中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (31): 5063-5069.doi: 10.12307/2024.723
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
外泌体微小RNA与骨关节疾病:作用与机制
袁 平1,王志华1,王伟舟2,王文通1,何 飞3
- 昆明医科大学第一附属医院,1创伤中心,2骨科,云南省昆明市 650032;3昆明医科大学附属曲靖医院骨科,云南省曲靖市 655099
-
收稿日期:2023-09-06接受日期:2023-11-01出版日期:2024-11-08发布日期:2024-01-23 -
通讯作者:何飞,博士,主任医师,昆明医科大学附属曲靖医院骨科,云南省曲靖市 655099 -
作者简介:袁平,男,1997年生,云南省曲靖市人,汉族,在读硕士,主要从事脊柱侧弯、外泌体miRNA及生物材料(水凝胶)相关的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金地区科学基金项目(82160417),项目负责人:何飞;云南省应用基础研究(昆医联合专项重点项目)(202101AY070001-013),项目负责人:何飞;云岭产业技术领军人才(YLXL20170046),项目负责人:何飞
Exosome-derived microRNA with bone and joint diseases: role and mechanism
Yuan Ping1, Wang Zhihua1, Wang Weizhou2, Wang Wentong1, He Fei3
- 1Trauma Center, 2Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Qujing Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Qujing 655099, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2023-09-06Accepted:2023-11-01Online:2024-11-08Published:2024-01-23 -
Contact:He Fei, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Qujing Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Qujing 655099, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Yuan Ping, Master candidate, Trauma Center, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (Regional Project), No. 82160417 (to HF); Applied Basic Research in Yunnan Province (Key Project of Kunming Medical University Joint Project), No. 202101AY070001-013 (to HF); Cloud-Ridge Industry Technology Leader Grant, No. YLXL20170046 (to HF)
摘要:
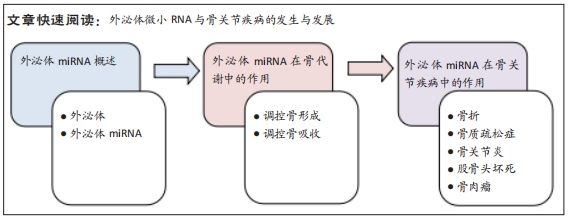
文题释义:
外泌体微小RNA:是一种由约22个核苷酸组成的单链非编码RNA,可以在外泌体的运输作用下转移至近端或者远端的靶细胞,与靶细胞内mRNA相互作用来调节转录后基因的表达,进而调控靶细胞的生物活动,发挥细胞间信息传递的作用。骨关节疾病:为骨骼或关节发生的原发性和继发性疾病,又分为局部疾病和全身疾病。局部疾病如关节退变、骨折、各关节疾病以及骨肿瘤等,全身性疾病如骨质疏松、风湿性关节炎等一些骨代谢性疾病。
背景:外泌体是一种细胞以胞吐形式分泌到胞外的囊泡状结构,其中包含了大量的微小RNA,具有重要的细胞间通讯作用。外泌体中的微小RNA依靠外泌体运输,能够进入靶细胞发挥重要的生物学调控效应。在常见的骨关节疾病中,由于骨骼代谢异常或受损会释放大量的外泌体,其中一些外泌体微小RNA促进骨关节疾病的进展。因此,外泌体微小RNA与骨骼系统关系密切,对许多骨关节疾病的发生发展以及诊疗都具有重要意义。
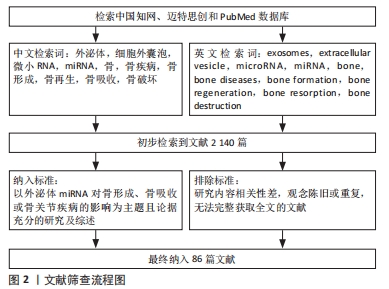
目的:综述外泌体微小RNA在骨代谢和骨关节疾病中的研究进展。方法:以“外泌体,细胞外囊泡,微小RNA,miRNA,骨,骨疾病,骨形成,骨再生,骨吸收,骨破坏”为中文检索词,“exosomes,extracellular vesicle,microRNA,miRNA,bone,bone diseases,bone formation,bone regeneration,bone resorption,bone destruction”为英文检索词,在中国知网、迈特思创和PubMed数据库进行检索,最终纳入86篇文献进行归纳总结。
结果与结论:外泌体中的微小RNA可以通过影响骨形成和骨吸收调控骨代谢,并且与骨折愈合、骨质疏松症、骨关节炎、类风湿性关节炎、股骨头坏死和骨肉瘤等骨关节疾病的发生发展关系密切,外泌体微小RNA将是未来诊治某些骨关节疾病的有效手段。但目前关于外泌体微小RNA在骨关节疾病中的研究有限,想要利用外泌体微小RNA诊断治疗骨关节疾病仍然需要更多的探索和研究。
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-8148-9918 (袁平)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
袁 平, 王志华, 王伟舟, 王文通, 何 飞. 外泌体微小RNA与骨关节疾病:作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(31): 5063-5069.
Yuan Ping, Wang Zhihua, Wang Weizhou, Wang Wentong, He Fei. Exosome-derived microRNA with bone and joint diseases: role and mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 5063-5069.
外泌体分布广泛,可调节靶细胞蛋白表达发挥细胞间通讯作用[13];同时外泌体表面不表达组织免疫相容性复合物[14],使其在疾病诊疗方面具有巨大潜力。
外泌体miRNA是指外泌体中所包含的miRNA,其组成和宿主细胞内的miRNA存在不同[15-16],并且因细胞来源而异[17-18]。目前出现这种差异的机制尚不清楚。但有学者提出了以下5条可能的理论:①鞘氨醇酶2依赖性途径。KOSAKA等[19]证明鞘磷脂酶2促进了细胞外miRNA的分泌。②miRNA基序依赖性途径。miRNA中的特定序列决定了它们是在细胞外囊中分泌还是保留在细胞中。其中作用最强的碱基序列CGGGAG通过与RNA结合蛋白Alyref和Fus结合驱动miRNA进入外泌体[20]。③miRNA依赖途径的3′端修饰。KOPPERS-LALIC等[21]发现3′端poly(U)的miRNA在外泌体中相对较多。④内源性RNA介导的途径。细胞中miRNA靶点水平的变化可以促进miRNA从细胞质向外泌体转运而将miRNA分拣至外泌体内[22]。⑤miRNA诱导的沉默复合物相关途径。GUDURIC-FUCHS等[23]和FRANK等[24]发现,HEK293T细胞中Argonaute2基因敲除会导致外泌体miRNA释放减少,并且人类Argonaute2蛋白倾向于与miRNA 5′端的U或A结合,在miRNA分拣进入外泌体的过程中发挥了重要作用。这5个理论相互独立互不干扰。因此,研究外泌体miRNA在骨关节疾病中的作用具有独特意义,也成为了近年来的研究热点。
2.2 外泌体miRNA在骨代谢中的作用 骨稳态主要由破骨细胞介导的骨吸收和成骨细胞介导的骨形成之间的平衡关系所决定的。破骨细胞起源于局部招募的单核细胞,在成骨细胞衍生的受体激活剂核因子κB配体的刺激下,分解旧的骨组织;成骨细胞起源于骨髓间充质干细胞,由前成骨细胞分化成熟而来,前成骨细胞具有机械传感特性,成熟的成骨细胞可合成新的矿化细胞外基质。生理条件下,破骨细胞的活动与成骨细胞的活动保持着动态的平衡,当其中某一方功能亢进或抑制就会导致骨吸收和骨形成失衡,进而导致一系列骨关节疾病[25-26]。近年来研究发现,外泌体miRNA介导的细胞间通讯能够调节骨形成和吸收过程,其大致过程如图4。深入研究外泌体miRNA对骨代谢的影响对了解骨关节疾病发生机制具有重要意义。

2.2.1 外泌体miRNA调控骨形成过程 外泌体miRNA可以通过调控成骨分化过程或者软骨细胞的增殖分化,在骨形成过程中发挥正向和负向的双重调控作用。在细胞层面骨形成主要有2种途径:一种是由骨髓间充质干细胞介导的成骨分化途径,即骨髓间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞,成骨细胞进一步分化为骨细胞;另一种则是软骨细胞介导软骨内成骨。研究表明,各种细胞来源的外泌体miRNA可以促进成骨分化,如M2巨噬细胞来源外泌体中含有的miR-26a-5p可以促进碱性磷酸酶、Runt相关转录因子2、骨桥蛋白和Ⅱ型胶原的表达,促进成骨分化[27]。M2巨噬细胞衍生的外泌体中miR-5106可以通过直接靶向盐诱导激酶2和3基因来诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[28]。骨髓间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体miR-101可抑制WD-40域蛋白7表达调节缺氧诱导转录因子1α/叉头蛋白3信号轴,促进成骨分化[29]。源自类风湿关节炎患者关节成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞的外泌体miR-486-5p通过人ErbB2酪氨酸激酶受体转录因子1 /骨形态发生蛋白/Smad和Mad相关蛋白途径诱导成骨细胞分化[30]。
此外,成骨细胞可以分泌含有let-7的外泌体通过调节高迁移率族蛋白AT-Hook2和轴抑制蛋白2来促进骨形成[31]。外泌体miRNA也可调节软骨的代谢影响骨形成,例如:ZHOU等[32]研究发现大鼠滑膜成纤维细胞衍生的外泌体miR-126-3p可以抑制软骨细胞凋亡。滑膜细胞衍生的外泌体miR-221、人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体中的miR-23a-3p等可促进软骨细胞外基质分泌以及软骨细胞的增殖和再生[33-34]。外泌体miRNA也可抑制骨形成。后纵韧带骨化细胞来源的外泌体miR-140-5p通过靶向胰岛素样生长因子1受体抑制肾组织胰岛素受体底物1/磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/丝氨酸-苏氨酸激酶/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白途径的磷酸化来抑制成骨分化[35]。破骨细胞来源的外泌体miR-214-3p可通过靶向激活转导因子4基因的3′非翻译区抑制成骨细胞活性,减少成骨细胞外基质矿化[36]。综上所述,外泌体miRNA可通过调节成骨分化、成骨细胞活性以及软骨细胞活性来调节骨形成,这些外泌体miRNA可能是治疗骨形成障碍相关骨关节疾病的新手段。
2.2.2 外泌体miRNA调控骨吸收过程 破骨细胞主要源自髓系单核巨噬细胞,成熟破骨细胞通过分泌氢离子的方式发挥骨吸收功能,外泌体miRNA可通过调控破骨细胞的增殖和活性进而调控骨吸收。外泌体miRNA可促进破骨细胞的形成与激活,促进骨吸收,例如:前列腺癌细胞来源的外泌体miR-92a-1-5p可以靶向Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 ɑ1链基因,下调Ⅰ型胶原表达促进破骨细胞的形成并抑制成骨细胞生成,促进骨吸收[37]。骨肉瘤细胞来源的外泌体miR-501-3p可以通过张力蛋白同源基因/磷脂酰激醇-3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路促进破骨细胞分化,促进骨吸收[38]。胰腺癌细胞来源的外泌体miR-125a-5p不仅可以诱导小鼠股骨破骨细胞分化,还可通过肿瘤坏死因子受体超家族成员1B信号通路,促进破骨细胞的骨吸收作用[39]。也有研究发现,一些外泌体miRNA可以抑制破骨细胞的形成和功能,例如:成骨细胞可以释放含有miR-503-3p的外泌体,通过失活核因子κB受体活化因子及其配体的信号通路来抑制破骨细胞的形成[5];人骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体miR-186和血管内皮细胞来源的外泌体miR-155可抑制骨吸收[40-41]。总之,外泌体miRNA是破骨细胞成熟和功能的调节剂,通过进一步调控外泌体miRNA可以调节骨吸收的生理学过程。
2.3 外泌体miRNA在骨关节疾病中的作用 外泌体miRNA不仅参与调控许多骨关节疾病发生发展,也能做为生物标记物监测疾病进展[42]。近年来许多研究表明外泌体miRNA与骨折、骨质疏松症、关节炎、股骨头坏死及骨肉瘤等骨关节疾病关系密切,该文章围绕外泌体miRNA在以上骨关节疾病中的作用及机制进行总结。
2.3.1 外泌体miRNA与骨折 骨折是最常见的骨科疾病,治疗骨折首要任务便是促进骨折断端愈合。骨折愈合受到骨髓间充质干细胞活性、免疫及机械刺激等多种因素影响。研究发现,外泌体miRNA通过多种途径调控骨折愈合,各种干细胞来源的外泌体miRNA在促骨折愈合方面表现出了巨大潜力,例如:小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体miR-25可调节成骨细胞SMAD特异E3泛素蛋白连接酶1促进Runt相关转录因子2的泛素化降解,促进成骨细胞的分化、增殖和迁移[43]。低氧环境会产生缺氧诱导因子1α促进骨髓间充质干细胞分泌外泌体miR-126,通过1型芽生性相关络氨酸激酶结构域/Ras蛋白/细胞外调节蛋白激酶信号通路促进骨折愈合[44]。骨髓间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体miR-335可靶向成骨细胞膜蛋白相关蛋白B激活Wnt /β-联蛋白途径促进成骨分化,促骨折愈合[45]。外泌体miRNA也可以通过免疫调节促骨折愈合。脂肪干细胞外泌体miR-451a可下调巨噬细胞游走抑制因子的表达,促进巨噬细胞向M2巨噬细胞极化,从而促进骨愈合[46]。M2巨噬细胞可分泌外泌体miR-5106直接靶向盐诱导激酶2和3基因诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,促进骨折愈合[28]。此外,也有研究者发现应力刺激可下调骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体miR-214-3p,从而促进局部血管生成和骨折愈合,但具体机制尚不清楚[47]。除了上述外泌体miRNA,也有研究发现一些可以抑制骨折愈合的外泌体miRNA,如:大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体中富含miR-128-3p可抑制转导蛋白5表达,从而抑制骨折愈合[48]。糖尿病患者骨髓源巨噬细胞衍生的外泌体miR-144-5p可以通过靶向Smad同源物1转移到骨髓间充质干细胞中调节骨再生,抑制骨折愈合[49]。总之,不同细胞来源的外泌体miRNA作用于不同的靶基因影响骨折愈合,它们既可以促进骨折愈合也可以抑制骨折愈合,见表1。因此,选择性干预外泌体miRNA活性可以更大化骨折愈合效率,有望成为未来治疗骨折延迟愈合或不愈合的有效手段。
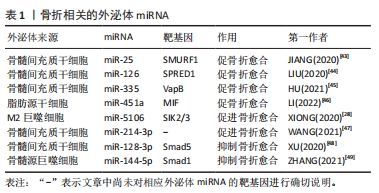
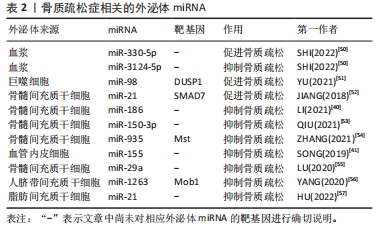
2.3.2 外泌体miRNA与骨质疏松症 骨质疏松症是一种因骨代谢失衡导致骨量减少的全身性骨骼疾病,无论是骨形成抑制还是骨吸收亢进均会导致骨质疏松。近年来研究发现各种外泌体miRNA可以对骨质疏松症产生影响,见表2。起初SHI等[50]在绝经后骨质疏松症患者血浆外泌体中筛查出了特异性的miRNA,其中有5个与骨密度有关,分别是miR-324-3P、miR-766-3P、miR-1247-5P、miR-330-5P、miR-3124-5P,其中miR-330-5P可以抑制成骨,加剧骨质疏松症;而miR-3124-5P可促进成骨,治疗骨质疏松症,证明了外泌体miRNA不仅可以作为骨质疏松症的特异性分子标记物,也可以用于治疗骨质疏松,但具体机制不明。此后,越来越多的研究发现了外泌体miRNA可通过调控骨代谢影响骨质疏松,如:巨噬细胞来源的外泌体miR-98可下调双特异性磷酸酶1并激活c-Jun氨基末端激酶信号通路抑制骨形成[51]、骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体miR-21可通过靶向Smad同源物7通路抑制成骨分化[52],造成成骨细胞生成和细胞外矿化减少,骨形成能力下降,进而导致或者加剧骨质疏松。相反,一些可以增强成骨细胞增殖分化或抑制骨吸收的外泌体miRNA则可以缓解骨质疏松进程,如:人骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体miR-150-3p、miR-935 和miR-186均可增强成骨细胞增殖分化促进骨形成,其中miR-186可通过Hippo信号通路抑制骨吸收,是治疗骨质疏松的有利靶点[40,53-54];SONG等[41]发现血管内皮细胞来源外泌体miR-155也可抑制骨吸收,改善卵巢切除小鼠骨质疏松;骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体miR-29a可显著促进血管生成和成骨[55]、人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体miR-1263靶向骨髓间充质干细胞单极纺锤体-结合蛋白1抑制Hippo信号通路,有效抑制骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡[56];HU等[57]通过动物实验验证了外泌体miR-21可治疗强直性脊柱炎脊柱骨质疏松,进一步证实了利用外泌体miRNA治疗骨质疏松的可行性。虽然其中部分机制尚不清楚,但种种结果表明,外泌体miRNA既可以促进骨质疏松也可抑制骨质疏松,通过监测或干预外泌体miRNA的表达可能是未来诊断、预防和治疗骨质疏松的手段之一。
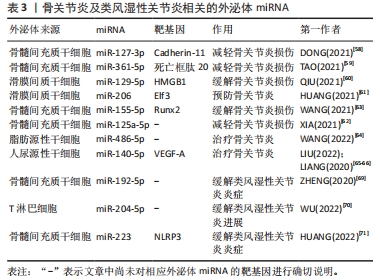
2.3.3 外泌体miRNA与关节炎 骨关节炎是最常见的关节炎,主要以关节软骨病变为主。外泌体miRNA可以通过调节炎症、软骨细胞外基质分泌和软骨细胞活动来预防或缓解骨关节炎。研究发现,人骨髓间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体miR-361-5p、miR-127-3p可通过不同机制减轻骨关节炎中的软骨细胞损伤,其中miR-361-5p通过靶向软骨细胞的DDX20抑制核因子κB信号通路改善白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞损伤;miR-127-3p则通过抑制软骨细胞的重组人钙黏附蛋白11,阻断Wnt/β-联蛋白通路,改善白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞损伤[58-59]。此外,人滑膜间质干细胞分泌的外泌体miR-129-5p和miR-155-5p也可通过不同机制影响骨关节炎,前者通过抑制高迁移率族蛋白B1的释放而抑制白细胞介素1β介导的软骨细胞凋亡,缓解骨关节炎;后者通过靶向Runt相关转录因子2促进软骨细胞外基质的分泌可预防骨关节炎[60-61]。其它的骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体miR-125a-5p和miR-326也可以缓解骨关节炎,其中miR-125a-5p通过促进骨关节炎软骨细胞迁移和减轻细胞外基质降解改善骨关节炎,miR-326则通过靶向组蛋白去乙酰化酶3激活信号转导与转录激活因子1/核因子κB p65通路抑制软骨细胞的凋亡来改善骨关节炎[62-63]。目前已有研究团队利用外泌体miRNA治疗骨关节炎取得了重大进展。WANG等[64]发现向骨关节炎大鼠关节内注射含有miR-486-5p的外泌体与直接注射miR-486-5p相比治疗效果更好。LIU等[65]发现人尿源性干细胞来源外泌体miR-140靶向血管内皮生长因子A增加了软骨细胞外基质的分泌,可以治疗大鼠骨关节炎,且与常规人尿源性干细胞外泌体相比对大鼠骨关节炎的治疗效果更好。LIANG等[66]利用软骨细胞亲和肽外泌体携带miR-140进入软骨细胞成功抑制软骨降解蛋白酶,缓解大鼠骨关节炎的进展。外泌体miRNA可以通过多种途径影响骨关节炎的进程,与单纯外泌体或miRNA相比,外泌体miRNA在治疗骨关节炎的动物实验中表现出更好的疗效,未来通过人造外泌体携带miRNA治疗骨关节炎可能是一种新的方法。
目前关于外泌体miRNA与类风湿性关节炎的研究也较多。类风湿性关节炎是一种以滑膜中免疫细胞浸润为主的自身免疫性疾病。目前类风湿性关节炎早期诊断困难,而外泌体miRNA不仅有望成为早期诊断类风湿性关节炎的特异性标记物,还可以通过各种途径缓解疾病进程。
RODRíGUEZ-MUGURUZA等[67]从类风湿性关节炎患者血清中筛查出了2个外泌体miRNA可作为类风湿性关节炎早期诊断的标志物,分别是miR-451a和miR-25-3p,其准确性高达95.6%。XU等[68]发现外泌体包裹的miR-6089也可能作为类风湿性关节炎的一个有前途的生物标志物。除了诊断,外泌体在类风湿性关节炎的治疗方面同样发挥着作用。ZHENG等[69]发现向类风湿性关节炎大鼠体内注射骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体miR-192-5p具有延缓炎症的作用;WU等[70]发现人类T淋巴细胞外泌体miR-204-5p可以介导免疫细胞和滑膜成纤维细胞间的信号交流,缓解疾病进展;HUANG等[71]发现骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体miR-223可以靶向抑制NLR家族含吡啶域3的表达,抑制炎症反应,治疗类风湿性关节炎。
综上,外泌体miRNA在骨关节炎与类风湿关节炎的诊断和治疗中具有巨大潜力,见表3。
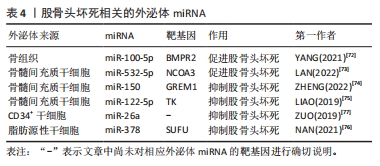
2.3.4 外泌体miRNA与股骨头坏死 股骨头坏死是由于缺血导致成骨细胞凋亡和成骨抑制进而出现股骨头骨组织死亡的疾病,依据病因可分为创伤性、非创伤性以及特发性股骨头坏死。其中特发性和非创伤性股骨头坏死病因复杂,而外泌体miRNA异常可能是导致股骨头坏死的发病因素之一,如:外泌体miR-100-5p可通过靶向骨形态发生蛋白受体2并抑制骨形成蛋白2受体/Smad同源蛋白1、Smad同源蛋白5、Smad同源蛋白9信号通路而抑制成骨和血管生成,导致股骨头坏死[72]。骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体miR-532-5p可靶向核受体辅助因子3抑制成骨,加剧股骨头坏死[73]。股骨头坏死目前尚无特效药物,主要治疗手段仍为保守和手术,骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体miRNA有望成为治疗股骨头坏死的新手段。目前研究发现,外泌体miR-150可通过介导Gremlin1/核因子κB轴抑制成骨细胞凋亡,进而减轻股骨头坏死[74];外泌体miR-122-5p通过酪氨酸激酶/Ras蛋白/间质原激活蛋白激酶信号通路下调Sprouty2促进成骨,减轻股骨头坏死[75]。此外,还有一些研究发现富含miR-378及miR-26a的外泌体可通过促血管生成和成骨来预防糖皮质激素引起的股骨头坏死,外泌体miR-26a的作用机制尚不清楚,而外泌体miR-378则是通过负向调控融合抑制因子发挥作用的[76-77]。各种外泌体miRNA对股骨头坏死的影响见表4。外泌体miRNA通过多种途径调控了股骨头坏死的发生发展,未来利用外泌体miRNA对股骨头坏死进行预防和治疗具有广泛研究前景。
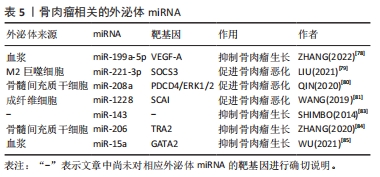
2.3.5 外泌体miRNA与骨肉瘤 骨肉瘤是青少年常见的原发恶性骨肿瘤。外泌体miRNA可以影响骨肉瘤的生长并用于骨肉瘤的诊断。ZHANG等[78]发现骨肉瘤患者血浆中有高表达miR-663a、miR-199a-5p和miR-223-3p的外泌体,并进一步研究发现这些外泌体可调节肿瘤血管生长,其中外泌体miR-199a-5p可靶向作用于血管内皮生长因子A抑制骨肉瘤及其血管的生长。此外,血清中肿瘤相关的M2巨噬细胞衍生外泌体含有miR-221-3p可作用于细胞因子信号通路抑制因子3从而激活Janus激酶2/转录激活蛋白3通路,促进骨肉瘤的进展[79]。骨髓间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体miR-208a通过靶向抑制骨肉瘤细胞程序性细胞死亡因子4和激活胞外信号调节激酶1/2途径,以及成纤维细胞外泌体miR-1228通过直接靶向骨肉瘤细胞侵袭抑制因子,促进骨肉瘤细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭[80-81]。骨肉瘤本身所分泌的外泌体miRNA也可调控肿瘤微环境[82]。这些外泌体miRNA均促进骨肉瘤的发生发展,与疾病的恶化密切相关,抑制这些外泌体miRNA的表达或阻断其通路可能是治疗骨肉瘤的新方法。
此外,一些学者还发现外泌体miRNA可抑制骨肉瘤的进展。例如:外泌体miR-143转移到骨肉瘤细胞可抑制其迁移[83]。骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体miR-206可通过靶向Transformer2基因抑制骨肉瘤生长[84]。血清外泌体miR-15a通过P53信号通路抑制GATA结合蛋白2/双微体同源基因2轴抑制骨肉瘤生长[85]。这些都可能是未来通过外泌体miRNA治疗骨肉瘤的可能靶点。此外,XU等[86]发现骨肉瘤化疗不良反应重的患者血清外泌体中miR-124、miR-133a、miR-199a-3p和miR-385水平显著降低,而miR-135b、miR-148A、miR-27a和miR-9水平显著升高,说明外泌体miRNA的差异表达与骨肉瘤的化疗不良反应相关。各种外泌体miRNA对骨肉瘤的影响见表5。外泌体miRNA对于改善骨肉瘤化疗不良反应及抑制骨肉瘤进展均有作用,但仍需进一步的临床研究去证实。
| [1] 崔爽爽,赵丽坤,马信龙,等.中国老年髋部骨折流行病学和疾病经济负担研究现状[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2020,26(3):567-570. [2] 张鹤令,景青玲,宗群川,等.人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体对大鼠骨折愈合的影响及其作用机制研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2022,32(22):63-68. [3] HAO Z, REN L, ZHANG Z, et al. A multifunctional neuromodulation platform utilizing Schwann cell-derived exosomes orchestrates bone microenvironment via immunomodulation, angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Bioact Mater. 2022;23:206-222. [4] 王岚,何明宇,张敏,等.MicroRNA调控抗病毒免疫和病毒复制[J].畜牧兽医学报,2023,54(2):463-472. [5] GAO M, GAO W, PAPADIMITRIOU JM, et al. Exosomes-the enigmatic regulators of bone homeostasis. Bone Res. 2018;6:36. [6] RAPOSO G, NIJMAN HW, STOORVOGEL W, et al. B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med. 1996;183(3):1161-1172. [7] PAROLINI I, FEDERICI C, RAGGI C, et al. Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(49):34211-34222. [8] ANTWI-BAFFOUR S, MALIBHA-PINCHBECK M, STRATTON D, et al. Plasma mEV levels in Ghanain malaria patients with low parasitaemia are higher than those of healthy controls, raising the potential for parasite markers in mEVs as diagnostic targets. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019;9(1):1697124. [9] MODANI S, TOMAR D, TANGIRALA S, et al. An updated review on exosomes: biosynthesis to clinical applications. J Drug Target. 2021;29(9):925-940. [10] SUBRA C, GRAND D, LAULAGNIER K, et al. Exosomes account for vesicle-mediated transcellular transport of activatable phospholipases and prostaglandins. J Lipid Res. 2010;51(8):2105-2120. [11] WEI Z, BATAGOV AO, SCHINELLI S, et al. Coding and noncoding landscape of extracellular RNA released by human glioma stem cells. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1): 1145. [12] YE Q, LI Z, LI Y, et al. Exosome-Derived microRNA: Implications in Melanoma Progression, Diagnosis and Treatment. Cancers (Basel). 2022;15(1):80. [13] ZHANG J, LI S, LI L, et al. Exosome and exosomal microRNA: trafficking, sorting, and function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2015;13(1):17-24. [14] HOLLIDAY LS, MCHUGH KP, ZUO J, et al. Exosomes: novel regulators of bone remodelling and potential therapeutic agents for orthodontics. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2017;20 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):95-99. [15] RATAJCZAK J, MIEKUS K, KUCIA M, et al. Embryonic stem cell-derived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia. 2006;20(5):847-856. [16] SKOG J, WÜRDINGER T, VAN RIJN S, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(12):1470-1476. [17] PALMA J, YADDANAPUDI SC, PIGATI L, et al. MicroRNAs are exported from malignant cells in customized particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(18):9125-9138. [18] WANG K, ZHANG S, WEBER J, et al. Export of microRNAs and microRNA-protective protein by mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(20):7248-7259. [19] KOSAKA N, IGUCHI H, HAGIWARA K, et al. Neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2)-dependent exosomal transfer of angiogenic microRNAs regulate cancer cell metastasis. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(15):10849-10859. [20] GARCIA-MARTIN R, WANG G, BRANDÃO BB, et al. MicroRNA sequence codes for small extracellular vesicle release and cellular retention. Nature. 2022; 601(7893):446-451. [21] KOPPERS-LALIC D, HACKENBERG M, BIJNSDORP IV, et al. Nontemplated nucleotide additions distinguish the small RNA composition in cells from exosomes. Cell Rep. 2014;8(6):1649-1658. [22] SQUADRITO ML, BAER C, BURDET F, et al. Endogenous RNAs modulate microRNA sorting to exosomes and transfer to acceptor cells. Cell Rep. 2014;8(5):1432-1446. [23] GUDURIC-FUCHS J, O’CONNOR A, CAMP B, et al. Selective extracellular vesicle-mediated export of an overlapping set of microRNAs from multiple cell types. BMC Genomics. 2012;13:357. [24] FRANK F, SONENBERG N, NAGAR B. Structural basis for 5’-nucleotide base-specific recognition of guide RNA by human AGO2. Nature. 2010;465(7299):818-822. [25] 李苗苗,罗炯,张庭然,等.骨质代谢与运动训练:骨重塑与骨细胞增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(34):5544-5549. [26] XU J, YE Z, CHEN C, et al. Abaloparatide Improves Rotator Cuff Healing Via Anabolic Effects on Bone Remodeling in a Chronic Rotator Cuff Tear Model of Rat With Osteoporosis: A Comparison With Denosumab: Response. Am J Sports Med. 2023;51(1):NP3-NP4. [27] BIN-BIN Z, DA-WA ZX, CHAO L, et al. M2 macrophagy-derived exosomal miRNA-26a-5p induces osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):137. [28] XIONG Y, CHEN L, YAN C, et al. M2 Macrophagy-derived exosomal miRNA-5106 induces bone mesenchymal stem cells towards osteoblastic fate by targeting salt-inducible kinase 2 and 3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):66. [29] LI Y, WANG J, MA Y, et al. miR-101-loaded exosomes secreted by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells requires the FBXW7/HIF1α/FOXP3 axis, facilitating osteogenic differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(6):4258-4272. [30] CHEN J , LIU M , LUO X , et al. Exosomal miRNA-486-5p derived from rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes induces osteoblast differentiation through the Tob1/BMP/Smad pathway. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(12):3430-3442. [31] WEI J, LI H, WANG S, et al. let-7 enhances osteogenesis and bone formation while repressing adipogenesis of human stromal/mesenchymal stem cells by regulating HMGA2. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(13):1452-1463. [32] ZHOU Y, MING J, LI Y, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-126-3p-overexpressing synovial fibroblasts suppress chondrocyte inflammation and cartilage degradation in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):37. [33] HU H, DONG L, BU Z, et al. miR-23a-3p-abundant small extracellular vesicles released from Gelma/nanoclay hydrogel for cartilage regeneration. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;9(1):1778883. [34] LI N, CHEN Z, FENG W, et al. Triptolide improves chondrocyte proliferation and secretion via down-regulation of miR-221 in synovial cell exosomes. Phytomedicine. 2022;107:154479. [35] TANG Y, SUN Y, ZENG J, et al. Exosomal miR-140-5p inhibits osteogenesis by targeting IGF1R and regulating the mTOR pathway in ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):452. [36] LI D, LIU J, GUO B, et al. Osteoclast-derived exosomal miR-214-3p inhibits osteoblastic bone formation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10872. [37] YU L, SUI B, FAN W, et al. Exosomes derived from osteogenic tumor activate osteoclast differentiation and concurrently inhibit osteogenesis by transferring COL1A1-targeting miRNA-92a-1-5p. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(3):e12056. [38] LIN L, WANG H, GUO W, et al. Osteosarcoma-derived exosomal miR-501-3p promotes osteoclastogenesis and aggravates bone loss. Cell Signal. 2021;82: 109935. [39] ZHOU Y, ZHU Y, DONG X, et al. Exosomes Derived from Pancreatic Cancer Cells Induce Osteoclast Differentiation Through the miR125a-5p/TNFRSF1B Pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2021;14:2727-2739. [40] LI L, ZHOU X, ZHANG JT, et al. Exosomal miR-186 derived from BMSCs promote osteogenesis through hippo signaling pathway in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):23. [41] SONG H, LI X, ZHAO Z, et al. Reversal of Osteoporotic Activity by Endothelial Cell-Secreted Bone Targeting and Biocompatible Exosomes. Nano Lett. 2019; 19(5):3040-3048. [42] 王治帮,关道宏,谢彝忠,等.结肠癌患者血清外泌体miR-320的表达及其临床意义[J].肿瘤药学,2023,13(4):461-465. [43] JIANG Y, ZHANG J, LI Z, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-25 Regulates the Ubiquitination and Degradation of Runx2 by SMURF1 to Promote Fracture Healing in Mice. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7: 577578. [44] LIU W, LI L, RONG Y, et al. Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote bone fracture healing by the transfer of miR-126. Acta Biomater. 2020;103:196-212. [45] HU H, WANG D, LI L, et al. Role of microRNA-335 carried by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles in bone fracture recovery. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(2):156. [46] LI R, LI D, WANG H, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells regulate M1/M2 macrophage phenotypic polarization to promote bone healing via miR-451a/MIF. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):149. [47] WANG X, LI X, LI J, et al. Mechanical loading stimulates bone angiogenesis through enhancing type H vessel formation and downregulating exosomal miR-214-3p from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. FASEB J. 2021;35(1):e21150. [48] XU T, LUO Y, WANG J, et al. Exosomal miRNA-128-3p from mesenchymal stem cells of aged rats regulates osteogenesis and bone fracture healing by targeting Smad5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):47. [49] ZHANG D, WU Y, LI Z, et al. MiR-144-5p, an exosomal miRNA from bone marrow-derived macrophage in type 2 diabetes, impairs bone fracture healing via targeting Smad1. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):226. [50] SHI H, JIANG X, XU C, et al. MicroRNAs in Serum Exosomes as Circulating Biomarkers for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:819056. [51] YU L, HU M, CUI X, et al. M1 macrophage-derived exosomes aggravate bone loss in postmenopausal osteoporosis via a microRNA-98/DUSP1/JNK axis. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(12):2452-2463. [52] JIANG LB, TIAN L, ZHANG CG. Bone marrow stem cells-derived exosomes extracted from osteoporosis patients inhibit osteogenesis via microRNA-21/SMAD7. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(19):6221-6229. [53] QIU M, ZHAI S, FU Q, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomal MicroRNA-150-3p Promotes Osteoblast Proliferation and Differentiation in Osteoporosis. Hum Gene Ther. 2021;32(13-14):717-729. [54] ZHANG Y, CAO X, LI P, et al. microRNA-935-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes enhance osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in osteoporotic rats. Life Sci. 2021;272:119204. [55] LU GD, CHENG P, LIU T, et al. BMSC-Derived Exosomal miR-29a Promotes Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:608521. [56] YANG BC, KUANG MJ, KANG JY, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes act via the miR-1263/Mob1/Hippo signaling pathway to prevent apoptosis in disuse osteoporosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;524(4):883-889. [57] HU L, GUAN Z, TANG C, et al. Exosomes derived from microRNA-21 overexpressed adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate spine osteoporosis in ankylosing spondylitis mice. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022;16(7):634-642. [58] DONG J, LI L, FANG X, et al. Exosome-Encapsulated microRNA-127-3p Released from Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviates Osteoarthritis Through Regulating CDH11-Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. J Pain Res. 2021; 14:297-310. [59] TAO Y, ZHOU J, WANG Z, et al. Human bone mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal miRNA-361-5p alleviates osteoarthritis by downregulating DDX20 and inactivating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Bioorg Chem. 2021;113:104978. [60] QIU M, LIU D, FU Q. MiR-129-5p shuttled by human synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes relieves IL-1β induced osteoarthritis via targeting HMGB1. Life Sci. 2021;269:118987. [61] HUANG Y, ZHANG X, ZHAN J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-206 promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in osteoarthritis by reducing Elf3. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(16):7734-7745. [62] XIA Q, WANG Q, LIN F, et al. miR-125a-5p-abundant exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells suppress chondrocyte degeneration via targeting E2F2 in traumatic osteoarthritis. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):11225-11238. [63] WANG Z, YAN K, GE G, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-155-5p-overexpressing synovial mesenchymal stem cells prevent osteoarthritis via enhancing proliferation and migration, attenuating apoptosis, and modulating extracellular matrix secretion in chondrocytes. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021;37(1):85-96. [64] WANG Y, FAN A, LU L, et al. Exosome modification to better alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress induced chondrocyte apoptosis and osteoarthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022;206:115343. [65] LIU Y, ZENG Y, SI HB, et al. Exosomes Derived From Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells Overexpressing miR-140-5p Alleviate Knee Osteoarthritis Through Downregulation of VEGFA in a Rat Model. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(4):1088-1105. [66] LIANG Y, XU X, LI X, et al. Chondrocyte-Targeted MicroRNA Delivery by Engineered Exosomes toward a Cell-Free Osteoarthritis Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(33):36938-36947. [67] RODRÍGUEZ-MUGURUZA S, ALTUNA-COY A, CASTRO-OREIRO S, et al. A Serum Biomarker Panel of exomiR-451a, exomiR-25-3p and Soluble TWEAK for Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:790880. [68] XU D, SONG M, CHAI C, et al. Exosome-encapsulated miR-6089 regulates inflammatory response via targeting TLR4. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(2):1502-1511. [69] ZHENG J, ZHU L, IOK IN I, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells-secreted exosomal microRNA-192-5p delays inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;78:105985. [70] WU LF, ZHANG Q, MO XB, et al. Identification of novel rheumatoid arthritis-associated MiRNA-204-5p from plasma exosomes. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(3): 334-345. [71] HUANG Y, LU D, MA W, et al. miR-223 in exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis via downregulation of NLRP3 expression in macrophages. Mol Immunol. 2022;143:68-76. [72] YANG W, ZHU W, YANG Y, et al. Exosomal miR-100-5p inhibits osteogenesis of hBMSCs and angiogenesis of HUVECs by suppressing the BMPR2/Smad1/5/9 signalling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):390. [73] LAN X, MA H, XIONG Y, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes mediate nuclear receptor coactivator-3 expression in osteoblasts by delivering miR-532-5p to influence osteonecrosis of the femoral head development. Cell Biol Int. 2022;46(12):2185-2197. [74] ZHENG LW, LAN CN, KONG Y, et al. Exosomal miR-150 derived from BMSCs inhibits TNF-α-mediated osteoblast apoptosis in osteonecrosis of the femoral head by GREM1/NF-κB signaling. Regen Med. 2022;17(10):739-753. [75] LIAO W, NING Y, XU HJ, et al. BMSC-derived exosomes carrying microRNA-122-5p promote proliferation of osteoblasts in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019;133(18):1955-1975. [76] NAN K, ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Exosomes from miRNA-378-modified adipose-derived stem cells prevent glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by enhancing angiogenesis and osteogenesis via targeting miR-378 negatively regulated suppressor of fused (Sufu). Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):331. [77] ZUO R, KONG L, WANG M, et al. Exosomes derived from human CD34+ stem cells transfected with miR-26a prevent glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by promoting angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):321. [78] ZHANG L, CAO H, GU G, et al. Exosomal MiR-199a-5p Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Angiogenesis by Targeting VEGFA in Osteosarcoma. Front Oncol. 2022;12:884559. [79] LIU W, LONG Q, ZHANG W, et al. miRNA-221-3p derived from M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophage exosomes aggravates the growth and metastasis of osteosarcoma through SOCS3/JAK2/STAT3 axis. Aging (Albany NY). 2021; 13(15):19760-19775. [80] QIN F, TANG H, ZHANG Y, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-208a promotes osteosarcoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(5):4734-4745. [81] WANG JW, WU XF, GU XJ, et al. Exosomal miR-1228 From Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion of Osteosarcoma by Directly Targeting SCAI. Oncol Res. 2019;27(9):979-986. [82] RAIMONDI L, DE LUCA A, GALLO A, et al. Osteosarcoma cell-derived exosomes affect tumor microenvironment by specific packaging of microRNAs. Carcinogenesis. 2020;41(5):666-677. [83] SHIMBO K, MIYAKI S, ISHITOBI H, et al. Exosome-formed synthetic microRNA-143 is transferred to osteosarcoma cells and inhibits their migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;445(2):381-387. [84] ZHANG H, WANG J, REN T, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-206 inhibits osteosarcoma progression by targeting TRA2B. Cancer Lett. 2020;490:54-65. [85] WU C, LI Z, FENG G, et al. Tumor suppressing role of serum-derived exosomal microRNA-15a in osteosarcoma cells through the GATA binding protein 2/murine double minute 2 axis and the p53 signaling pathway. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):8378-8395. [86] XU JF, WANG YP, ZHANG SJ, et al. Exosomes containing differential expression of microRNA and mRNA in osteosarcoma that can predict response to chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 2017;8(44):75968-75978. |
| [1] | 陈凯佳, 刘景云, 曹 宁, 孙建波, 周 燕, 梅建国, 任 强. 组织工程技术在股骨头坏死治疗中的应用及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [2] | 郭苏童, 冯德宏, 郭 宇, 王 凌, 丁育健, 刘 仪, 钱正瑛, 李明洋. 正常与骨质疏松髋关节模型的建立及有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1342-1346. |
| [3] | 李永杰, 付申宇, 夏 渊, 张达宽, 刘洪举. 膝骨关节炎女性伸膝肌力、步态时空参数与峰值膝关节屈曲/内收力矩关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1354-1358. |
| [4] | 齐浩东, 鲁 超, 徐韩博, 王孟飞, 郝阳泉. 糖尿病对初次全膝关节置换围术期失血量和疼痛的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [5] | 牛河钢, 杨 昆, 张晶晶, 闫怡竹, 张银顺. 新型成人后路寰椎骨折钉板复位内固定系统的设计[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1399-1402. |
| [6] | 王梦晗, 齐 涵, 张 元, 陈言智. 3种3D打印模型辅助治疗Robinson ⅡB2型锁骨骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1403-1408. |
| [7] | 杜长岭, 石 辉, 张寿涛, 孟 涛, 刘 栋, 李 健, 曹 恒, 徐 闯. 氨甲环酸不同使用方法在胫骨高位截骨过程中的安全及有效性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1409-1413. |
| [8] | 杨策凯, 蔡卓延, 陈 明, 刘 昊, 翁 汭, 崔健超, 张顺聪, 姚珍松. 绝经后女性椎旁肌退化与经皮穿刺椎体成形后再骨折的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1414-1419. |
| [9] | 盛思琪, 谢 琳, 赵翔宇, 姜怡邓, 吴 凯, 熊建团, 杨安宁, 郝银菊, 焦 运. miR-144-3p参与高蛋氨酸饮食诱导Cbs+/-小鼠的肝细胞自噬[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1289-1294. |
| [10] | 林泽玉, 徐 林. 痛风致骨破坏机制的研究与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1295-1300. |
| [11] | 章晓云, 刘 桦, 柴 源, 陈 锋, 曾 浩, 高振罡, 黄有荣. 益肾固疏方干预老年性骨质疏松症患者骨代谢标志物的变化及临床疗效[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1155-1160. |
| [12] | 黄夏荣, 胡莉芝, 孙光华, 彭昕珂, 廖 瑛, 廖 源, 刘 静, 尹林伟, 钟培瑞, 彭 婷, 周 君, 屈萌艰. 电针干预老年膝骨关节炎大鼠关节软骨及软骨下骨P53、P21的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [13] | 赵嘎日达, 任逸众, 韩长旭, 孔令跃, 贾岩波. 蒙药额尔敦-乌日勒修复骨关节炎大鼠模型的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1193-1199. |
| [14] | 代越星, 郑利钦, 吴敏辉, 李志鸿, 李少彬, 郑德声, 林梓凌. 血管数量对小血管网计算流体力学的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1206-1210. |
| [15] | 李 蕊, 张桂红, 王 涛, 樊 萍. 人参多糖干预创伤性骨关节炎模型大鼠前列腺素E2/6-酮-前列腺素F1α的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1235-1240. |
外泌体是细胞分泌的一类具有细胞间通讯作用的囊泡,其中包含了大量的微小RNA(microRNAs,miRNA)[2]。研究表明,外泌体miRNA可随外泌体运输,发挥细胞间通讯作用[3]。通过研究外泌体miRNA的功能,可以揭示疾病发生机制并提供新的诊疗方式[4]。近年来大量研究报道了外泌体miRNA在骨形成和骨吸收中的作用机制[5]。该文章就外泌体miRNA在骨关节疾病中的研究现状进行综述。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2023年1月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2019年1月至2023年1月,以及少数2019年以前的经典文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网、迈特思创和PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索途径 标题/摘要检索。
1.1.5 检索词 中文检索词:“外泌体,细胞外囊泡,微小RNA,miRNA,骨,骨疾病,骨形成,骨再生,骨吸收,骨破坏”;英文检索词:“exosomes,extracellular vesicle,microRNA,miRNA,bone,bone diseases,bone formation,bone regeneration,bone resorption,bone destruction”。
1.1.6 检索文献类型 研究原著和综述。
1.1.7 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.8 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。

1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 以外泌体miRNA对骨形成、骨吸收或骨关节疾病的影响为主题且论据充分的研究及综述。
1.2.2 排除标准 研究内容相关性差,观念陈旧或重复,无法完整获取全文的文献。
1.3 质量评估和数据获取 初步检索文献2 140篇,其中来源于PubMed数据库的文献1 116篇;来源于迈特思创数据库的文献814篇;来源于中国知网数据库的文献210篇。依据纳入排除标准,排除低质量及重复文献2 054篇,纳入高质量文献86篇,其中中文文献5篇,英文文献81篇,下载这些文献全文进行泛读或精读,见图2。
目前外泌体miRNA在骨关节疾病中的研究仍是冰山一角,在众多的骨关节疾病中,大部分研究都与骨折、骨质疏松症、骨关节炎和骨肉瘤相关,而其他还有许多骨关节疾病仍处于空白状态,并且研究的深度大多止步于细胞及动物层面,其中有部分学者对机制进行了初步探索,只有极少数研究者尝试利用外泌体miRNA治疗疾病,但仍限于动物层面。而未来想要利用外泌体miRNA诊治骨关节疾病还需克服以下困难:①批量制备外泌体miRNA:目前外泌体缺乏经济高效的提纯手段,外泌体产量很难满足临床需求,已有研究者尝试利用生物工程手段制备半人工外泌体或全人工外泌体,但仍缺乏稳定、方便、可控、通用的工程方法;②明确外泌体miRNA治疗的不良反应及是否存在伦理问题;③将细胞及动物实验转换为临床试验。相信随着外泌体miRNA研究的深入,会为更多疑难骨关节疾病的诊疗带来新转机,同时也为更多骨关节疾病的病理生理机制补充更多细节。
3.2 综述的特点、局限及意义 目前大部分综述阐述了外泌体与骨之间的关系,但外泌体内容物丰富,包括脂质、蛋白质和非编码RNA。文章主要将目光聚焦于外泌体非编码RNA中的miRNA上,主要阐述近年来研究发现的与骨关节疾病有关的外泌体miRNA及其作用机制。由于外泌体miRNA与骨关节疾病的研究是近年来才逐渐增多的,加上广义的骨关节疾病包涵太多疾病,因此该文章主要对一些近年来研究证据较多的骨关节疾病进行了综述,包括骨折愈合、骨质疏松症、骨关节炎、类风湿性关节炎、股骨头坏死和骨肉瘤。但目前的研究大多在分子层面,缺少临床研究,虽然也有少部分研究通过临床样本验证了一些外泌体miRNA可以作为疾病诊断的标志物,但仍缺乏实际临床应用研究。该综述通过总结近年来在骨关节疾病中已有的研究证据,对骨折愈合、骨质疏松症、骨关节炎、类风湿性关节炎、股骨头坏死和骨肉瘤发挥作用的外泌体miRNA及其机制进行归纳,揭示了外泌体miRNA在骨关节疾病领域的研究潜力。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
外泌体微小RNA:是一种由约22个核苷酸组成的单链非编码RNA,可以在外泌体的运输作用下转移至近端或者远端的靶细胞,与靶细胞内mRNA相互作用来调节转录后基因的表达,进而调控靶细胞的生物活动,发挥细胞间信息传递的作用。骨关节疾病:为骨骼或关节发生的原发性和继发性疾病,又分为局部疾病和全身疾病。局部疾病如关节退变、骨折、各关节疾病以及骨肿瘤等,全身性疾病如骨质疏松、风湿性关节炎等一些骨代谢性疾病。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
外泌体微小RNA作为外泌体发挥细胞间通讯功能的重要物质之一,近年来受到了广泛关注。研究发现外泌体微小RNA不仅可以作为疾病的诊断标志物,有的外泌体miRNA还可以通过调控mRNA的表达参与许多疾病的发生发展,甚至有研究者通过人工外泌体负载特定miRNA在动物实验中验证了其治疗效果。但现有研究仍停留在实验阶段,未来需要更多临床研究来证实其临床有效性。此外,骨关节疾病作为人类常见的一类疾病,在外泌体miRNA领域的研究相对较少,许多疾病仍处于研究空白的状态。因此,本综述系统总结了近年来研究发现的与骨代谢和骨关节疾病有关的外泌体miRNA及其潜在的机制通路,旨在让更多人了解外泌体miRNA在骨代谢及各种骨关节疾病中的研究现状,探索更多外泌体miRNA与骨关节疾病的关系。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||