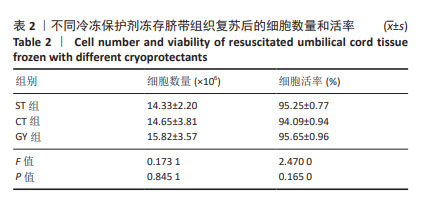
[1] MURRAY KA, GIBSON MI. Chemical approaches to cryopreservation. Nat Rev Chem. 2022;6(8):579-593.
[2] 胡方方,李延,崔趁趁,等.人卵巢组织玻璃化冷冻及移植的影响因素分析[J].中国计划生育和妇产科,2023,15(9):20-24.
[3] SHAHID MA, KIM WH, KWEON OK. Cryopreservation of heat-shocked canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells with 10% dimethyl sulfoxide and 40% serum results in better viability, proliferation, anti-oxidation, and in-vitro differentiation. Cryobiology. 2020;92:92-102.
[4] DING Y, LIU S, LIU J, et al. Cryopreservation with DMSO affects the DNA integrity, apoptosis, cell cycle and function of human bone mesenchymal stem cells. Cryobiology. 2024;114:104847.
[5] 赵刚,周学迅,高大勇.细胞低温保存原理与进展[J].中国科学:生命科学,2024,54(6):1109-1128.
[6] SUGISHITA Y, MENG L, SUZUKI-TAKAHASHI Y, et al. Quantification of residual cryoprotectants and cytotoxicity in thawed bovine ovarian tissues after slow freezing or vitrification. Hum Reprod. 2022;37(3):522-533.
[7] BAHSOUN S, COOPMAN K, AKAM EC. The impact of cryopreservation on bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a systematic review. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):397.
[8] 刘代艳,于泊洋,孔群芳,等.海藻酸微囊替代DMSO和FBS的STO细胞冷冻保存研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2012,12(33):6413-6418.
[9] MANTRI S, KANUNGO S, MOHAPATRA PC. Cryoprotective Effect of Disaccharides on Cord Blood Stem Cells with Minimal Use of DMSO. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2015;31(2):206-212.
[10] CROWLEY CA, SMITH WPW, SEAH KTM, et al. Cryopreservation of Human Adipose Tissues and Adipose-Derived Stem Cells with DMSO and/or Trehalose: A Systematic Review. Cells. 2021;10(7):1837.
[11] FUJITA Y, NISHIMURA M, KOMORI N, et al. Protein-free solution containing trehalose and dextran 40 for cryopreservation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Cryobiology. 2021;100:46-57.
[12] 张鹏,刘宝林.人脐带间充质干细胞新型冻存液实验研究[J/OL].制冷学报,1-10[2024-07-05].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2182.tb.20240524.1119.002.html.
[13] HALME DG, KESSLER DA. FDA regulation of stem-cell-based therapies. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(16):1730-1735.
[14] BARRO L, BURNOUF PA, CHOU ML, et al. Human platelet lysates for human cell propagation. Platelets. 2021;32(2):152-162.
[15] CHEN MS, WANG TJ, LIN HC, et al. Four types of human platelet lysate, including one virally inactivated by solvent-detergent, can be used to propagate Wharton jelly mesenchymal stromal cells. N Biotechnol. 2019; 49:151-160.
[16] LEE S, JOO Y, LEE EJ, et al. Successful expansion and cryopreservation of human natural killer cell line NK-92 for clinical manufacturing. PLoS One. 2024;19(2):e0294857.
[17] GAO L, ZHOU Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Dimethyl Sulfoxide-Free Cryopreservation of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Based on Zwitterionic Betaine and Electroporation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(14):7445.
[18] 吕玲,邢义高,张秀涛,等.通用型细胞冻存保护液的探索[J].中国医药生物技术,2022,17(4):347-349.
[19] 姬广超,王晓明,王玉琪,等.临床用途细胞冻存保护液探索实验[J].中国医药生物技术,2021,16(2):158-160.
[20] MARQUEZ-CURTIS LA, ELLIOTT JAW. Mesenchymal stromal cells derived from various tissues: Biological, clinical and cryopreservation aspects: Update from 2015 review. Cryobiology. 2024;115:104856.
[21] AL-SAQI SH, SALIEM M, QUEZADA HC, et al. Defined serum- and xeno-free cryopreservation of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2015; 16(2):181-193.
[22] HUANG Z, LIU W, MA T, et al. Slow Cooling and Controlled Ice Nucleation Enabling the Cryopreservation of Human T Lymphocytes with Low-Concentration Extracellular Trehalose. Biopreserv Biobank. 2023;21(4): 417-426.
[23] WANG J, SHI X, XIONG M, et al. Trehalose glycopolymers for cryopreservation of tissue-engineered constructs. Cryobiology. 2022;104:47-55.
[24] NTAI A, LA SPADA A, DE BLASIO P, et al. Trehalose to cryopreserve human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2018;31:102-112.
[25] AL-SAQI SH, SALIEM M, QUEZADA HC, et al. Correction to: Defined serum- and xeno-free cryopreservation of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2019;20(2):329-330.
[26] 马洁,刘彩霞,谭琴,等.细胞产品质量控制与质量管理[J].药物评价研究,2021,44(2):273-292.
[27] 窦蒙家,张明宽,饶伟,等.人体低温保存:通向未来“永生”之路?[J].科学,2017,69(6):1-4+69.
[28] 刘威,郭明伟,郭治宇,等.胞内冰形成机理研究进展[J].制冷学报, 2018,39(3):126-134.
[29] 邱佳裔,贾晓青,黄岗,等.细胞、组织冻存方法及应用的研究进展[J].中国生物制品学志,2017,30(5):546-550.
[30] ARUTYUNYAN I, FATKHUDINOV T, SUKHIKH G. Umbilical cord tissue cryopreservation: a short review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):236.
[31] PAVÓN A, BELOQUI I, SALCEDO JM, et al. Cryobanking Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1590:191-196.
[32] AWAN M, BURIAK I, FLECK R, et al. Dimethyl sulfoxide: a central player since the dawn of cryobiology, is efficacy balanced by toxicity? Regen Med. 2020;15(3):1463-1491.
[33] DAS S, NIEMEYER E, LEUNG ZA, et al. Human Natural Killer Cells Cryopreserved without DMSO Sustain Robust Effector Responses. Mol Pharm. 2024;21(2):651-660.
[34] HEISKANEN A, SATOMAA T, TIITINEN S, et al. N-glycolylneuraminic acid xenoantigen contamination of human embryonic and mesenchymal stem cells is substantially reversible. Stem Cells. 2007;25(1):197-202.
[35] JURKUNAS UV, YIN J, JOHNS LK, et al. Cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell (CALEC) transplantation: Development of manufacturing process and clinical evaluation of feasibility and safety. Sci Adv. 2023;9(33):eadg6470.
[36] HU Y, LIU X, LIU F, et al. Trehalose in Biomedical Cryopreservation-Properties, Mechanisms, Delivery Methods, Applications, Benefits, and Problems. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(3):1190-1204.
[37] 刘宝林,赵子威.红细胞低温保存中海藻糖的加载方法[J].上海理工大学学报,2022,44(1):11-17.
[38] WHALEY D, DAMYAR K, WITEK RP, et al. Cryopreservation: An Overview of Principles and Cell-Specific Considerations. Cell Transplant. 2021;30: 963689721999617.
[39] WILL RG, IRONSIDE JW, ZEIDLER M, et al. A new variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the UK. Lancet. 1996;347(9006):921-925.
[40] PEDEN AH, SULEIMAN S, BARRIA MA. Understanding Intra-Species and Inter-Species Prion Conversion and Zoonotic Potential Using Protein Misfolding Cyclic Amplification. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:716452.
[41] WENG L. Cell Therapy Drug Product Development: Technical Considerations and Challenges. J Pharm Sci. 2023;112(10):2615-2620.
[42] LIANG X, HU X, HU Y, et al. Recovery and functionality of cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells using five different xeno-free cryoprotective solutions. Cryobiology. 2019;86:25-32.
[43] MARESCHI K, ADAMINI A, CASTIGLIA S, et al. Cytokine-Induced Killer (CIK) Cells, In Vitro Expanded under Good Manufacturing Process (GMP) Conditions, Remain Stable over Time after Cryopreservation. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020;13(5):93.
[44] XU R, SHI X, HUANG H, et al. Development of a Me2SO-free cryopreservation medium and its long-term cryoprotection on the CAR-NK cells. Cryobiology. 2024;114:104835.
[45] YAMATOYA K, NAGAI Y, TERAMOTO N, et al. Dimethyl Sulfoxide-Free Cryopreservation of Differentiated Human Neuronal Cells. Biopreserv Biobank. 2023;21(6):631-634. |