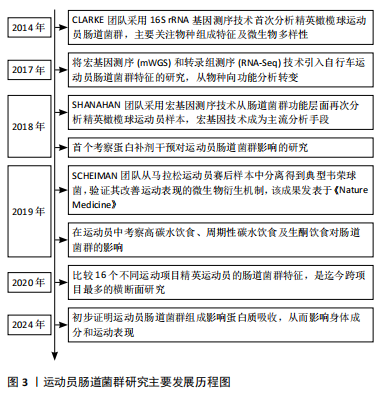
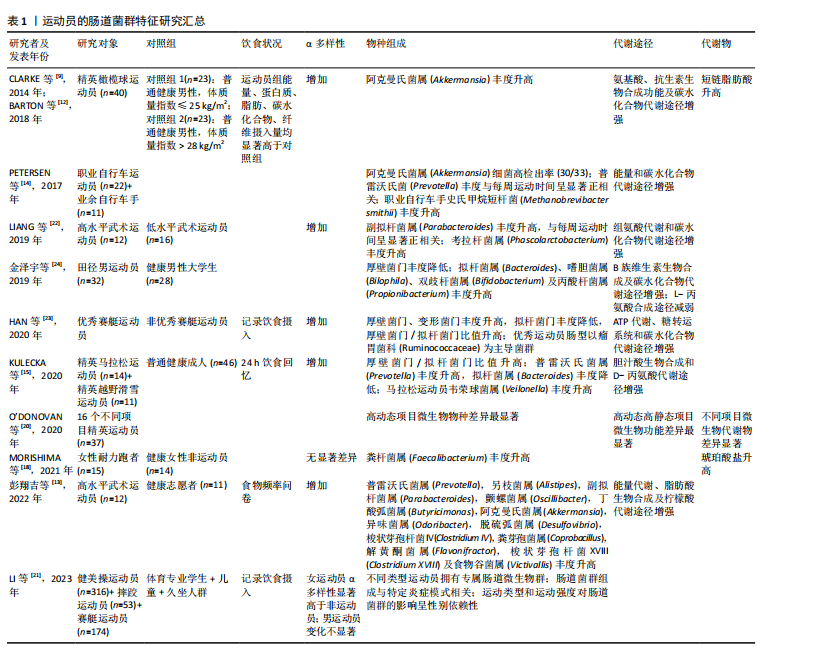
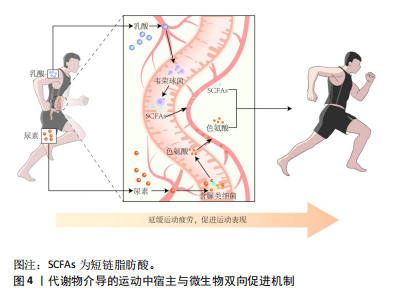
[1] O’BRIEN MT, O’SULLIVAN O, CLAESSON MJ, et al. The Athlete Gut Microbiome and its Relevance to Health and Performance: A Review. Sports Med. 2022;52(Suppl 1):119-128.
[2] CLAUSS M, GERARD P, MOSCA A, et al. Interplay Between Exercise and Gut Microbiome in the Context of Human Health and Performance. Front Nutr. 2021;8:637010.
[3] WEGIERSKA AE, CHARITOS IA, TOPI S, et al. The Connection Between Physical Exercise and Gut Microbiota: Implications for Competitive Sports Athletes. Sports Med. 2022;52(10):2355-2369.
[4] BONOMINI-GNUTZMANN R, PLAZA-DIAZ J, JORQUERA-AGUILERA C, et al. Effect of Intensity and Duration of Exercise on Gut Microbiota in Humans: A Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022; 19(15):9518.
[5] CHEN Y, ZHOU J, WANG L. Role and Mechanism of Gut Microbiota in Human Disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:625913.
[6] HUGHES RL, HOLSCHER HD. Fueling Gut Microbes: A Review of the Interaction between Diet, Exercise, and the Gut Microbiota in Athletes. Adv Nutr. 2021;12(6):2190-2215.
[7] BONOMINI-GNUTZMANN R, PLAZA-DIAZ J, JORQUERA-AGUILERA C, et al. Effect of Intensity and Duration of Exercise on Gut Microbiota in Humans: A Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022; 19(15):9518.
[8] MANKOWSKA K, MARCHELEK-MYSLIWIEC M, KOCHAN P, et al. Microbiota in sports. Arch Microbiol. 2022;204(8):485.
[9] CLARKE SF, MURPHY EF, O’SULLIVAN O, et al. Exercise and associated dietary extremes impact on gut microbial diversity. Gut. 2014;63(12): 1912-1920.
[10] SCHEIMAN J, LUBER JM, CHAVKIN TA, et al. Meta-omics analysis of elite athletes identifies a performance-enhancing microbe that functions via lactate metabolism. Nat Med. 2019;25(7):1104-1109.
[11] EVERARD A, BELZER C, GEURTS L, et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(22):9066-9071.
[12] BARTON W, PENNEY NC, CRONIN O, et al. The microbiome of professional athletes differs from that of more sedentary subjects in composition and particularly at the functional metabolic level. Gut. 2018;67(4):625-633.
[13] 彭翔吉,梁茹,谭振林,等.基于高通量测序分析高水平武术运动员肠道菌群及其代谢通路特征[J].北京体育大学学报,2022,45(3): 84-93.
[14] PETERSEN LM, BAUTISTA EJ, NGUYEN H, et al. Community characteristics of the gut microbiomes of competitive cyclists. Microbiome. 2017;5(1):98.
[15] KULECKA M, FRACZEK B, MIKULA M, et al. The composition and richness of the gut microbiota differentiate the top Polish endurance athletes from sedentary controls. Gut Microbes. 2020;11(5):1374-1384.
[16] DURK RP, CASTILLO E, MARQUEZ-MAGANA L, et al. Gut Microbiota Composition Is Related to Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Healthy Young Adults. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2019;29(3):249-253.
[17] KASPEREK MC, MAILING L, PICCOLO BD, et al. Exercise training modifies xenometabolites in gut and circulation of lean and obese adults. Physiol Rep. 2023;11(6):e15638.
[18] MORISHIMA S, AOI W, KAWAMURA A, et al. Intensive, prolonged exercise seemingly causes gut dysbiosis in female endurance runners. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2021;68(3):253-258.
[19] FERNANDEZ-VELEDO S, VENDRELL J. Gut microbiota-derived succinate: Friend or foe in human metabolic diseases. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2019;20(4):439-447.
[20] O’DONOVAN CM, MADIGAN SM, GARCIA-PEREZ I, et al. Distinct microbiome composition and metabolome exists across subgroups of elite Irish athletes. J Sci Med Sport. 2020;23(1):63-68.
[21] LI Y, CHENG M, ZHA Y, et al. Gut microbiota and inflammation patterns for specialized athletes: a multi-cohort study across different types of sports. mSystems. 2023;8(4):e0025923.
[22] LIANG R, ZHANG S, PENG X, et al. Characteristics of the gut microbiota in professional martial arts athletes: A comparison between different competition levels. PLoS One. 2019;14(12):e0226240.
[23] HAN M, YANG K, YANG P, et al. Stratification of athletes’ gut microbiota: the multifaceted hubs associated with dietary factors, physical characteristics and performance. Gut Microbes. 2020;12(1):1-18.
[24] 金泽宇,李威,孙宝林.宏基因组测序分析男性运动员肠道菌群物种组成及代谢通路特点[J].生物学杂志,2019,36(4):7-13.
[25] ZHAO X, ZHANG Z, HU B, et al. Response of Gut Microbiota to Metabolite Changes Induced by Endurance Exercise. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:765.
[26] GROSICKI G, DURK RP, BAGLEY JR. Rapid gut microbiome changes in a world-class ultramarathon runner. Physiol Rep. 2019;7(24):e14313.
[27] TABONE M, BRESSA C, GARCIA-MERINO JA, et al. The effect of acute moderate-intensity exercise on the serum and fecal metabolomes and the gut microbiota of cross-country endurance athletes. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):3558.
[28] SATO M, SUZUKI Y. Alterations in intestinal microbiota in ultramarathon runners. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):6984.
[29] 潘凤伟,张磊,张晨虹,等.不同运动强度对女游泳运动员肠道菌群的影响[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2019,38(5):1837-1846.
[30] AKAZAWA N, NAKAMURA M, EDA N, et al. Gut microbiota alternation with training periodization and physical fitness in Japanese elite athletes. Front Sports Act Living. 2023;5:1219345.
[31] KEOHANE DM, WOODS T, O’CONNOR P, et al. Four men in a boat: Ultra-endurance exercise alters the gut microbiome. J Sci Med Sport. 2019;22(9):1059-1064.
[32] CRAVEN J, COX AJ, BELLINGER P, et al. The influence of exercise training volume alterations on the gut microbiome in highly-trained middle-distance runners. Eur J Sport Sci. 2022;22(8):1222-1230.
[33] NEGLIA A. Nutrition, Eating Disorders, and Behavior in Athletes. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2021;44(3):431-441.
[34] MOORE DR, SYGO J, MORTON JP. Fuelling the female athlete: Carbohydrate and protein recommendations. Eur J Sport Sci. 2022; 22(5):684-696.
[35] PODLOGAR T, WALLIS GA. New Horizons in Carbohydrate Research and Application for Endurance Athletes. Sports Med. 2022;52(Suppl 1):5-23.
[36] WASTYK HC, FRAGIADAKIS GK, PERELMAN D, et al. Gut-microbiota-targeted diets modulate human immune status. Cell. 2021;184(16): 4137-4153.
[37] KOPONEN KK, SALOSENSAARI A, RUUSKANEN MO, et al. Associations of healthy food choices with gut microbiota profiles. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021;114(2):605-616.
[38] GUAN Z, YU EZ, FENG Q. Soluble Dietary Fiber, One of the Most Important Nutrients for the Gut Microbiota. Molecules. 2021;26(22): 6802.
[39] HEE B, WELLS JM. Microbial Regulation of Host Physiology by Short-chain Fatty Acids. Trends Microbiol. 2021;29(8):700-712.
[40] CAREY RA, MONTAG D. Exploring the relationship between gut microbiota and exercise: short-chain fatty acids and their role in metabolism. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2021;7(2):e000930.
[41] PORTINCASA P, BONFRATE L, VACCA M, et al. Gut Microbiota and Short Chain Fatty Acids: Implications in Glucose Homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1105.
[42] IGUDESMAN D, Crandell J, CORBIN KD. The Intestinal Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Association with Advanced Metrics of Glycemia and Adiposity Among Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes and Overweight or Obesity. Curr Dev Nutr. 2022;6(10):nzac107.
[43] BARBE C, MEGO M, SABATER C, et al. Differential Effects of Western and Mediterranean-Type Diets on Gut Microbiota: A Metagenomics and Metabolomics Approach. Nutrients. 2021;13(8):2638.
[44] ZHU C, SAWREY-KUBICEK L, BEALS E, et al. Human gut microbiome composition and tryptophan metabolites were changed differently by fast food and Mediterranean diet in 4 days: a pilot study. Nutr Res. 2020;77:62-72.
[45] JANG LG, CHOI G, KIM SW, et al. The combination of sport and sport-specific diet is associated with characteristics of gut microbiota: an observational study. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2019;16(1):21.
[46] CHRISTENSEN L, VUHOLM S, ROAGER HM, et al. Prevotella Abundance Predicts Weight Loss Success in Healthy, Overweight Adults Consuming a Whole-Grain Diet Ad Libitum: A Post Hoc Analysis of a 6-Wk Randomized Controlled Trial. J Nutr. 2019;149(12):2174-2181.
[47] MA W, NGUYEN LH, SONG M, et al. Dietary fiber intake, the gut microbiome, and chronic systemic inflammation in a cohort of adult men. Genome Med. 2021;13(1):102.
[48] HECTOR AJ, PHILLIPS SM. Protein Recommendations for Weight Loss in Elite Athletes: A Focus on Body Composition and Performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2018;28(2):170-177.
[49] HSU KJ, CHIEN KY, TSAI SC, et al. Effects of Exercise Alone or in Combination with High-Protein Diet on Muscle Function, Aerobic Capacity, and Physical Function in Middle-Aged Obese Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Nutr Health Aging. 2021;25(6):727-734.
[50] BAGHERI R, KARGARFARD M, SADEGHI R, et al. Effects of 16 weeks of two different high-protein diets with either resistance or concurrent training on body composition, muscular strength and performance, and markers of liver and kidney function in resistance-trained males. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2023;20(1):2236053.
[51] CAI J, CHEN Z, WU W, et al. High animal protein diet and gut microbiota in human health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(22):6225-6237.
[52] OLIPHANT K, ALLEN-VERCOE E. Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome: major fermentation by-products and their impact on host health. Microbiome. 2019;7(1):91.
[53] MORENO-PEREZ D, BRESSA C, BAILEN M, et al. Effect of a Protein Supplement on the Gut Microbiota of Endurance Athletes: A Randomized, Controlled, Double-Blind Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2018;10(3):337.
[54] BUTTEIGER DN, HIBBERD AA, MCGRAW NJ, et al. Soy Protein Compared with Milk Protein in a Western Diet Increases Gut Microbial Diversity and Reduces Serum Lipids in Golden Syrian Hamsters. J Nutr. 2016;146(4):697-705.
[55] FRITZ P, FRITZ R, BODAY P, et al. Gut microbiome composition: link between sports performance and protein absorption. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2024;21(1):2297992.
[56] ASHTARY-LARKY D, BAGHERI R, BAVI H, et al. Ketogenic diets, physical activity and body composition: a review. Br J Nutr. 2022;127(12):1898-1920.
[57] VARGAS-MOLINA S, GOMEZ-URQUIZA JL, GARCIA-ROMERO J, et al. Effects of the Ketogenic Diet on Muscle Hypertrophy in Resistance-Trained Men and Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(19):12629.
[58] MURPHY NE, CARRIGAN CT, MARGOLIS LM. High-Fat Ketogenic Diets and Physical Performance: A Systematic Review. Adv Nutr. 2021;12(1): 223-233.
[59] MURTAZA N, BURKE LM, VLAHOVICH N, et al. The Effects of Dietary Pattern during Intensified Training on Stool Microbiota of Elite Race Walkers. Nutrients. 2019;11(2):261.
[60] WAN Y, WANG F, YUAN J, et al. Effects of dietary fat on gut microbiota and faecal metabolites, and their relationship with cardiometabolic risk factors: a 6-month randomised controlled-feeding trial. Gut. 2019; 68(8):1417-1429.
[61] COLLINS SL, STINE JG, BISANZ JE, et al. Bile acids and the gut microbiota: metabolic interactions and impacts on disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2023;21(4):236-247.
[62] PAOLI A, MANCIN L, BIANCO A, et al. Ketogenic Diet and Microbiota: Friends or Enemies. Genes (Basel). 2019;10(7):534.
[63] WOLTERS M, AHRENS J, ROMANI-PEREZ M, et al. Dietary fat, the gut microbiota, and metabolic health - A systematic review conducted within the MyNewGut project. Clin Nutr. 2019;38(6):2504-2520.
[64] FU Y, WANG Y, GAO H, et al. Associations among Dietary Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, the Gut Microbiota, and Intestinal Immunity. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:8879227.
[65] MANCIN L, AMATORI S, CAPRIO M, et al. Effect of 30 days of ketogenic Mediterranean diet with phytoextracts on athletes’ gut microbiome composition. Front Nutr. 2022;9:979651.
|