1.1 设计 细胞学体外实验,组间比较采用单因素方差分析。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2022年3月至2023年3月在河南省中医药大学SPF级实验动物中心完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 细胞株 啮齿动物前成骨细胞系MC3T3-E1购自中国科学院细胞库。
1.3.2 主要试剂 地塞米松(D4902)购自Sigma(马萨诸塞州圣路易斯);3-甲基腺嘌呤(3-Methyladenine,3-MA)(HY-19312)购自MCE;Anti-Bax抗体(ab32503)、Anti-Bcl-2抗体(ab32124)、Anti-LC3B抗体(ab192890)、Anti-SQSTM1/p62抗体(ab109012)、Anti-AMP蛋白激活激酶(AMP-activatedproteinkinase,AMPK)抗体(ab32047)、Anti-p-AMPK抗体(ab133448)和Anti-GAPDH抗体(ab8245)购自Abcam;α-MEM培养基(22571038)、胎牛血清(10099141C)、青霉素-链霉素(15140148)、TRIzol试剂(10296010CN)和细胞转染试剂Lipofectamine 3000TM(L3000008)购自美国Life Technologies;反转录试剂盒(638315)购自TaKaRa;QuantiFast SYBR® Green荧光定量PCR试剂盒(204056)购自德国QIAGEN;RIPA裂解缓冲液(P0013M)和BCA蛋白测定试剂盒(P0012S)购自上海碧云天生物科技有限公司;半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶3(cysteine aspastic acid-specific protease,Caspase-3)活性检测ELISA检测试剂盒(G015-1-3)购自南京建成工程研究所有限公司。
1.3.3 主要仪器 Multiskan FC酶标仪、-80 ℃超低温冰箱、Nano Drop 2000荧光分光光度计购自美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;Tanon 4100凝胶成像系统购自上海天能公司;Mini-PROTEAN Tetra蛋白电泳仪、The Trans-Blot Turbo蛋白转膜仪、IQ5实时荧光定量PCR仪购自美国Bio-Rad公司。
1.4 方法
1.4.1 细胞培养和处理 MC3T3-E1细胞以6.0×108 L-1的细胞密度接种于24孔培养板中培养,每孔1 mL,培养基采用含有体积分数10%胎牛血清和100 U青霉素/链霉素的α-MEM培养基,在37 ℃体积分数5%的CO2箱中培养。为了诱导成骨细胞分化,在上述混合培养基中补充10 mmol/L β-甘油磷酸和50 μg/mL抗坏血酸,然后加入10 μmol/L地塞米松制备成骨诱导培养基,进行诱导处理,3 d后收集细胞。阴性对照组的细胞用相同体积的载体处理,不暴露于药物。为了评估圣草素对成骨细胞的影响,在存在或不存在3-MA (5 μmol/L) 的情况下,将MC3T3-E1细胞维持在含有地塞米松(10 μmol/L)和圣草素(0.5,1,2.5,5和10 μmol/L)的成骨培养基中培养。
1.4.2 分组及药物处理
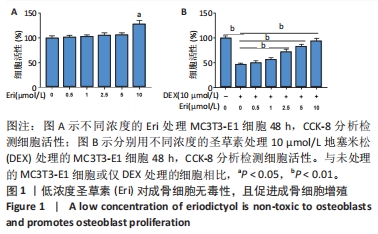
(1)圣草素对成骨细胞的毒理学测定:将细胞分为6组,分别为空白对照组、0.5,1,2.5,5和10 μmol/L圣草素处理组。分别采用含有0.5,1,2.5,5和10 μmol/L圣草素的成骨培养基培养MC3T3-E1细胞48 h,空白对照组直接采用成骨培养基培养。观察不同浓度圣草素对成骨细胞活力的影响,筛选合适浓度的圣草素用于后续实验。
(2)圣草素对地塞米松诱导的成骨细胞活力的影响:将细胞分为7组,分别为空白对照组、地塞米松处理组和地塞米松+不同浓度圣草素(0.5,1,2.5,5和10 μmol/L)处理组。分别采用含有10 μmol/L地塞米松的成骨培养基和含有10 μmol/L地塞米松,以及0,0.5,1,2.5,5和10 μmol/L圣草素的成骨培养基培养MC3T3-E1细胞48 h,空白对照组直接采用成骨培养基培养。观察细胞活力,分析圣草素对地塞米松诱导的成骨细胞增殖的影响。
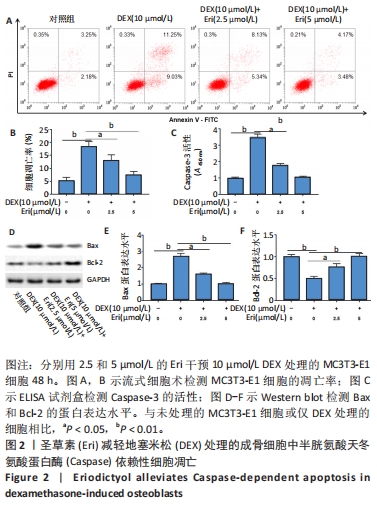
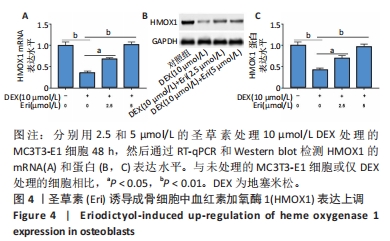
(3)圣草素对成骨细胞自噬、凋亡和HMOX1表达的调节作用:将细胞分为4组,分别为空白对照组、地塞米松处理组、地塞米松+2.5 μmol/L圣草素处理组和地塞米松+5 μmol/L圣草素处理组。分别采用含有10 μmol/L地塞米松的成骨培养基和含有10 μmol/L地塞米松,以及2.5和5 μmol/L圣草素的成骨培养基培养MC3T3-E1细胞48 h,空白对照组直接采用成骨培养基培养。观察不同组中细胞自噬相关蛋白的表达水平、凋亡细胞百分比和HMOX1的水平表达,探究圣草素对地塞米松诱导的成骨细胞自噬和凋亡的影响。
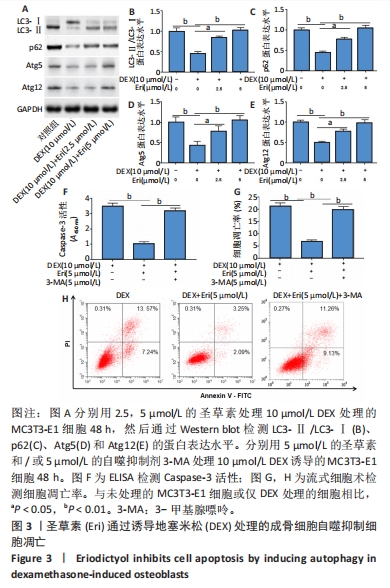
(4)圣草素对成骨细胞凋亡的自噬依赖性调节作用:将细胞分为3组,分别为地塞米松处理组、地塞米松+圣草素处理组和地塞米松+圣草素+3-MA处理组。分别采用含有10 μmol/L地塞米松的成骨培养基,含有10 μmol/L地塞米松和5 μmol/L圣草素的成骨培养基,以及含有10 μmol/L地塞米松、5 μmol/L圣草素和5 μmol/L自噬抑制剂3-MA的成骨培养基培养MC3T3-E1细胞48 h,空白对照组直接采用成骨培养基培养。观察不同组中凋亡细胞百分比和Caspase-3活性水平,探究圣草素对成骨细胞凋亡的抑制作用是否依赖于自噬激活。
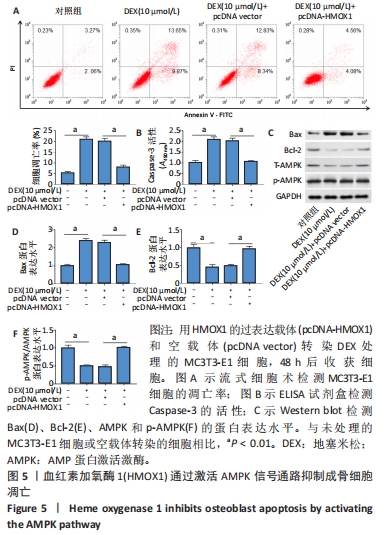
(5)过表达HMOX1对成骨细胞凋亡的调节作用:将细胞分为4组,分别为空白对照组、地塞米松处理组、地塞米松+pcDNA vector组、地塞米松+pcDNA-HMOX1组。地塞米松+pcDNA vector组和地塞米松+pcDNA-HMOX1组分别采用pcDNA vector和pcDNA-HMOX1转染MC3T3-E1细胞48 h,然后采用含有10 μmol/L地塞米松的成骨培养基培养48 h,空白对照组直接采用成骨培养基培养。观察不同组中凋亡细胞百分比、凋亡相关蛋白表达水平和AMPK通路蛋白表达水平,探究过表达HMOX1对AMPK通路的调节作用和对成骨细胞凋亡的调节作用。
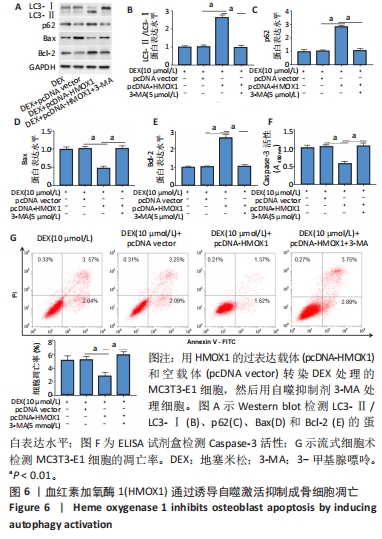
(6)HMOX1对成骨细胞凋亡的自噬依赖性调节作用:将细胞分为4组,分别为地塞米松处理组、地塞米松+pcDNA vector组、地塞米松+pcDNA-HMOX1组、地塞米松+pcDNA-HMOX1+3-MA组。地塞米松+pcDNA vector组和地塞米松+pcDNA-HMOX1组分别采用pcDNA vector和pcDNA-HMOX1转染MC3T3-E1细胞48 h,然后采用含有10 μmol/L地塞米松的成骨培养基培养48 h;地塞米松+pcDNA-HMOX1+3-MA组细胞在pcDNA-HMOX1转染48 h后,采用含有10 μmol/L地塞米松和5 μmol/L自噬抑制剂3-MA的成骨培养基培养48 h;空白对照组直接采用成骨培养基培养。观察不同组中自噬相关蛋白表达水平、凋亡细胞百分比和凋亡相关蛋白表达水平,探究HMOX1对成骨细胞凋亡的抑制作用是否依赖于自噬途径。
1.4.3 载体构建 用PCR扩增人血红素加氧酶1(heme oxygenase 1,HMOX1)CDS序列,提取总RNA,克隆到pmdtm19-T载体上,并进行全序列测定,然后将HMOX1片段亚克隆到pcDNA3.1载体(赛默飞世尔科技有限公司,上海)的多克隆位点中,并通过DNA测序对其进行鉴定。
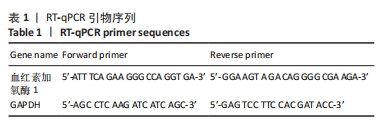
1.4.4 RT-qPCR 使用TRIzol试剂提取成骨细胞中的总RNA。运用反转试剂盒将总RNA反转录成cDNA。利用miScript SYBR Green 荧光定量PCR试剂盒进行实时定量PCR。RT-qPCR循环条件为95 ℃ 3 min,之后进行35个循环(95 ℃ 35 s,58 ℃ 45 s,72 ℃ 30 s),72 ℃ 10 min。引物序列如表1所示,GAPDH作为内参基因,并通过2-ΔΔCt方法分析基因的相对表达。
1.4.5 蛋白印迹分析 利用RIPA裂解缓冲液提取成骨细胞中的总蛋白,然后利用BCA蛋白测定试剂盒评估蛋白浓度。将30 μg的总蛋白在12%的SDS-PAGE上分离并转移到PVDF膜上。在室温下用体积分数5%牛血清白蛋白封闭1 h,用Anti-Bax抗体(1∶1 000,ab32503)、Anti-Bcl-2抗体(1∶1 000,ab32124)、Anti-LC3B抗体(1∶1 000,ab192890)、Anti-SQSTM1/p62抗体(1∶1 000,ab109012)、Anti-AMPK抗体(1∶1 000,ab32047)、Anti-p-AMPK抗体(1∶1 000,ab133448)和Anti-GAPDH抗体(1∶1 000,ab8245)在4 ℃孵育过夜。然后与特异性山羊抗鼠IgG(1∶1 000,ab150113)在室温下孵育2 h。采用ECL化学发光试剂盒使条带可视化,并通过化学发光成像系统拍照,Image J软件用于量化条带灰度值。
1.4.6 CCK-8分析 将处于对数生长期的细胞接种到96孔板中(1×103个/孔),然后向每个孔中加入10 μL的CCK-8溶液,在37 ℃孵育4 h,然后使用酶标仪检测450 nm处的吸光度(A),计算活细胞的数目。细胞活性(%) = (实验组A值 / 对照组A值) × 100%。
1.4.7 流式细胞术分析 收集细胞并用PBS洗涤2次,将100 μL的细胞悬液(1×109 L-1)转移到培养管中,然后在黑暗中与5 μL膜联蛋白V-FITC和5 μL碘化丙啶一起室温孵育20 min。最后,加入400 μL结合缓冲液,通过流式细胞仪测定凋亡细胞数。
1.4.8 ELISA检测 根据制造商的说明,采用ELISA试剂盒检测Caspase-3的活性,所有步骤均严格按照制造商的说明进行。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①细胞活力;②细胞凋亡率;③HMOX1 mRNA表达水平;④Bax、Bcl-2、LC3-Ⅰ、LC3-Ⅱ、p62、Atg5、Atg12、HMOX1、p-AMPK和AMPK蛋白表达水平;⑤Caspase-3活性。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS 20.0软件进行统计学分析,所有数据均表示为x±s。采用t检验进行两组之间的比较,单因素方差分析(ANOVA)进行多组之间比较。P < 0.05被认为差异有显著性意义。此文统计学方法已经河南中医药大学生物统计学专家审核。