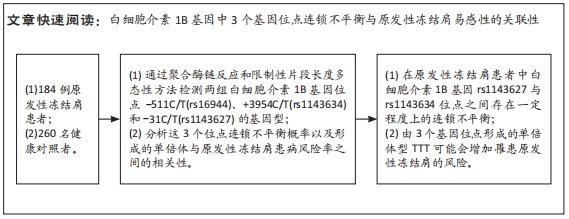
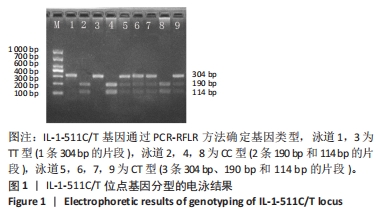
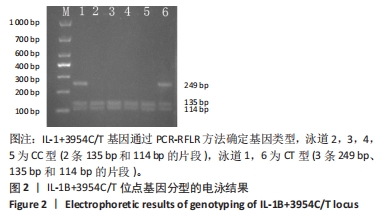
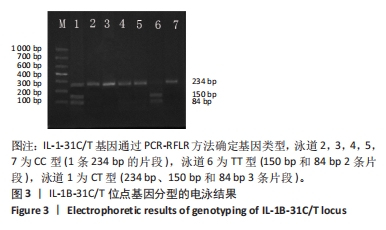
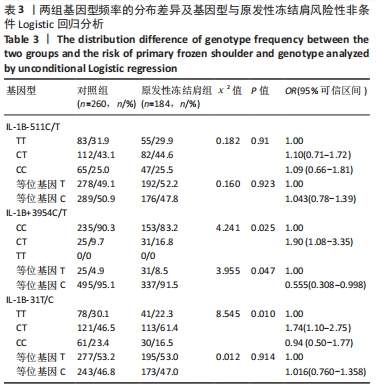
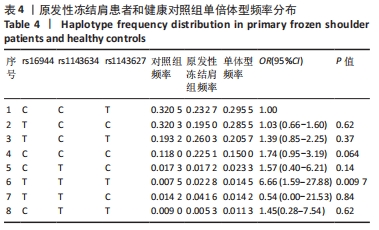
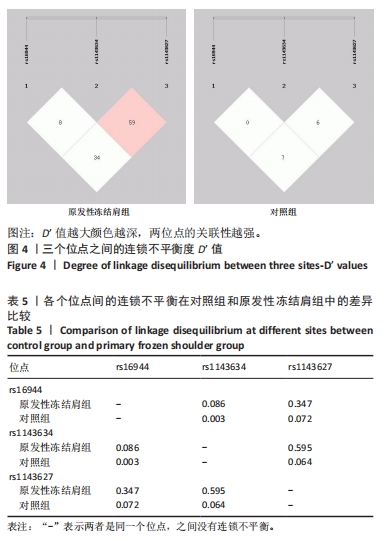
[1] TAMAI K, AKUTSU M, YANO Y. Primary frozen shoulder: brief review of pathology and imaging abnormalities. J Orthop Sci. 2014;19(1):1-5.
[2] RAMIREZ J. Adhesive Capsulitis: Diagnosis and Management. Am Fam Physician. 2019;99(5):297-300.
[3] NEVIASER AS, HANNAFIN JA. Adhesive capsulitis: a review of current treatment. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(11):2346-2356.
[4] WANG K, HO V, HUNTER-SMITH DJ, et al. Risk factors in idiopathic adhesive capsulitis: a case control study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013; 22(7):e24-29.
[5] KORDELLA T. Frozen shoulder & diabetes. Frozen shoulder affects 20 percent of people with diabetes. Proper treatment can help you work through it. Diabetes Forecast. 2002;55(8):60-64.
[6] BALCI N, BALCI MK, TÜZÜNER S. Shoulder adhesive capsulitis and shoulder range of motion in type II diabetes mellitus: association with diabetic complications. J Diabetes Complications. 1999;13(3):135-140.
[7] AUSTIN DC, GANS I, PARK MJ, et al. The association of metabolic syndrome markers with adhesive capsulitis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(7):1043-1051.
[8] LO SF, CHU SW, MUO CH, et al. Diabetes mellitus and accompanying hyperlipidemia are independent risk factors for adhesive capsulitis: a nationwide population-based cohort study (version 2). Rheumatol Int. 2014;34(1):67-74.
[9] HAKIM AJ, CHERKAS LF, SPECTOR TD, et al. Genetic associations between frozen shoulder and tennis elbow: a female twin study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003;42(6):739-742.
[10] COHEN C, LEAL MF, LOYOLA LC, et al. Genetic variants involved in extracellular matrix homeostasis play a role in the susceptibility to frozen shoulder: A case-control study. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(4): 948-956.
[11] FU LY, QIU X, DENG QL, et al. The IL-1B Gene Polymorphisms rs16944 and rs1143627 Contribute to an Increased Risk of Coronary Artery Lesions in Southern Chinese Children with Kawasaki Disease. J Immunol Res. 2019;2019:4730507.
[12] CARDOSO JM, RIBEIRO AC, PALOS C, et al. Association between IL-1A and IL-1B gene polymorphisms with peri-implantitis in a Portuguese population-a pilot study. PeerJ. 2022;10:e13729.
[13] KALSOOM F, SAJJAD-UR-RAHMAN, MAHMOOD MS, et al. Association of Interleukin-1B gene Polymorphism with H. pylori infected Dyspeptic Gastric Diseases and Healthy Population. Pak J Med Sci. 2020;36(4): 825-830.
[14] NEVIASER AS, NEVIASER RJ. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19(9):536-542.
[15] KRIEG T, ABRAHAM D, LAFYATIS R. Fibrosis in connective tissue disease: the role of the myofibroblast and fibroblast-epithelial cell interactions. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S4.
[16] RODEO SA, HANNAFIN JA, TOM J, et al. Immunolocalization of cytokines and their receptors in adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. J Orthop Res. 1997;15(3):427-436.
[17] BUNKER TD, REILLY J, BAIRD KS, et al. Expression of growth factors, cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases in frozen shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(5):768-773.
[18] BLAINE TA, KIM YS, VOLOSHIN I, et al. The molecular pathophysiology of subacromial bursitis in rotator cuff disease. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14(1 Suppl S):84S-89S.
[19] LHO YM, HA E, CHO CH, et al. Inflammatory cytokines are overexpressed in the subacromial bursa of frozen shoulder. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(5):666-672.
[20] KABBABE B, RAMKUMAR S, RICHARDSON M. Cytogenetic analysis of the pathology of frozen shoulder. Int J Shoulder Surg. 2010;4(3):75-78.
[21] LIU Z, PEI Y, ZENG H, et al. Recombinant TSG-6 protein inhibits the growth of capsule fibroblasts in frozen shoulder via suppressing the TGF-β/Smad2 signal pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):564.
[22] ZHAO H, KONG L, SHEN J, et al. Tetrandrine inhibits the occurrence and development of frozen shoulder by inhibiting inflammation, angiogenesis, and fibrosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;140:111700.
[23] CHO JH, CHOI JS, CHUN SW, et al. The IL-1B Genetic Polymorphism Is Associated with Aspirin-Induced PepticUlcers in a Korean Ethnic Group. Gut Liver. 2016;10(3):362-368.
[24] ZHENG W, CHEN M, SI X. Associations between interleukin-1-B gene -511G/A polymorphism and sepsis risk: A meta-analysis. Cytokine. 2022;157:155953.
[25] VARLJEN T, SEKULOVIC G, RAKIC O, et al. Genetic variant rs16944 in IL1B gene is a risk factor for early-onset sepsis susceptibility and outcome in preterm infants. Inflamm Res. 2020;69(2):155-157.
[26] KAPELSKI P, SKIBINSKA M, MACIUKIEWICZ M, et al. Association study of functional polymorphisms in interleukins and interleukin receptors genes: IL1A, IL1B, IL1RN, IL6, IL6R, IL10, IL10RA and TGFB1 in schizophrenia in Polish population. Schizophr Res. 2015;169(1-3):1-9.
[27] WANG X, JIANG F, LIANG Y, et al. Interleukin-1β-31C/T and -511T/C polymorphisms were associated with preeclampsia in Chinese Han population. PLoS One. 2014;9(9):e106919.
[28] SMITH AJ, KEEN LJ, BILLINGHAM MJ, et al. Extended haplotypes and linkage disequilibrium in the IL1R1-IL1A-IL1B-IL1RN gene cluster: association with knee osteoarthritis. Genes Immun. 2004;5(6):451-460.
[29] ALGHAMDI A, ALYAMI AH, ALTHAQAFI RMM 2ND, et al. Cytokines’ Role in the Pathogenesis and Their Targeting for the Prevention of Frozen Shoulder: A Narrative Review. Cureus. 2023;15(3):e36070. |