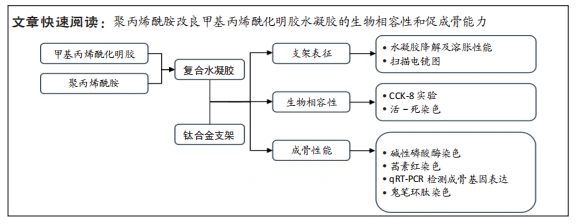
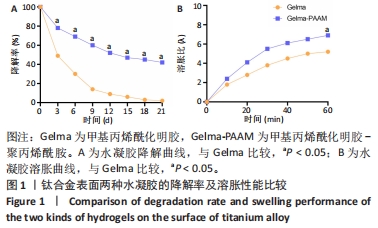
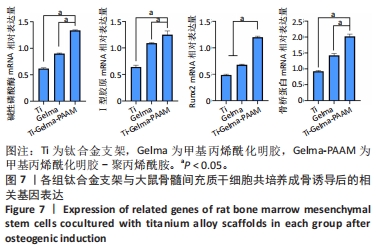
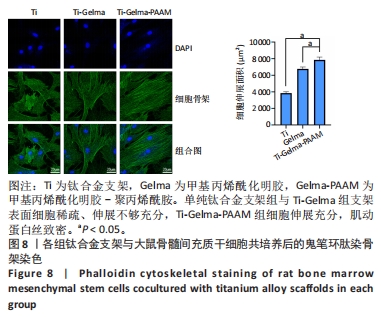
[1] ZHANG LC, CHEN LY. A Review on Biomedical Titanium Alloys: Recent Progress and Prospect. Adv Eng Mater. 2019;21(4):1801215.
[2] CHEN LY, CUI YW, ZHANG LC. Recent Development in Beta Titanium Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Metals. 2020;10(9):1139.
[3] TAKIZAWA T, NAKAYAMA N, HANIU H, et al. Titanium Fiber Plates for Bone Tissue Repair. Adv Mater. 2018;30(4):1703608.
[4] LIU X, CHEN S, TSOI JKH, et al. Binary titanium alloys as dental implant materials-a review. Regen Biomater. 2017;4(5):315.
[5] TORSTRICK FB, LIN ASP, POTR D, et al. Porous PEEK improves the bontee-implant interface compared to plasma-sprayed titanium coating on PEEK. Biomaterials. 2018;185:106-116.
[6] RUBSHTEIN AP, TRAKHTENBERG I, MAKAROVA EB, et al. Porous material based on spongy titanium granules: structure, mechanical properties, and osseointegration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;35:363-369.
[7] CHEN J, ZHANG X, HUANG C, et al. Osteogenic activity and antibacterial effect of porous titanium modified with metal-organic framework films. Journal of biomedical materials research Part A. 2017;105(3):834-846.
[8] KIM J, KIM HN, LIM KT, et al. Synergistic effects of nanotopography and co-culture with endothelial cells on osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2013;34(30):7257-7268.
[9] LLOPIS-GRIMALT MA, ARBOS A, GIL-MIR M, et al. Multifunctional Properties of Quercitrin-Coated Porous Ti-6Al-4V Implants for Orthopaedic Applications Assessed In Vitro. J Clin Med. 2020;9(3):855.
[10] SMIRNOV IV, DEEV RV, BOZO II, et al. Octacalcium phosphate coating for 3D printed cranioplastic porous titanium implants. Surf Coat Technol. 2020; 383:125192.
[11] ZHAO Z, GAO W, BAI H. A mineral layer as an effective binder to achieve strong bonding between a hydrogel and a solid titanium substrate. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(23):3859-3864.
[12] GARCIA GARCIA A, HÉBRAUD A, DUVAL JL, et al. Poly(ε-caprolactone)/Hydroxyapatite 3D Honeycomb Scaffolds for a Cellular Microenvironment Adapted to Maxillofacial Bone Reconstruction. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018; 4(9):3317-3326.
[13] SUN Y, ZHANG X, LUO M, et al. Plasma Spray vs. Electrochemical Deposition: Toward a Better Osteogenic Effect of Hydroxyapatite Coatings on 3D-Printed Titanium Scaffolds. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:727386.
[14] XIE M, YU K, SUN Y, et al. Protocols of 3D Bioprinting of Gelatin Methacryloyl Hydrogel Based Bioinks. J Vis Exp. 2019;(154). doi: 10.3791/60545.
[15] HERRERA-RUIZ A, TOVAR BB, GARCÍA RG, et al. Nanomaterials-Incorporated Chemically Modified Gelatin Methacryloyl-Based Biomedical Composites: A Novel Approach for Bone Tissue Engineering. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(12): 2645.
[16] YUE K, TRUJILLO-DE SANTIAGO G, ALVAREZ MM, et al. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;73:254-271.
[17] MAMIDI N, IJADI F, NORAHAN MH. Leveraging the Recent Advancements in GelMA Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: An Assessment of Challenges and Opportunities. Biomacromolecules. 2023.doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.3c00279.
[18] ZHANG S, GUO Y, DONG Y, et al. A novel nanosilver/nanosilica hydrogel for bone regeneration in infected bone defects. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(21):13242-13250.
[19] TODA H, YAMAMOTO M, UYAMA H, et al. Fabrication of hydrogels with elasticity changed by alkaline phosphatase for stem cell culture. Acta Biomater. 2016;29:215-227.
[20] HE M, HOU Y, ZHU C, et al. 3D-Printing Biodegradable PU/PAAM/Gel Hydrogel Scaffold with High Flexibility and Self-Adaptibility to Irregular Defects for Nonload-Bearing Bone Regeneration. Bioconjug Chem. 2021; 32(8):1915-1925.
[21] Wang S, Zhao X, Hsu Y, et al. Surface modification of titanium implants with Mg-containing coatings to promote osseointegration. Acta biomaterialia. 2023;169:19-44.
[22] SARRAF M, REZVANI GHOMI E, ALIPOUR S, et al. A state-of-the-art review of the fabrication and characteristics of titanium and its alloys for biomedical applications. Biodes Manuf. 2021;5(2):371-395.
[23] SHAO H, MA M, WANG Q, et al. Advances in the superhydrophilicity-modified titanium surfaces with antibacterial and pro-osteogenesis properties: A review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:1000401.
[24] MENG F, YIN Z, REN X, et al. Construction of Local Drug Delivery System on Titanium-Based Implants to Improve Osseointegration. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(5):1069.
[25] LENG J, HE Y, YUAN Z, et al. Enzymatically-degradable hydrogel coatings on titanium for bacterial infection inhibition and enhanced soft tissue compatibility via a self-adaptive strategy. Bioactive materials. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12):4670-4685.
[26] ZHAO C, ZHOU L, CHIAO M, et al. Antibacterial hydrogel coating: Strategies in surface chemistry. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020;285:102280.
[27] YANG Z, YANG Z, DING L, et al. Self-Adhesive Hydrogel Biomimetic Periosteum to Promote Critical-Size Bone Defect Repair via Synergistic Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(32): 36395-36410.
[28] GENG X, QI Y, LIU X, et al. A multifunctional antibacterial and self-healing hydrogel laden with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for accelerating diabetic wound healing. Biomater Adv. 2022;133:112613.
[29] ECHAVE MC, EREZUMA I, GOLAFSHAN N, et al. Bioinspired gelatin/bioceramic composites loaded with bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) promote osteoporotic bone repair. Biomaterials advances. 2022;134: 112539.
[30] WU X, LIU S, CHEN K, et al. 3D printed chitosan-gelatine hydrogel coating on titanium alloy surface as biological fixation interface of artificial joint prosthesis. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;182:669-679.
[31] LI Y, LIU Y, BAI H, et al. Sustained Release of VEGF to Promote Angiogenesis and Osteointegration of Three-Dimensional Printed Biomimetic Titanium Alloy Implants. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:757767.
[32] ZHENG J, WANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Gelatin/Hyaluronic Acid Photocrosslinked Double Network Hydrogel with Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite for Potential Application in Bone Repair. Gels. 2023;9(9):742.
[33] GUO B, LIANG Y, DONG R. Physical dynamic double-network hydrogels as dressings to facilitate tissue repair. Nat Protoc. 2023;18(11):3322-3354.
[34] ZHANG Z, HU Y, MA H, et al. MXene/Gelatin/Polyacrylamide Nanocomposite Double Network Hydrogel with Improved Mechanical and Photothermal Properties. Polymers. 2022;14(23):5247.
[35] CHEN H, DING Z, YAN D, et al. Double-network composites based on inorganic fillers reinforced dextran-based hydrogel with high strength. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;296:119900.
[36] DONG W, MA W, ZHAO S, et al. The surface modification of long carbon fiber reinforced polyether ether ketone with bioactive composite hydrogel for effective osteogenicity. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;130:112451.
[37] HE M, HOU Y, ZHU C, et al. 3D-Printing Biodegradable PU/PAAM/Gel Hydrogel Scaffold with High Flexibility and Self-Adaptibility to Irregular Defects for Nonload-Bearing Bone Regeneration. Bioconjug Chem. 2021; 32(8):1915-1925.
[38] XUE X, ZHANG H, LIU H, et al. Rational Design of Multifunctional CuS Nanoparticle‐PEG Composite Soft Hydrogel‐Coated 3D Hard Polycaprolactone Scaffolds for Efficient Bone Regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(33):2202470.
[39] ZHANG J, TONG D, SONG H, et al. Osteoimmunity‐Regulating Biomimetically Hierarchical Scaffold for Augmented Bone Regeneration. Adv Mater. 2022; 34(36):e2202044.
[40] BERNAR A, GEBETSBERGER JV, BAUER M, et al. Optimization of the Alizarin Red S Assay by Enhancing Mineralization of Osteoblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 24(1):723.
|