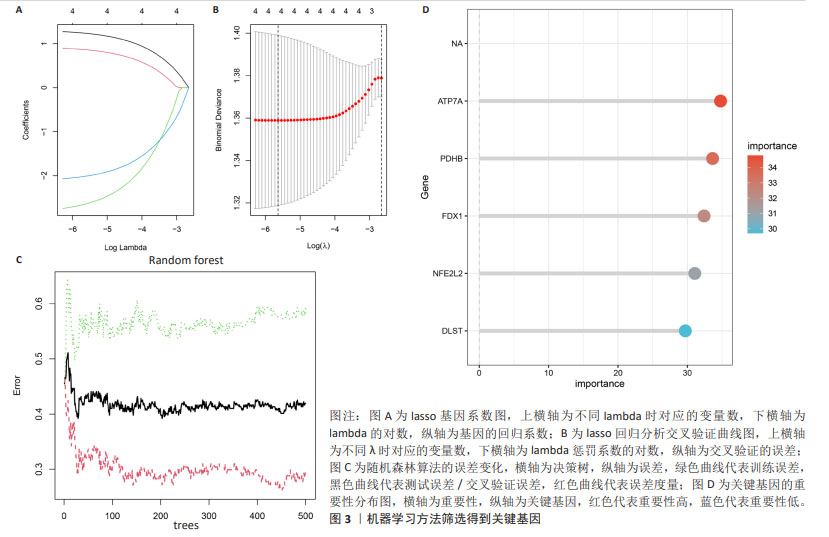
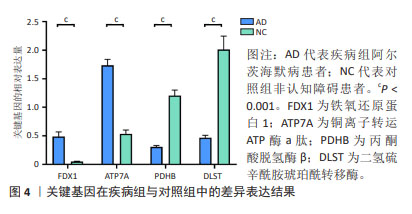
[1] MATTHEWS KA, XU W, GAGLIOTI AH, et al. Racial and ethnic estimates of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias in the United States (2015-2060) in adults aged ≥65 years. Alzheimers Dement. 2019;15(1):17-24.
[2] BENILOVA I, KARRAN E, DE STROOPER B. The toxic Aβ oligomer and Alzheimer’s disease: an emperor in need of clothes. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15(3):349-57.
[3] LU Y, LI K, HU Y, et al. Expression of immune related genes and possible regulatory mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Immunol. 2021;12:768966.
[4] LIU Z, LI H, PAN S. Discovery and validation of key biomarkers based on immune infiltrates in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Genet. 2021;12:658323.
[5] ZHANG Y, FUNG ITH, SANKAR P, et al. Depletion of NK cells improves cognitive function in the Alzheimer disease mouse model. J Immunol. 2020;205(2):502-510.
[6] JEVTIC S, SENGAR AS, SALTER MW, et al. The role of the immune system in Alzheimer disease: etiology and treatment. Ageing Res Rev. 2017;40:84-94.
[7] WYATT-JOHNSON SK, BRUTKIEWICZ RR. The complexity of microglial interactions with innate and adaptive immune cells in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020;12:592359.
[8] MOYNIER F, CREECH J, DALLAS J, et al. Serum and brain natural copper stable isotopes in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):11894.
[9] SQUITTI R, VENTRIGLIA M, SIMONELLI I, et al. Copper imbalance in Alzheimer’s disease: meta-analysis of serum, plasma, and brain specimens, and replication study evaluating ATP7B gene variants. Biomolecules. 2021;11(7):960.
[10] TSVETKOV P, COY S, PETROVA B, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 2022;375(6586):1254-1261.
[11] TANG D, CHEN X, KROEMER G. Cuproptosis: a copper-triggered modality of mitochondrial cell death. Cell Res. 2022; 32(5):417-418.
[12] CHEN L, MIN J, WANG F. Copper homeostasis and cuproptosis in health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):378.
[13] NOBILI A, LATAGLIATA EC, VISCOMI MT, et al. Dopamine neuronal loss contributes to memory and reward dysfunction in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Commun. 2017; 8:14727.
[14] PISOSCHI AM, POP A, IORDACHE F, et al. Oxidative stress mitigation by antioxidants – an overview on their chemistry and influences on health status. Eur J Med Chem. 2021;209:112891.
[15] KALITA J, KUMAR V, MISRA UK, et al. Memory and learning dysfunction following copper toxicity: biochemical and immunohistochemical basis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018;55:3800-3811.
[16] LI X, CHEN X, GAO X. Copper and cuproptosis: new therapeutic approaches for Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023;15:1300405.
[17] LAI Y, LIN C, LIN X, et al. Identification and immunological characterization of cuproptosis-related molecular clusters in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:932676.
[18] ZHANG E, DAI F, CHEN T, et al. Diagnostic models and predictive drugs associated with cuproptosis hub genes in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurol. 2023;13:1064639.
[19] ZOU Q, MROZEK D, MA Q, et al. Scalable data mining algorithms in computational biology and biomedicine. BioMed Res. Int. 2017;2017:5652041.
[20] KOCH I, ANDRADE-NAVARRO M, SCHULZ MH, et al. Bioinformatics in theory and application - highlights of the 36th german conference on bioinformatics. J Biol Chem. 2021;402(8):869-870.
[21] MCKHANN GM, KNOPMAN DS, CHERTKOW H, et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the national institute on aging-Alzheimer’s association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7(3):263-269.
[22] RITCHIE ME, PHIPSON B, WU D, et al. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(7):e47.
[23] ENGEBRETSEN S, BOHLIN J. Statistical predictions with glmnet. Clin Epigenetics. 2019;11(1):123.
[24] YILDIZ GULHAN P, EROZ R, ATAOGLU O, et al. The evaluation of both the expression and serum protein levels of Caspase-3 gene in patients with different degrees of SARS-CoV2 infection. J Med Virol. 2022;94(3):897-905.
[25] LAM B, MASELLIS M, FREEDMAN M, et al. Clinical, imaging, and pathological heterogeneity of the Alzheimer’s disease syndrome. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2013; 5(1):1.
[26] BYUN MS, KIM SE, PARK J, et al. Heterogeneity of regional brain atrophy patterns associated with distinct progression rates in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0142756.
[27] 郭佳旗,魏颖鸿,张慧,等.阿尔茨海默病发病机制及基于神经递质治疗的研究进展[J].医学综述,2021,27(19):3761-3766.
[28] FENG D, ZHAO Y, LI W, et al. Copper neurotoxicity: induction of cognitive dysfunction: a review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(48):e36375.
[29] GRINBERG AV, HANNEMANN F, SCHIFFLER B, et al. Adrenodoxin: structure, stability, and electron transfer properties. Proteins. 2000;40(4):590-612.
[30] ZHANG Z, MA Y, GUO X,et al. FDX1 can impact the prognosis and mediate the metabolism of lung adenocarcinoma. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:749134.
[31] ZHANG J,KONG X,ZHANG Y,et al. FDXR regulates TP73 tumor suppressor via IRP2 to modulate aging and tumor suppression. J Pathol. 2020;251(3):284-296.
[32] ZHANG Y, ZHOU Q, LU L, et al. Copper induces cognitive impairment in mice via modulation of cuproptosis and CREB signaling. Nutrients. 2023;15(4):972.
[33] CHEN G, ZHANG J, TENG W, et al. FDX1 inhibits thyroid cancer malignant progression by inducing cuprotosis. Heliyon. 2023;9(8):e18655.
[34] PETRIS MJ, MERCER JF, CULVENOR JG, et al. Ligand-regulated transport of the Menkes copper P-type ATPase efflux pump from the Golgi apparatus to the plasma membrane: a novel mechanism of regulated trafficking. EMBO J. 1996; 15(22):6084-6095.
[35] YAMAGUCHI Y, HEINY ME, SUZUKI M, et al. Biochemical characterization and intracellular localization of the Menkes disease protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93(24):14030-14035.
[36] ZHENG Z, WHITE C, LEE J, et al. Altered microglial copper homeostasis in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 2010;114(6):1630-1638.
[37] CHEN L, HUANG D, ZHENG G, et al. Lead exposure aggravates Aβ1-42-induced microglial activation and copper ion accumulation in microglial cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023;43(10): 1752-1760.
[38] KEßLER M, BERGER IM, JUST S, et al. Loss of dihydrolipoyl succinyltransferase (DLST) leads to reduced resting heart rate in the zebrafish. Basic Res Cardiol. 2015;110(2):14.
[39] KANAMSORI T, NISHIMAKI K, AOH S, et al. Truncated product of the bifunctional DLST gene involved in biogenesis of the respiratory chain. EMBO J. 2003;22(12): 2913-2923.
[40] SCHULZ JB, LINDENAU J, SEYFRIED J, et al. Glutathione, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Eur J Biochem. 2000; 267(16):4904-4911.
[41] CHEN W, ZHOU X, DUAN Y, et al. Association of OGG1 and DLST promoter methylation with Alzheimer’s disease in Xinjiang population. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(4):3135-3142.
[42] SOLMONSON A, DEBERARDINIS RJ. Lipoic acid metabolism and mitochondrial redox regulation. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(20): 7522-7530.
[43] WANG H, YANG Z, HE X, et al. Cuproptosis related gene PDHB is identified as a biomarker inversely associated with the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2023;23(1):804.
[44] JIA D, WANG F, YU H. Systemic alterations of tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1206688.
[45] KOMAI M, NODA Y, IKEDA A, et al. Nuclear SphK2/S1P signaling is a key regulator of ApoE production and Aβ uptake in astrocytes. J Lipid Res. 2024;25:100510.
[46] STRITTMATTER WJ, SAUNDERS AM, SCHMECHEL D, et al. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90(5):1977-1981.
[47] LIU Y, TAN Y, ZHANG Z, et al. The interaction between ageing and Alzheimer’s disease: insights from the hallmarks of ageing. Transl Neurodegener. 2024;13(1):7.
[48] OVEISGHARAN S, ARVANITAKIS Z, YU L, et al. Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease and common neuropathologies of aging. Acta Neuropathol. 2018;136(6):887-900.
[49] BIECHELE G, RAUCHMANN BS, JANOWITZ D,et al. Associations between sex, body mass index and the individual microglial response in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2024;21(1):30.
[50] KAMSTRUP PR. Lipoprotein(a) and cardiovascular disease. Clin Chem. 2021; 67(1):154-166.
[51] LARSSON SC, GILL D, MASON AM, et al. Lipoprotein(a) in Alzheimer, atherosclerotic, cerebrovascular, thrombotic, and valvular disease: mendelian randomization investigation. Circulation. 2020;141(22):1826-1828.
[52] GONG J, HARRIS K, PETERS SAE, et al. Serum lipid traits and the risk of dementia: a cohort study of 254,575 women and 214,891 men in the UK Biobank. EClinicalMedicine. 2022;54:101695. |