨细胞后,p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶磷酸化水平下降,p53的Ser15位点磷酸化减少,基质金属蛋白酶13表达量降低,细胞存活率提高[37],这一机制的发现为骨关节炎的治疗提供了新策略,即通过调节p53相关的信号通路来保护软骨细胞,减少细胞凋亡,从而延缓骨关节炎的进展。
综上所述,p53通过双向调控网络参与骨关节炎进展,在软骨细胞凋亡、关节软骨退化中有着多重作用(表2),提示开发靶向p53效应分子(如靶向特定下游分子)的精准干预策略可能是未来治疗骨关节炎的关键方向。
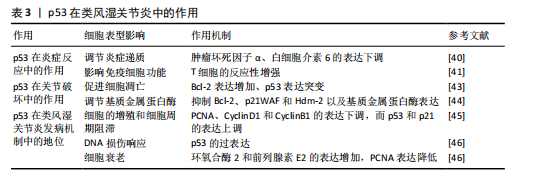
2.5 p53在类风湿关节炎中的作用 类风湿关节炎作为全球重大的公众卫生问题,其患病率呈显著地域异质性,对患者的生活质量造成了重大影响[38]。该疾病不仅引起关节疼痛,还伴随着一系列全身性症状,表现为持续性发热、乏力和食欲不振。尽管类风湿关节炎的严重性已得到广泛认识,但目前尚无根治方法,部分原因是类风湿关节炎的具体病因尚未完全明确。WHO在2000年启动的“骨骼与关节十年”计划中,将类风湿关节炎列为优先干预疾病,旨在减轻社会压力和经济负担[39]。在类风湿关节炎的病理过程中,p53蛋白在炎症反应、关节损伤以及类风湿关节炎的发病机制中起着关键作用。
2.5.1 p53在炎症反应中的作用
(1)调节炎症递质:在类风湿关节炎的发病机制中,p53蛋白扮演着调节炎症递质的关键角色。p53通过调控炎症递质的表达,例如肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6,对类风湿关节炎的炎症反应产生影响。此外,ZHANG等[40]发现类风湿关节炎患者滑膜成纤维细胞中p53表达水平较健康对照组升高。p53通过抑制核因子κB信号通路,使肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的分泌量减少。p53敲除关节炎模型小鼠滑膜炎症评分增加,表明p53通过抑制炎症递质减轻类风湿关节炎症状。
(2)影响免疫细胞功能:p53在类风湿关节炎中影响免疫细胞的功能,如T细胞和B细胞的活化、增殖和凋亡。研究表明,缺乏p53的小鼠表现出增强的T细胞反应。在活性胶原蛋白诱导的关节炎模型中,缺失p53的小鼠适应性免疫反应更强,导致疾病更加严重,这一现象并非由抗体介导的反应引起,而是与T细胞的反应性增强有关[41]。
2.5.2 p53在关节破坏中的作用
(1)促进细胞凋亡:p53可以通过加快滑膜细胞和软骨细胞的凋亡,从而加重关节的破坏过程。细胞凋亡增加可能导致关节组织损伤和骨侵蚀[42]。此外,类风湿关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞中,p53突变导致抗凋亡因子Bcl-2表达增加,同时p21WAF和Hdm-2表达下降。p53通过调控Bcl-2家族蛋白,显著抑制了滑膜细胞凋亡,促进关节破坏[43]。
(2)调节基质金属蛋白酶:基质金属蛋白酶能够分解细胞外基质,使
类风湿关节炎中的炎症细胞更容易侵入关节,从而加剧关节损伤。研究发现,细胞外S100A4蛋白在类风湿关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中增强了p53抑癌基因表达,并影响了p53靶基因(Bcl-2、p21WAF和Hdm-2)的表达水平 [44],这些靶基因的调节对于控制细胞凋亡和炎症反应至关重要。因此,p53通过影响基质金属蛋白酶的表达和活性,间接加重了关节损伤。
2.5.3 p53在类风湿关节炎发病机制中的地位
(1)细胞周期控制:在类风湿关节炎的病理过程中,p53的异常表达可能会导致细胞周期失调,进而促进滑膜细胞的过度增殖。研究发现,NK4能够下调细胞增殖标志物PCNA以及细胞周期蛋白D1和细胞周期蛋白B1的表达水平,同时上调p53和p21的表达水平,抑制类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞和MH7A细胞的增殖,并阻滞细胞周期的进展[45]。
(2)DNA损伤响应:p53参与并调控多种DNA修复途径。在类风湿关节炎中,氧化应激和炎症会损伤DNA。此时,p53的激活对于修复DNA损伤是十分重要的,它有助于预防细胞癌变的发展。p53在类风湿关节炎中维护基因组稳定性和抑制细胞的异常增殖,在疾病进展中起到了保护作用[46]。
(3)细胞衰老:在类风湿关节炎的病理状态下,p53可能通过促进细胞衰老,以减缓炎症反应和组织损伤的发展。在复制衰老细胞的过程中,环氧合酶2和前列腺素E2的表达水平明显上升,而体外老化的成纤维细胞则表现出增殖能力下降,这就可能归咎于p53蛋白表达增加和细胞增殖标志物PCNA蛋白表达降低所致[47]。
上述研究表明,p53通过调控细胞衰老进程与增殖活性,在类风湿关节炎病理机制中起核心作用,其通过抑制促炎因子释放及维持细胞外基质稳态,显著缓解关节组织病理性损伤(表3)。
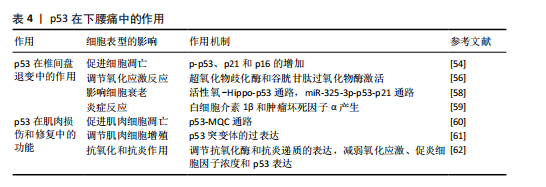
2.6 p53在下腰痛发生中的作用 下腰痛发生的普遍性已经引发了全球关注,该健康问题已上升为重大公共卫生挑战,并且严重了影响患者的生活质量[48-49],其病理基础涵盖了椎间盘
退化、骶髂关节炎和小关节综合征等多种病理性改变[50]。其中,小关节变性是引起慢性腰痛的一个重要因素,约占30% [51]。在临床治疗中,传统的物理疗法往往难以持久的缓解症状,而手术治疗又存在加重关节损伤的风险[52]。研究表明,p53可以通过调控特定靶基因的表达,直接干预椎间盘退变细胞的衰老以及物质的代谢过程[53]。
2.6.1 p53在椎间盘退变中的作用
(1)促进细胞凋亡:p53的激活会促进凋亡途径,影响椎间盘细胞的存活。在椎间盘退变过程中,p53的激活可能导致细胞停止生长并死亡,从而使椎间盘细胞的数量减少,破坏其正常功能。研究表明,原花青素预处理能够阻止白细胞介素1β诱导的髓核细胞凋亡,还可以抑制白细胞介素1β处理的髓核细胞中p-p53、p21和p16的表达[54];同时,激活特定保护性蛋白Sirt1可能通过减少p53相关蛋白的表达,延缓髓核细胞凋亡和衰老进程。这些发现表明,Sirt1/P53轴可能在糖尿病相关的椎间盘退行性变的发病机制和治疗中发挥重要作
用[55]。通过调节Sirt1/P53轴可能成为治疗椎间盘退变的新思路。
(2)调节氧化应激反应:p53可以启动抗氧化基因的表达,如超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶,可以帮助细胞抵抗氧化损伤,从而有效减轻氧化应激对椎间盘细胞的损伤。在非生理幅度的循环机械张力作用下,髓核细胞的DNA损伤增强,导致髓核细胞的氧化应激反应[56]。因此,p53通过调节抗氧化基因的表达,减少氧化应激对细胞的破坏,从而保护椎间盘细胞的正常功能。
(3)影响细胞衰老:在椎间盘退变中,p53激活会促进细胞更快进入衰老状态,这一点可以通过衰老相关β-半乳糖苷酶活性增加和p53依赖的衰老标志物的表达来证实。研究表明,桑斛苷能够通过抑制活性氧-Hippo-p53通路来防止髓核细胞过早的老化,这一作用为椎间盘退变的治疗提供了新思路[57]。此外,miR-325-3p通过激活p53/p21通路,不仅可以减缓软骨细胞衰老,还能改善由机械超载引起的腰椎小关节变性,这可能是延缓腰椎小关节变性进展的潜在治疗策略[58],揭示p53在椎间盘退变和腰椎小关节变性中的作用,通过精准调节p53信号网络可能成为治疗退行性骨关节疾病的新策略。
(4)炎症反应:p53通过调控关键炎症因子(如白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α)的产生,影响疼痛信号传递和局部炎症的发展。研究表明,类黄酮能够抑制髓核细胞的炎症反应和衰老,为椎间盘退变提供了一种新的治疗策略[59]。类黄酮通过抑制丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/核因子κB信号通路,减少肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的细胞外基质降解,下调了细胞外基质破坏相关酶(基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶9和基质金属蛋白酶13)的表达,并上调SOX9和COL2A1的表达,从而缓解退变进程[59]。
2.6.2 p53在肌肉损伤和修复中的功能
(1)促进肌肉细胞凋亡:p53的激活可引起肌肉细胞死亡,从而影响肌肉修复和再生能力。体内实验表明,在p53基因敲除组织中,线粒体功能异常加重,并伴有神经支配应激能力下降,这表明 p53 通过调节肌肉萎缩的线粒体质量控制通路来维持细胞器的稳定[60]。由此可见,p53在肌肉损伤和修复过程中发挥着双重作用,既是细胞凋亡的调节因子,也是细胞器健康的守护者。
(2)调节肌肉细胞增殖:研究表明,骨骼肌中显性阴性p53突变体的过表达会干扰肌肉质量、肌纤维大小、代谢表型等,同时干扰肌肉蛋白质合成和降解之间的动态平衡[61],表明p53不仅调控肌肉细胞的凋亡,还可能通过调节肌肉干细胞的分裂能力影响修复效率。因此,p53可能决定了肌肉修复的成功与否。通过调节p53的活性,可能为改善肌肉损伤后的修复和再生提供新的治疗手段。
(3)抗氧化和抗炎作用:p53通过增强抗氧化酶的表达并抑制炎症相关信号通路,帮助肌肉减轻氧化应激和炎症反应。例如,运动治疗可以减少腰痛患者的氧化应激、促炎细胞因子浓度和p53异常激活[62]。此外,柚皮苷通过下调核因子κB通路并下调p53活性,有效抑制白细胞介素1干预的人髓核细胞基质金属蛋白酶分解代谢和炎症,为延缓椎间盘退变提供了潜在的治疗思路[63]。
这些发现揭示了p53在腰痛治疗中的潜在作用,为未来的治疗策略提供了新的方向(表4)。
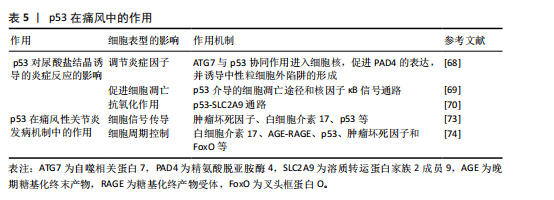
2.7 p53在痛风中的作用 痛风是嘌呤代谢异常以及尿酸排泄障碍共同诱发的自身免疫性疾病[64-65],全球流行病学调查显示,该病患病率存在显著地域差异(1%-6.8%)[66]。在中国,痛风的发病率逐渐增加,据研究显示,2000年和2014年高尿酸血症和痛风的患病率分别为1.1%和13.3% [67]。p53蛋白在此类关节炎中发挥着多维度的调控作用,其功能在尿酸盐结晶诱导的炎症反应中表现突出。通过调节抗氧化酶和抗炎递质的表达,p53能有效缓解氧化应激损伤,并且能够减少局部炎症的扩散,同时促进受损肌肉修复。
2.7.1 p53对尿酸盐结晶诱导的炎症反应的影响
(1)调节炎症因子:在痛风性关节炎中,尿酸结晶触发的炎症反应是疾病进展的驱动因素,而p53可能通过调节炎症因子的表达,影响痛风的炎症过程。例如,尿酸钠晶体刺激的中性粒细胞产生自噬相关蛋白7与p53协同作用进入细胞核,从而驱动肽基精氨酸脱亚胺酶4的表达,使中性粒细胞释放胞外陷阱[68],这一过程揭示了p53在痛风性关节炎炎症损伤中的放大机制。通过干预此类炎症递质的作用,p53有助于控制痛风性关节炎的炎症活动,从而对疾病的进展产生影响。
(2)促进细胞凋亡:在痛风性关节炎中,尿酸结晶引发的炎症可以加剧细胞损伤。p53作为一个重要的凋亡调节因子,可能通过引发细胞凋亡来清除尿酸盐结晶,从而影响疾病的进程。基于“肾络通调”理论研发的肾草复方,其作用机制可能是干预p53介导的细胞凋亡途径以及核因子κB信号通路,以此来抑制肾脏细胞的凋亡和炎症反应[69],研究结果不仅阐释了痛风的跨器官损伤机制,更为糖尿病肾病等继发性肾脏损伤提供干预思路。所以,调节p53和核因子κB等关键分子,有助于减缓痛风患者的炎症,保护肾脏。
(3)抗氧化作用:痛风性关节炎的关键病理特征在于氧化应激,p53通过调节抗氧化相关基因(如超氧化物歧化酶)的表达,来帮助细胞抵御氧化应激。此外,新进发现的p53-SLC2A9 通路揭示了尿酸代谢的双向调节,该通路可维持活性氧的稳态,并阻止活性氧相关损伤的积累。研究表明,p53可以诱导SLC2A9表达,而SLC2A9抑制会显著增加活性氧水平,从而提升癌细胞对化疗药物的敏感性[70]。相反,SLC2A9的表达能够减少活性氧并保护细胞免受DNA损伤和死亡,显示其抗氧化功能。因此,该通路在痛风性关节炎治疗中具有双重价值,不仅有助于缓解痛风的氧化应激反应,还可以降低其他氧化相关疾病的风险。
2.7.2 p53在痛风性关节炎发病机制中的作用
(1)细胞信号传导:突破传统凋亡调控的认知,p53可以通过核因子κB和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶等关键信号通路来调节炎症进程。研究表明,核因子κB的异常激活与炎症因子的释放密切相关,其在疾病进展中发挥着核心调控作用[71]。同时,丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路也参与了调控炎症相关基因表达,影响痛风性关节炎的炎症反应进程[72]。实验发现,中药司苗粉通过调控肿瘤坏死因子、白细胞介素17及p53等,有效抑制炎症信号通路的过度激活,从而缓解关节炎症损伤[73],该发现不仅阐释了多靶点协同干预原理,更奠定了药效学基础。
(2)细胞周期控制:p53可能通过影响细胞周期相关蛋白的表达,对痛风性关节炎的细胞增殖和凋亡产生影响。研究表明,山奈酚作为一种具有治疗潜力的化合物,对痛风性关节炎的疗效可能是通过调节白细胞介素17、AGE-RAGE、p53、肿瘤坏死因子和 FoxO 等信号通路实现的[74],并可能成为开发新疗法的有力候选。
这些研究结果强调了p53在痛风性关节炎中的重要作用,并为未来的治疗策略奠定了基础(表5)。
2.8 p53在脊柱侧弯中的作用 脊柱侧弯是一种以脊柱三维结构异常为特征的肌肉骨骼疾病,发病机制呈现遗传易感性、生物力学失衡、细胞代谢异常等多维度交互。全球流行病学数据显示,青少年特发性脊柱侧弯患病率为2%-3%,女性患者比例明显高于男性,严重的脊柱侧弯畸形可导致心肺功能受限及神经压迫,临床治疗面临着巨大挑战[75]。目前治疗的方式主要为早期矫形及后期手术,而p53可以通过调控椎旁肌肉细胞凋亡和氧化应激等机制来影响脊柱侧弯的病理进程,所以p53功能异常可能成为疾病进展的关键驱动因素。
2.8.1 p53对椎旁肌肉细胞凋亡的调控 椎旁肌肉功能失衡是脊柱侧弯生物力学异常的核心环节。研究表明,在去神经支配诱导的肌肉萎缩过程中,Bax(促凋亡蛋白)的mRNA和蛋白表达显著增加,而Bcl-2(抗凋亡蛋白)的mRNA和蛋白表达虽然也有所增加,但Bax/Bcl-2比值显著升高,表明促凋亡信号在肌肉细胞中占据主导地位;与此同时,p53蛋白在细胞核和细胞质中的含量显著增加,提示p53可能通过调控Bax和Bcl-2的表达,参与肌肉细胞凋亡信号通路的激活,从而促进肌肉萎缩[76],进而加剧脊柱侧弯的进展。
2.8.2 p53介导的氧化应激与椎间盘退变 脊柱侧弯常伴随椎间盘退变,而氧化应激是椎间盘退变的核心病理环节。氧化应激导致的DNA损伤会激活p53,进而通过p53-p21CIP1途径诱导细胞周期停滞和细胞衰老。此外,p53还通过调控抗氧化酶的表达来影响细胞对氧化应激的响应。在椎间盘细胞中,氧化应激诱导的p53激活会导致细胞衰老和衰老相关分泌表型分泌白细胞介素6、基质金属蛋白酶3等促炎因子,进一步加剧椎间盘退变[77],这一机制发现为脊柱侧弯的预防提供了新的策略。
2.9 p53在肌肉骨骼疾病中的潜在治疗靶点
2.9.1 p53作为骨质疏松的潜在靶点 在药物干预方面,研究p53抑制剂或激活剂可能对调节骨代谢、促进骨形成和抑制骨吸收具有积极作用。在地塞米松作用下的成骨细胞中,衰老相关标志物p53和p21的水平显著增加;使用p53抑制剂能够逆转地塞米松诱导的成骨细胞损伤,而硫化氢给药则通过减轻成骨细胞衰老来缓解这一过程[78-79]。
在基因治疗领域,利用CRISPR/Cas9等基因编辑技术可以特异性地敲除或修复与p53相关的基因,以改善骨质疏松的症状。研究表明,在p53敲除小鼠中,无论贝前列素如何给药,骨量都保持稳定,这表明p53在贝前列素调节骨量中起着至关重要的作用[80-81]。此外,胶原代谢过程和细胞外基质-受体相互作用失调可能是骨质疏松小鼠骨修复受损的原因之一,而Ccnb2和Rrm2等上调基因可能参与调节对骨愈合至关重要的p53通路[76],这些发现为骨质疏松症的治疗提供了新的策略和潜在的干预靶点。
2.9.2 p53作为骨关节炎的潜在靶点 研究表明,p53可以引起软骨细胞周期停滞和激活外源性及内在凋亡途径,从而促进剪切诱导的软骨细胞凋亡。因此,调控软骨细胞凋亡及细胞外基质分解相关的信号通路,可能成为干预骨关节炎病理进程的新方
向[77],从而为改善患者治疗效果提供理论支持。
2.9.3 p53作为类风湿关节炎的潜在靶点 在类风湿关节炎患者的外周血单核细胞中,调控细胞凋亡、细胞存活、炎症递质产生和增殖相关的多个基因均呈现表达下调,这些基因与类风湿关节炎发病机制密切相关。其中miR-16-5p、miR-34a-5p和miR-335-5p与TP53和FOXO1的表达存在关联,这就表明它们是可以作为治疗的潜在靶点[78],进一步探索p53在免疫调节中的作用及干预策略。
2.9.4 p53作为下腰痛的潜在靶点 研究发现,p53驱动细胞凋亡相关基因的表达,加速退变椎间盘细胞的凋亡。此外,当椎间盘受到异常的机械应力或炎症刺激等损伤因素时,p53通路直接被触发,从而影响细胞内信号转导,调节椎间盘细胞的增殖、分化和细胞外基质合成等过程。未来需深入解析p53在下腰痛中的具体机制,探索其作为治疗靶点的可行性。
2.9.5 p53作为痛风的潜在靶点 通过调节p53的活性及其下游信号通路,可以抑制痛风中炎症反应和细胞损伤,进一步研究需明确p53在尿酸结晶诱导的炎症级联反应中的动态作用,开发精准干预手段。
2.9.6 p53作为脊柱侧弯的潜在靶点 通过调节p53的活性可能改善肌肉功能失衡和缓解氧化应激损伤,从而延缓椎间盘退变的进程,这一发现不仅可以预测脊柱侧弯的发生,甚至可以终止甚至逆转脊柱侧弯的进程。
| [1] NAYAK SK, PANESAR PS, KUMAR H. p53-Induced apoptosis and inhibitors of p53. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(21):2627-2640. [2] PIETRANCOSTA N, MOUMEN A, DONO R, et al. Imino-tetrahydro-benzothiazole derivatives as p53 inhibitors: discovery of a highly potent in vivo inhibitor and its action mechanism. J Med Chem. 2006; 49(12):3645-3652. [3] WHYTE MK, MEAGHER LC, MACDERMOT J, et al. Impairment of function in aging neutrophils is associated with apoptosis. J Immunol. 1993;150(11):5124-5134. [4] BRIGGS AM, WOOLF AD, DREINHÖFER K, et al. Reducing the global burden of musculoskeletal conditions. Bull World Health Organ. 2018;96(5):366-368. [5] HERNÁNDEZ BORRERO LJ, EL-DEIRY WS. Tumor suppressor p53: Biology, signaling pathways, and therapeutic targeting. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021; 1876(1):188556. [6] MAY P, MAY E. Twenty years of p53 research: structural and functional aspects of the p53 protein. Oncogene. 1999;18(53):7621-7636. [7] HAFNER A, BULYK ML, JAMBHEKAR A, et al. The multiple mechanisms that regulate p53 activity and cell fate. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(4):199-210. [8] MEEK DW, ANDERSON CW. Posttranslational modification of p53: cooperative integrators of function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009;1(6):a000950. [9] WEI H, QU L, DAI S, et al. Structural insight into the molecular mechanism of p53-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2280. [10] MOHAMAD KAMAL NS, SAFUAN S, SHAMSUDDIN S, et al. Aging of the cells: Insight into cellular senescence and detection Methods. Eur J Cell Biol. 2020; 99(6):151108. [11] VADIVEL GNANASUNDRAM S, BONCZEK O, WANG L, et al. p53 mRNA Metabolism Links with the DNA Damage Response. Genes (Basel). 2021;12(9):1446. [12] GORGOULIS V, ADAMS PD, ALIMONTI A, et al. Cellular Senescence: Defining a Path Forward. Cell. 2019;179(4):813-827. [13] COMPSTON JE, MCCLUNG MR, LESLIE WD. Osteoporosis. Lancet. 2019;393(10169): 364-376. [14] YU T, WANG Z, YOU X, et al. Resveratrol promotes osteogenesis and alleviates osteoporosis by inhibiting p53. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(11):10359-10369. [15] ZHANG M, XIE Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Exendin-4 enhances proliferation of senescent osteoblasts through activation of the IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;516(1):300-306. [16] KOMORI T. Cell Death in Chondrocytes, Osteoblasts, and Osteocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):2045. [17] XIA C, JIANG T, WANG Y, et al. The p53/miR-145a Axis Promotes Cellular Senescence and Inhibits Osteogenic Differentiation by Targeting Cbfb in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021; 11:609186. [18] WU M, WANG Y, SHAO JZ, et al. Cbfβ governs osteoblast-adipocyte lineage commitment through enhancing β-catenin signaling and suppressing adipogenesis gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(38):10119-10124. [19] ZHENG HL, XU WN, ZHOU WS, et al. Beraprost ameliorates postmenopausal osteoporosis by regulating Nedd4-induced Runx2 ubiquitination. Cell Death Dis. 2021; 12(5):497. [20] XIAO Y, CUI J, LI YX, et al. Expression of genes associated with bone resorption is increased and bone formation is decreased in mice fed a high-fat diet. Lipids. 2010;45(4):345-355. [21] QIAO W, YU S, SUN H, et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D insufficiency accelerates age-related bone loss by increasing oxidative stress and cell senescence. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(2): 507-518. [22] HUANG C, ZHANG GF, HAN J, et al. Mechanism of age-related changes of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in senile osteoporosis. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2016;30(2):565-569. [23] WANG C, YU T, TAN L, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of gene expression profile in callus tissues of osteoporotic phenotype mice induced by osteoblast-specific Krm2 overexpression. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016; 19(12):1263-1271. [24] ALLEN KD, THOMA LM, GOLIGHTLY YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):184-195. [25] DESHPANDE BR, KATZ JN, SOLOMON DH, et al. Number of Persons With Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis in the US: Impact of Race and Ethnicity, Age, Sex, and Obesity. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016;68(12):1743-1750. [26] LO J, CHAN L, FLYNN S. A Systematic Review of the Incidence, Prevalence, Costs, and Activity and Work Limitations of Amputation, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Back Pain, Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord Injury, Stroke, and Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: A 2019 Update. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102(1):115-131. [27] YAN S, WANG M, ZHAO J, et al. MicroRNA-34a affects chondrocyte apoptosis and proliferation by targeting the SIRT1/p53 signaling pathway during the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med. 2016;38(1): 201-209. [28] QI H, ZHAO Z, XU L, et al. Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Therapy on miR-181a-5p Alleviates Cartilage Degradation of Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis via Promoting SIRT1. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:898334. [29] WANG CC, WANG CT, CHOU WC, et al. Hyaluronic acid injection reduces inflammatory and apoptotic markers through modulation of AKT by repressing the oxidative status of neutrophils from osteoarthritic synovial fluid. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;165(Pt B):2765-2772. [30] JACOB J, AGGARWAL A, AGGARWAL A, et al. Senescent chondrogenic progenitor cells derived from articular cartilage of knee osteoarthritis patients contributes to senescence-associated secretory phenotype via release of IL-6 and IL-8. Acta Histochem. 2022;124(3):151867. [31] ZHOU Y, LI J, XU F, et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 alleviates inflammation in osteoarthritis through interactions between TP53, IL-38, and IL-36 receptor. Bone Joint Res. 2022;11(8):594-607. [32] KAWAKITA K, NISHIYAMA T, FUJISHIRO T, et al. Akt phosphorylation in human chondrocytes is regulated by p53R2 in response to mechanical stress. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(12):1603-1609. [33] HUANG LW, HUANG TC, HU YC, et al. S-Equol Protects Chondrocytes against Sodium Nitroprusside-Caused Matrix Loss and Apoptosis through Activating PI3K/Akt Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):7054. [34] LI W, XIONG Y, CHEN W, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling may induce senescence of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(3):2631-2638. [35] HASHIMOTO S, NISHIYAMA T, HAYASHI S, et al. Role of p53 in human chondrocyte apoptosis in response to shear strain. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(8):2340-2349. [36] ZAN PF, YAO J, WU Z, et al. Cyclin D1 Gene Silencing Promotes IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis in Rat Chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 2018; 119(1):290-299. [37] SAKATA S, HAYASHI S, FUJISHIRO T, et al. Oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and matrix loss of chondrocytes is inhibited by eicosapentaenoic acid. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(3):359-365. [38] FIRESTEIN GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003; 423(6937):356-361. [39] YAGISHITA N, YAMASAKI S, NISHIOKA K, et al. Synoviolin, protein folding and the maintenance of joint homeostasis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2008;4(2):91-97. [40] ZHANG T, LI H, SHI J, et al. p53 predominantly regulates IL-6 production and suppresses synovial inflammation in fibroblast-like synoviocytes and adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016; 18(1):271. [41] SIMELYTE E, ROSENGREN S, BOYLE DL, et al. Regulation of arthritis by p53: critical role of adaptive immunity. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(6):1876-1884. [42] DUBIKOV AI, KALINICHENKO SG. Small molecules regulating apoptosis in the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2010;39(5):368-372. [43] MICHAEL VV, ALISA KE. Cell cycle implications in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Front Biosci. 2000;5: D594-D601. [44] KLINGELHÖFER J, SENOLT L, BASLUND B, et al. Up-regulation of metastasis-promoting S100A4 (Mts-1) in rheumatoid arthritis: putative involvement in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(3):779-789. [45] QUE W, LIU H, YANG Q, et al. NK4 inhibits the proliferation and induces apoptosis of human rheumatoid arthritis synovial cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 2018;36(5):273-279. [46] FIRESTEIN GS, NGUYEN K, AUPPERLE KR, et al. Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis: p53 overexpression in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Am J Pathol. 1996;149(6):2143-2151. [47] HAN JH, ROH MS, PARK CH, et al. Selective COX-2 inhibitor, NS-398, inhibits the replicative senescence of cultured dermal fibroblasts. Mech Ageing Dev. 2004;125(5): 359-366. [48] CHOU R. Low Back Pain. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174(8):ITC113-ITC128. [49] DIELEMAN JL, CAO J, CHAPIN A, et al. US Health Care Spending by Payer and Health Condition, 1996-2016. JAMA. 2020; 323(9):863-884. [50] DOWDELL J, ERWIN M, CHOMA T, et al. Intervertebral disk degeneration and repair. Neurosurgery. 2017;80(3S):S46-S54. [51] CARVAJAL ALEGRIA G, VOIRIN-HERTZ M, et al. Association of lumbosacral transitional vertebra and sacroiliitis in patients with inflammatory back pain suggesting axial spondyloarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(7):1679-1683. [52] O’LEARY SA, PASCHOS NK, LINK JM, et al. Facet joints of the spine: structure-function relationships, problems and treatments, and the potential for regeneration. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2018;20:145-170. [53] COHEN KR. Management of chronic low back pain. JAMA Intern Med. 2022;182(2): 222-223. [54] CHEN HW, LIU MQ, ZHANG GZ, et al. Proanthocyanidins inhibit the apoptosis and aging of nucleus pulposus cells through the PI3K/Akt pathway delaying intervertebral disc degeneration. Connect Tissue Res. 2022;63(6):650-662. [55] ZHANG Z, LIN J, NISAR M, et al. The Sirt1/P53 Axis in Diabetic Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Pathogenesis and Therapeutics. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019; 2019:7959573. [56] FENG C, YANG M, ZHANG Y, et al. Cyclic mechanical tension reinforces DNA damage and activates the p53-p21-Rb pathway to induce premature senescence of nucleus pulposus cells. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(6):3316-3326. [57] ZHOU C, YAO S, FU F, et al. Morroniside attenuates nucleus pulposus cell senescence to alleviate intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibiting ROS-Hippo-p53 pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:942435. [58] ZHAO J, LI C, QIN T, et al. Mechanical overloading-induced miR-325-3p reduction promoted chondrocyte senescence and exacerbated facet joint degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25(1):54. [59] YANG H, YANG X, RONG K, et al. Eupatilin attenuates the senescence of nucleus pulposus cells and mitigates intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibition of the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:940475. [60] MEMME JM, OLIVEIRA AN, HOOD DA. p53 regulates skeletal muscle mitophagy and mitochondrial quality control following denervation-induced muscle disuse. J Biol Chem. 2022;298(2):101540. [61] LANGER HT, MOSSAKOWSKI AA, SULE R, et al. Dominant-negative p53-overexpression in skeletal muscle induces cell death and fiber atrophy in rats. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(8):716. [62] CHENG YY, KAO CL, MA HI, et al. SIRT1-related inhibition of pro-inflammatory responses and oxidative stress are involved in the mechanism of nonspecific low back pain relief after exercise through modulation of Toll-like receptor 4. J Biochem. 2015;158(4):299-308. [63] LI N, WHITAKER C, XU Z, et al. Therapeutic effects of naringin on degenerative human nucleus pulposus cells for discogenic low back pain. Spine J. 2016;16(10):1231-1237. [64] DALBETH N, GOSLING AL, GAFFO A, et al. Gout. Lancet. 2021;397(10287):1843-1855. [65] CABĂU G, CRIȘAN TO, KLÜCK V, et al. Urate-induced immune programming: Consequences for gouty arthritis and hyperuricemia. Immunol Rev. 2020; 294(1):92-105. [66] DEHLIN M, JACOBSSON L, RODDY E. Global epidemiology of gout: prevalence, incidence, treatment patterns and risk factors. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(7): 380-390. [67] LIU R, HAN C, WU D, et al. Prevalence of Hyperuricemia and Gout in Mainland China from 2000 to 2014: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:762820. [68] HUANG S, WANG Y, LIN S, et al. Neutrophil autophagy induced by monosodium urate crystals facilitates neutrophil extracellular traps formation and inflammation remission in gouty arthritis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1071630. [69] TANG GY, LI S, XU Y, et al. Renal herb formula protects against hyperuricemic nephropathy by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation. Phytomedicine. 2023;116:154812. [70] ITAHANA Y, HAN R, BARBIER S, et al. The uric acid transporter SLC2A9 is a direct target gene of the tumor suppressor p53 contributing to antioxidant defense. Oncogene. 2015;34(14):1799-1810. [71] LIU T, ZHANG L, JOO D, et al. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2017;2:17023. [72] Jiang Y, Gong XW. Regulation of inflammatory responses by MAPK signal transduction pathways. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2000;52(4):267-271. [73] FAN Y, LIU W, JIN Y, et al. Integrated Molecular Docking with Network Pharmacology to Reveal the Molecular Mechanism of Simiao Powder in the Treatment of Acute Gouty Arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021; 2021:5570968. [74] LI N, CHEN S, DENG W, et al. Kaempferol Attenuates Gouty Arthritis by Regulating the Balance of Th17/Treg Cells and Secretion of IL-17. Inflammation. 2023;46(5):1901-1916. [75] THÉROUX J, STOMSKI N, HODGETTS CJ, et al. Prevalence of low back pain in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review. Chiropr Man Therap. 2017;25:10. [76] SIU PM, ALWAY SE. Mitochondria-associated apoptotic signalling in denervated rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 2005;565(Pt 1): 309-323. [77] SILWAL P, NGUYEN-THAI AM, MOHAMMAD HA, et al. Cellular Senescence in Intervertebral Disc Aging and Degeneration: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Opportunities. Biomolecules. 2023;13(4):686. [78] LI P, MAO WW, ZHANG S, et al. Sodium hydrosulfide alleviates dexamethasone-induced cell senescence and dysfunction through targeting the miR-22/sirt1 pathway in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(3):238. [79] QUICKE JG, CONAGHAN PG, CORP N, et al. Osteoarthritis year in review 2021: epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):196-206. [80] ZHU F, WANG P, KONTROGIANNI-KONSTANTOPOULOS A, et al. Prostaglandin (PG)D(2) and 15-deoxy-Delta(12,14)-PGJ(2), but not PGE(2), mediate shear-induced chondrocyte apoptosis via protein kinase A-dependent regulation of polo-like kinases. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17(8):1325-1334. [81] EBRAHIMIAN H, AKHTARI M, AKHLAGHI M, et al. Altered expression of apoptosis-related genes in rheumatoid arthritis peripheral blood mononuclear cell and related miRNA regulation. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023;11(7):e914. |
| [1] | 黎清斌, 林建辉, 黄文杰, 王明爽, 杜间开, 劳永锵. 膝关节周围骨巨细胞瘤病灶扩大刮除后填充骨水泥:软骨下植骨与不植骨的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [2] | 胡雄科, 刘少华, 谭 谦, 刘 昆, 朱光辉. 紫草素干预骨髓间充质干细胞改善老年小鼠股骨的微结构[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [3] | 宋浦蓁, 马贺宾, 陈宏广, 章亚东. 骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体联合转化生长因子β1对巨噬细胞的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1616-1623. |
| [4] | 吴治林, 何 秦, 王枰稀, 石 现, 袁 松, 张 骏, 王 浩. DYRK2:基于东亚和欧洲人群揭示类风湿关节炎合并骨质疏松症的治疗新靶点[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [5] | 李 豪, 陶红成, 曾 平, 刘金富, 丁 强, 牛驰程, 黄 凯, 康宏誉. 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路调控骨关节炎的发生发展:指导中药靶点治疗[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1476-1485. |
| [6] | 郭 英, 田 峰, 王春芳. 类风湿关节炎潜在药物靶点:来自欧洲数据库的大样本分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [7] | 黄 杰, 曾 浩, 王文驰, 吕柱成, 崔 伟. 脂代谢影响骨质疏松症的文献可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [8] | 李林臻, 焦泓焯, 陈伟南, 张铭哲, 王建龙, 张君涛. 淫羊藿苷含药血清对脂多糖诱导人软骨细胞炎症损伤的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1368-1374. |
| [9] | 陈 驹, 郑锦畅, 梁 振, 黄成硕, 林 颢, 曾 莉. β-石竹烯对小鼠膝骨关节炎的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1341-1347. |
| [10] | 温广伟, 甄颖豪, 郑泰铿, 周淑怡, 莫国业, 周腾鹏, 李海山, 赖以毅. 异银杏素对破骨细胞分化的影响和机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [11] | 吕国庆, 艾孜麦提江·肉孜, 熊道海. 鸢尾素抑制人关节软骨细胞中铁死亡的作用及其机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [12] | 杨志杰, 赵 瑞, 杨昊霖, 李小韵, 李扬博, 黄佳纯, 林燕平, 万 雷, 黄宏兴. 绝经后骨质疏松症:肌肉质量、握力、四肢骨骼肌质量指数的预测价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [13] | 周 坚, 张 涛, 周威力, 赵星丞, 王 军, 沈 杰, 钱 丽, 陆 明. 抗阻训练对骨质疏松并肌少症患者股四头肌质量及膝关节功能的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1081-1088. |
| [14] | 张 倩, 黄东锋. 加权基因共表达网络分析结合机器学习筛选及验证骨关节炎生物标记物[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1096-1105. |
| [15] | 部洋洋, 宁新丽, 赵 琛. 关节腔注射治疗颞下颌关节骨关节炎:不同药物与多种联合治疗方案[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
肌肉骨骼疾病主要包括骨质疏松症、类风湿关节炎、骨关节炎、下腰痛、痛风和脊柱侧弯等,在全球范围内是影响较为广泛的慢性疾病,这些疾病不仅导致患者运动功能进行性丧失,还会给社会医疗资源带来巨大的经济负担。流行病学数据显示,伴随着人口老龄化的严重,肌肉骨骼疾病的发病率呈持续上升趋势,尤其是在老年人群中,其临床症状呈不断加重的趋势[4]。肌肉骨骼疾病的发病机制涉及遗传、环境等多维度因素。所以深入研究肌肉骨骼疾病的病因和治疗方法具有重要的临床意义。
基于上述背景,此综述旨在系统总结p53信号通路在肌肉骨骼疾病发生、发展中的具体机制,并评估p53作为治疗靶点的潜力,为开发针对肌肉骨骼疾病的新疗法提供理论依据。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 杜彦利、汪屹在2024年12月进行文献检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2004年1月至2024年12月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词:P53,Osteoporosis,Post-Menopausal Osteoporosis,Osteoarthritis,Degenerative Arthritis,Rheumatoid Arthritis,Gout,Low Back Pains,Low Back Ache,Back Pain,Scoliosis。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 原始研究论文、综述文章、临床试验、系统综述、方法学论文。
1.1.6 检索策略 PubMed数据库检索策略见图1。
1.1.7 检索文献量 共检索到402篇相关文献。
1.3 排除标准 ①研究仅涉及临床现象描述,未深入探讨p53的分子机制;②同一研究在不同期刊重复发表,仅保留最早或最完整的版本;③研究数据不完整或无法获取全文的文献。
1.4 资料整合 共检索到402篇相关文献,排除321篇,实际纳入81篇,均为英文文献。检索流程见图2。
Conclusions and prospects
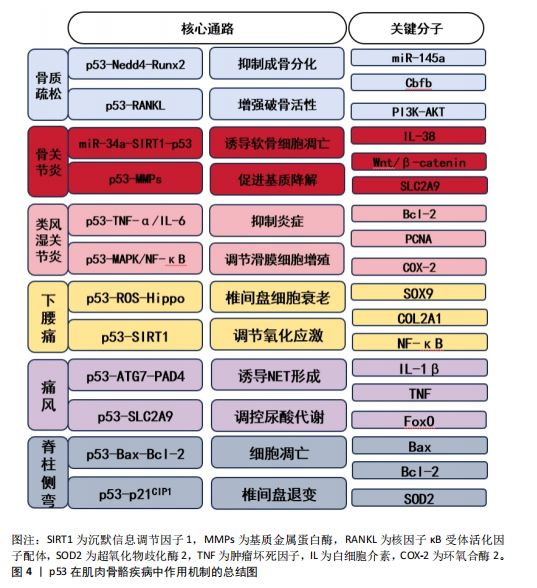
p53基因在肌肉骨骼疾病中具有重要的调控价值,其作用已经超过了传统的肿瘤抑制范畴(图4)。现有的研究仍存在诸多局限性:首先,大多数研究仅仅是单一疾病或者孤立通路,缺乏整合;其次,p53基因在不同疾病的病理阶段可能发挥促凋亡或抗炎等矛盾的效应,其动态调控规律没有探明;最后,临床转化不足,现有成果大多基于体外细胞或者动物模型,缺乏临床验证,并且p53调节剂的安全性与特异性需要进一步研究。
文章首次系统地综述了p53在六大肌肉骨骼疾病(骨质疏松症、骨关节炎、类风湿关节炎、下腰痛、痛风、脊柱侧弯)中的多维度调控作用,突破了传统单一疾病研究框架,整合了多个疾病的机制,系统归纳了p53基因通过凋亡、氧化应激、炎症及代谢调控等通路,揭示其在多种肌肉骨骼疾病中的共性机制(如骨质疏松症中p53-Nedd4-Runx2轴调控骨形成,骨关节炎中p53-miR-34a通路介导软骨细胞凋亡);在理论层面上,文章揭示了p53作为“分子枢纽”连接退变、炎症与代谢紊乱的共性病理机制;在应用层面上,为开发靶向p53的基因疗法(如CRISPR编辑)、小分子药物(如p53抑制剂)及天然产物(如桑斛苷)提供了依据,进而推动个体化医疗发展。基于这些发现,可以针对性调节p53的活性,有效干预疾病的病理过程,从而达到治疗的目的。虽然p53在基础研究中显示出了巨大的潜力,但是其临床应用上仍面临诸多挑战。例如,如何精确调控p53的活性,避免不良反应,以及怎样将基础研究成果转化为有效的临床治疗方案等。
根据目前的研究现状以及发展需求来看,未来需突破以下方向:第一,阐明p53在多种肌肉骨骼疾病中的分子作用网络,明确p53作为治疗靶点的可行性,研究特异性的p53调节剂,平衡治疗效果与潜在风险;第二,推进多中心临床试验验证p53靶向药物(如Sirt1激活剂)的临床适用性;第三,可以去融合基因编辑技术和细胞治疗等新兴技术,联合生物信息学、材料学与临床医学等多学科,探索p53信号网络在组织修复中的调控价值,构建涵盖诊断、治疗与康复的综合治疗体系。
综合来看,p53在肌肉骨骼疾病中的研究不仅拓展了对疾病的病理机制新的理解,也为创新性治疗方法的开发提供了方向。通过整合不同研究的观点和发现,可以更全面地理解p53的功能,并推动其在临床应用中的进展,当前可聚焦为机制解析、技术革新与临床验证三方面协同突破,最终实现从“分子洞察”到“临床获益”的跨越。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||