[1] HOQUE M, SHOWVA N, AHMED M, et al. Titanium and titanium alloys in dentistry: current trends, recent developments, and future prospects. Heliyon. 2022;8(11):e11300.
[2] 朱彦红,张博,刘亦洪,等.铸造支架式可摘局部义齿折断分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2012,44(1):80-83.
[3] 国家药品监督管理局.牙科学 增材制造 口腔固定和活动修复用激光选区熔化金属材料YY/T 1702-2020[S].2020.
[4] TIAN Y, CHEN C, XU X, et al. A review of 3D printing in dentistry: technologies, affecting factors and applications. scanning. 2021:2021;9950131.
[5] YU Z, CHEN Z, QU D, et al. Microstructure and electrochemical behavior of a 3D-printed Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(13):4473.
[6] QU B, LU L, WANG Q, et al. Mechanical properties of TC11 titanium alloy and graphene nanoplatelets/TC11 composites prepared by selective laser melting. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6134.
[7] ESHAWISH N, MALINOV S, SHA W, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V manufactured by selective laser melting after stress relieving, hot isostatic pressing treatment, and post-heat treatment. J Mater Eng Perform. 2021;30(7):1-7.
[8] 何英介,论国内外真空热处理技术的发展[J].工业炉通讯,1979(4):13-19.
[9] LUITEN CH.气氛热处理和真空热处理的设备及其工艺的发展[J].国外化学热处理,1980(3):29-41.
[10] 张绪虎,徐桂华,孙彦波.钛合金热等静压粉末冶金技术的发展现状[J].宇航材料工艺,2016,46(6):6-10.
[11] 山中久彦,王泉清.真空热处理[J].真空技术报导,1974(3):23-31.
[12] 胡志杰,冯军宁,马忠贤.我国钛及钛合金热处理标准现状[J].金属热处理, 2021,46(3):243-246.
[13] 吴怀远.增材制造内部缺陷检测及对力学性能影响机制研究[D].沈阳:沈阳航空航天大学,2020.
[14] 辛立正,氩基保护气氛热处理技术研究[J].工具技术,2021,55(3):62-67.
[15] SHAAZ G, REECE O, AISHA M, et al. Vacuum heat treatments of titanium porous structures. Addit Manuf. 2021;47:102262.
[16] LI C L, HONG J, NARAYANA P, et al. Realizing superior ductility of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V through a multi-step heat treatment. Mater Sci Eng A. 2021;799:140367.
[17] XI J, XING H, HU Y, et al. The low-cycle fatigue behavior, failure mechanism and prediction of SLM Ti-6Al-4V alloy with different heat treatment methods. Mater. 2021;14(21):6276.
[18] ZHANG K, HU R, LI J, et al. Grain Refinement of 1 at.% Ta-containing cast TiAl-based alloy by cyclic air-cooling heat treatment. Materials Letters. 2020;274:127940.
[19] ZOU Z, SIMONELLI M, KATRIB J, et al. Refinement of the grain structure of additive manufactured titanium alloys via epitaxial recrystallization enabled by rapid heat treatment. Scr Mater. 2020;180:66-70.
[20] BEESE AM, CARROLL BE. Review of mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V made by laser-based additive manufacturing using powder feedstock. JOM. 2016; 68(3):724-734.
[21] LI J Q, LIN X, WANG J, et al. Effect of stress-relief annealing on anodic dissolution behaviour of additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V via laser solid forming. Corros Sci. 2019;153:314-326.
[22] 张霜银,林鑫,陈静,等.热处理对激光成形TC4合金组织及性能的影响[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2007,36(7):1263-1266.
[23] 李文贤,易丹青,刘会群,等.热处理制度对选择性激光熔化成形TC4钛合金的组织与力学性能的影响[J].粉末冶金材料科学与工程,2017,22(1):70-78.
[24] 钦兰云,李明东,杨光,等.热处理对激光沉积TC4钛合金组织与力学性能的影响[J].稀有金属,2018,42(7):698-704.
[25] 王伟,周山琦,宫鹏辉,等.退火温度对TC4钛合金热轧板材的显微组织、织构和力学性能影响[J].材料研究学报,2023,37(1):70-80.
[26] LIANG Z, SUN Z, ZHANG W, et al. The effect of heat treatment on microstructure evolution and tensile properties of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V alloy. J Alloy Compd. 2018;782(C):1041-1048.
[27] VRANCKEN B, THIJS L, KRUTH JP, et al. Heat treatment of Ti6Al4V produced by selective laser melting: microstructure and mechanical properties. J Alloy Compd. 2012;541:177-185.
[28] TOBIAS, LIENEKE, STEFAN, et al. On the fatigue properties of metals manufactured by selective laser melting - The role of ductility. J Mater Res. 2014;29(17):1911-1919.
[29] 王俭,冯秋元,雷挺,等.退火温度对低成本TC4LCA钛合金板材组织和性能的影响[J].金属热处理,2022,47(11):82-86.
[30] LEE Y, WELSCH G. Young’s modulus and damping of Ti-6Al-4V alloy as a function of heat treatment and oxygen concentration. Mater Sci Eng A. 1990;128(1):77-89.
[31] CAO S, CHU R, ZHOU X, et al. Role of martensite decomposition in tensile properties of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V. J Alloy Compd. 2018;744:357-363.
[32] WANG W, XU X, MA R, et al. The influence of heat treatment temperature on microstructures and mechanical properties of titanium alloy fabricated by laser melting deposition. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(18):4087.
[33] ZAHMED N, ABBASI MS, HAIDER S, et al. Fit accuracy of removable partial denture frameworks fabricated with CAD/CAM, rapid prototyping, and conventional techniques: a systematic review. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:3194433.
[34] ZHANG M, GAN N, QIAN H, et al. Retentive force and fitness accuracy of cobalt-chrome alloy clasps for removable partial denture fabricated with SLM technique. J Prosthodont Res. 2022;66(3):459-465.
[35] TAKAHASHI K, TORII M, NAKATA T, et al. Fitness accuracy and retentive forces of additive manufactured titanium clasp. J Prosthodont Res. 2020;64(4):468-477.
[36] TORII M, NAKATA T, TAKAHASHI K, et al. Fitness and retentive force of cobalt-chromium alloy clasps fabricated with repeated laser sintering and milling. J Prosthodont Res. 2018;62(3):342-346.
[37] WANG Q, KONG J, LIU X, et al. The effect of a novel low-temperature vacuum heat treatment on the microstructure and properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloys manufactured by selective laser melting. Vacuum. 2021;193:110554.
[38] BAMBACH M, SIZOVA I, SZYNDLER J, et al. On the hot deformation behavior of Ti-6Al-4V made by additive manufacturing, J Mater Process Technol. 2021; 288:116840.
[39] LEUDERS S, THÖNE M, RIEMER A, et al. On the mechanical behaviour of titanium alloy TiAl6V4 manufactured by selective laser melting: fatigue resistance and crack growth performance. Int J Fatigue. 2013;48:300-307.
[40] REN Y, LIN X, GUO P, et al. Low cycle fatigue properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy fabricated by high-power laser directed energy deposition: Experimental and prediction. Int J Fatigue. 2019;127:58-73.
[41] 任永明,林鑫,黄卫东.增材制造Ti-6Al-4V合金组织及疲劳性能研究进展[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2017,46(10):3160-3168.
[42] Dai N, ZhANG L, ZhANG J, et al. Corrosion behavior of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy in NaCl solution. Corros Sci. 2016;102:484-489.
[43] DAI N, ZHANG J, YANG C, et al. Heat treatment degrading the corrosion resistance of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J Electrochem Soc. 2017;164:C428.
[44] FAN Z, FENG H. Study on selective laser melting and heat treatment of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Results Phys. 2018;10:660-664.
[45] SU C, YU H, WANG Z, et al. Controlling the tensile and fatigue properties of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy by post treatment. J Alloy Compds. 2020; 857:157552.
[46] SU J, JIANG F, LI J, TAN C, et al. Phase transformation mechanisms, microstructural characteristics and mechanical performances of an additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V alloy under dual-stage heat treatment. Mater Des. 2022;223:111240.
[47] MAO X, QU M, CHEN D, et al. Effect of third-stage heat treatments on microstructure and properties of dual-phase titanium alloy. Materials. 2021; 14(11):2776.
[48] 张颖,胡生双,郑超,等.双重退火对激光增材制造TC18钛合金组织和性能的影响[J].特种铸造及有色合金,2021,41(8):1006-1009.
[49] LIU C, WANG H, TIAN X, et al. Subtransus triplex heat treatment of laser melting deposited Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe near β titanium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2014; 590:30-36.
[50] SU B, WANG B, LUO L, et al. Tuning microstructure and improving the corrosion resistance of a Ti-6Al-3Nb-2Zr-1Mo alloy via solution and aging treatments. Corros Sci. 2022;208:110694.
[51] YAN X, CHEN C, HUANG C, et al. Effect of heat treatment on the phase transformation and mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V fabricated by selective laser melting. J Alloy Compd. 2018;764:1056-1071.
[52] PENG D, ANG ASM, MICHELSON A, et al. Analysis of the effect of machining of the surfaces of WAAM 18Ni 250 maraging steel specimens on their durability. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(24):8890.
[53] CHASTAND V, QUAEGEBEUR P, MAIA W, et al. Comparative study of fatigue properties of Ti-6Al-4V specimens built by electron beam melting (EBM) and selective laser melting (SLM). Mater Charact. 2018;143:76-81.
[54] PRABHU, VINCENT, CHAUDHARY, et al. Effect of microstructure and defects on fatigue behaviour of directed energy deposited Ti-6Al-4V. Sci Technol Weld Joi. 2015;20(8):659-669.
[55] DE JESUS J, MARTINS FERREIRA JA, BORREGO L, et al. Fatigue failure from inner surfaces of additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V components. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(4):737.
[56] RUSHIKESH S, SUMIT B, KAUSHIK C, et al. Globularization using heat treatment in additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V for high strength and toughness. Acta Materialia. 2018;162:239-254.
[57] CHONG Y, BHATTACHARJEE T, YI J, et al. Mechanical properties of fully martensite microstructure in Ti-6Al-4V alloy transformed from refined beta grains obtained by rapid heat treatment (RHT). Scripta Materialia. 2017;138:66-70.
[58] 无锡德润堂贸易有限责任公司.一种激光选区熔化钴铬合金义齿红外加热退火热处理方法:CN202010046481.5[P]. 2021-11-12.
[59] ZHANG X, FANG G, SANDER L, et al. Effect of subtransus heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J Alloy Compd. 2018;753:1562-1575.
[60] ELMER J, PALMER T, BABU S, et al. Low temperature relaxation of residual stress in Ti–6Al–4V. Scripta Materialia. 2005;52(10):1051-1056.
[61] HASSANIPOUR M, WATANABE S, HIRAYAMA K, et al. Short crack growth behavior and its transitional interaction with 3D microstructure in Ti-6Al-4V. Mater Sci Eng A. 2018;738:229-237.
|
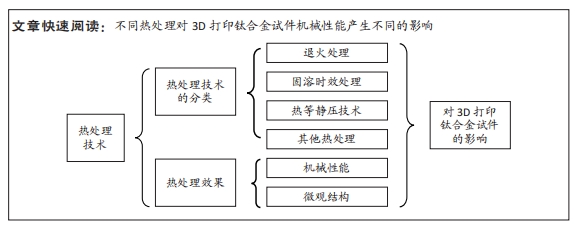
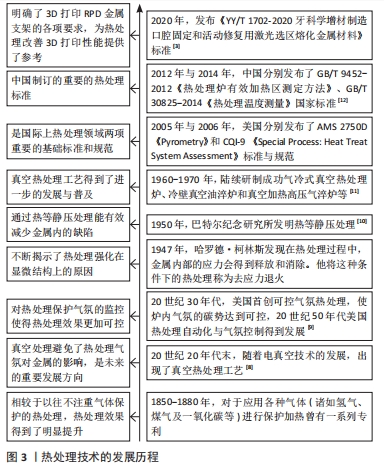
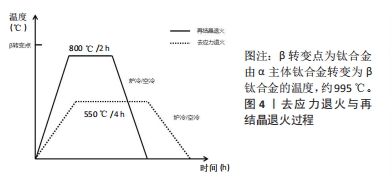
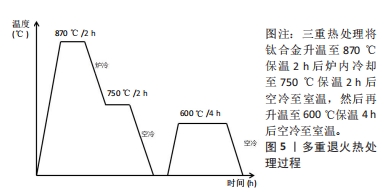
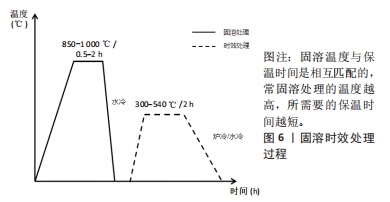
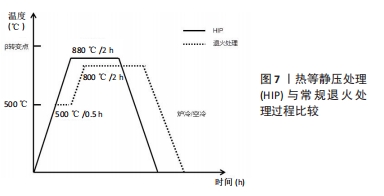
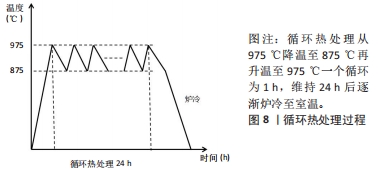
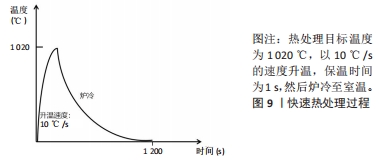
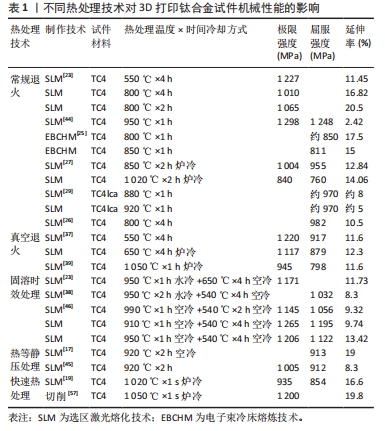
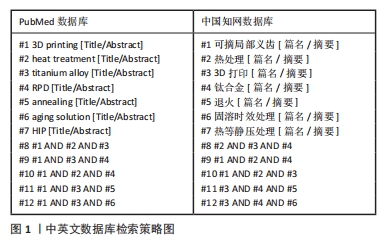

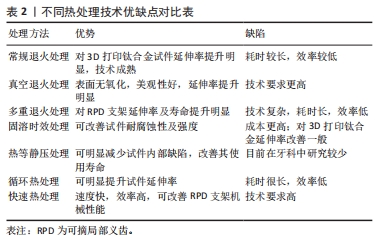 文章的发现在一定程度上为未来优化热处理技术研究指明方向:真空热处理技术可以减少热处理炉中气体对钛合金试件表面及机械性能的影响,去除气体杂质对钛合金影响后使得热处理效果变得更容易监控。快速热处理相较于以往的热处理技术效率更高,热处理效果不亚于其他热处理技术。最为重要的是文章为未来RPD钛合金支架热处理技术的研究提供了思路。
文章的发现在一定程度上为未来优化热处理技术研究指明方向:真空热处理技术可以减少热处理炉中气体对钛合金试件表面及机械性能的影响,去除气体杂质对钛合金影响后使得热处理效果变得更容易监控。快速热处理相较于以往的热处理技术效率更高,热处理效果不亚于其他热处理技术。最为重要的是文章为未来RPD钛合金支架热处理技术的研究提供了思路。