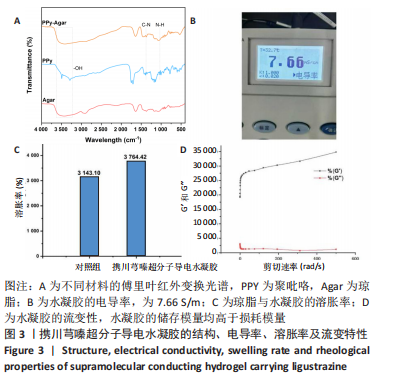
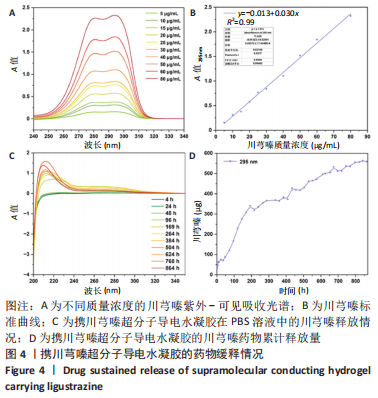
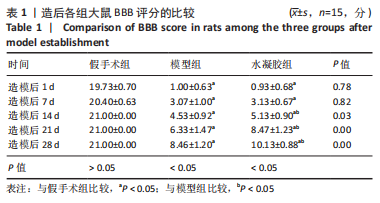
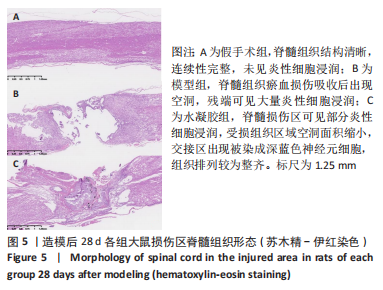
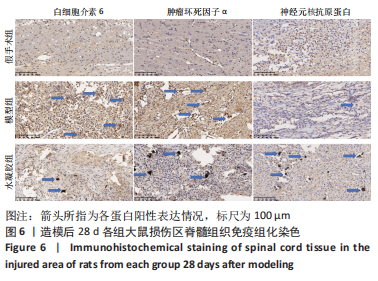
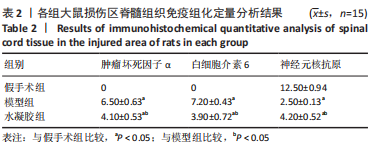
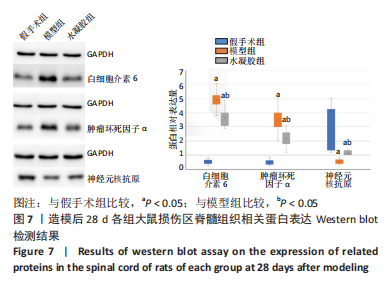
[1] ELI I, LERNER DP, GHOGAWALA Z. Acute traumatic spinal cord injury. Neurol Clin. 2021;39(2):471-488.
[2] QUADRI SA, FAROOQUI M, IKRAM A, et al. Recent update on basic mechanisms of spinal cord injury. Neurosurg Rev. 2020;43(2):425-441.
[3] DENG LX, LIU NK, WEN R, et al. Laminin-coated multifilament entubulation, combined with Schwann cells and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor,promotes unidirectional axonal regeneration in a rat model of thoracic spinal cord hemisection. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(1):186-191.
[4] SOARES S, VON BOXBERG Y, NOTHIAS F. Repair strategies for traumatic spinal cord injury, with special emphasis on novel biomaterial-based approaches. Revue Neurologique. 2020;176(4):252-260.
[5] ZOU Y, MA D, SHEN H, et al. Aligned collagen scaffold combination with human spinal cord-derived neural stem cells to improve spinal cord injury repair. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(18):5145-5156.
[6] LUO Y, FAN L, LIU C, et al. An injectable, self-healing, electroconductive extracellular matrix-based hydrogel for enhancing tissue repair after traumatic spinal cord injury. Bioact Mater. 2021;7:98-111.
[7] 王健豪,刘洋,付玄昊,等.3D打印组织工程支架联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植修复脊髓损伤[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(6):376-385.
[8] LI X, ZHANG C, HAGGERTY AE, et al. The effect of a nanofiber-hydrogel composite on neural tissue repair and regeneration in the contused spinal cord. Biomaterials. 2020;245:119978.
[9] KIM BS, CHO CS. Injectable Hydrogels for Regenerative Medicine. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;15(5):511-512.
[10] 曾园山,曾湘,赖碧琴,等.移植干细胞源性神经网络组织修复脊髓损伤的系列研究[J].解剖学研究,2023,45(1):105.
[11] 田祎,姚东晓,雷德强.生物材料结合细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].沈阳医学院学报,2023,25(1):78-82.
[12] 李键.负载BDNF的GelMA-OALG水凝胶生物支架用于修复脊髓损伤的研究[D].蚌埠:蚌埠医学院,2022.
[13] HE Z, ZANG H, ZHU L, et al. An anti-inflammatory peptide and brain-derived neurotrophic factor-modified hyaluronan-methylcellulose hydrogel promotes nerve regeneration in rats with spinal cord injury. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:721-732.
[14] 李姝君,漆国栋,漆伟,等.川芎嗪对脊髓损伤后小鼠神经保护作用的实验研究[J/OL].中国中药杂志:1-8[2023-03-07].
[15] 张厚君,蒋昇源,邓博文,等.川芎嗪改善脊髓损伤模型大鼠炎性微环境的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(11):1701-1707.
[16] 蒋昇源,邓博文,刘港,等.携载川芎嗪缓释微粒导电水凝胶修复脊髓损伤实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(1):65-73.
[17] 都芳涛,方继峰,李兴晶,等.不同剂量川芎嗪治疗脊髓损伤的临床效果比较[J].中国医药,2019,14(10):1511-1514.
[18] ZHANG LS, LU XY, GONG LH, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine Protects Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier Integrity by Modulating Microglia Polarization Through Activation of STAT3/SOCS3 and Inhibition of NF-кB Signaling Pathways in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021;41(4):717-731.
[19] 孙忠人,徐思禹,田洪昭,等.中药及有效成分治疗脊髓损伤的研究概况[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(6):3003-3006.
[20] 池红万.川芎嗪联合rTMS治疗外伤性截瘫的效果及对神经电生理和骨代谢的影响[J].实用中西医结合临床,2021,21(14):39-40.
[21] WANG CG, WANG M, XIA KS, et al. A bioactive injectable self-healing anti-inflammatory hydrogel with ultralong extracellular vesicles release synergistically enhances motor functional recovery of spinal cord injury. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(8):2523-2534.
[22] KHAING ZZ, EHSANIPOUR A, HOFSTETTER CP, et al. Injectable Hydrogels for Spinal Cord Repair: A Focus on Swelling and Intraspinal Pressure. Cells Tissues Organs. 2016;202(1-2):67-84.
[23] SENGELAUB DR, HAN Q, LIU NK, et al. Protective Effects of Estradiol and Dihydrotestosterone following Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35(6):825-841.
[24] 吴杨鹏,范筱,张俐.急性脊髓损伤动物模型的建立与评估[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(49):7341-7348.
[25] BINAN L, AJJI A, DE CRESCENZO G, et al. Approaches for Neural Tissue Regeneration. Stem Cell Revi Rep. 2014;10(1):44-59.
[26] SHI Z, YUAN S, SHI L, et al. Programmed cell death in spinal cord injury pathogenesis and therapy. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(3):e12992.
[27] PANG QM, CHEN SY, XU QJ, et al. Effects of astrocytes and microglia on neuroinflammation after spinal cord injury and related immunomodulatory strategies. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;108: 108754.
[28] PINELLI F, PIZZETTI F, VENERUSO V, et al. Biomaterial-mediated factor delivery for spinal cord injury treatment. Biomedicines. 2022;10(7): 1673.
[29] GUO S, REDENSKI I, LEVENBERG S. Spinal Cord Repair: From Cells and Tissue Engineering to Extracellular Vesicles. Cells. 2021;10(8): 1872.
[30] CHOI SW, GUAN W, CHUNG K. Basic principles of hydrogel-based tissue transformation technologies and their applications. Cell. 2021; 184(16):4115-4136.
[31] SHULTZ R,ZHONG Y. Hydrogel-based local drug delivery strategies for spinal cord repair. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(2):247-253.
[32] ZHOU L, FAN L, YI X, et al. Soft Conducting Polymer Hydrogels Cross-Linked and Doped by Tannic Acid for Spinal Cord Injury Repair. ACS Nano. 2018;12(11):10957-10967.
[33] WANG Y, LV HQ, CHAO X, et al. Multimodal therapy strategies based on hydrogels for the repair of spinal cord injury. Mil Med Res. 2022;9(1): 16.
[34] LV Z, DONG C, ZHANG T, et al. Hydrogels in spinal cord injury repair: A review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:931800.
[35] LU Y, YANG J, WANG X, et al. Research progress in use of traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;127:110136.
[36] 赵书杰,陈建,凡进,等.创伤性脊髓损伤后脊髓微环境失衡的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(10):942-947.
[37] LIN S, XU C, LIN J, et al. Regulation of inflammatory cytokines for spinal cord injury recovery. Histol Histopathol. 2021;36(2):137-142.
[38] 郭德华,吴成林,许洋,等.补阳还五汤对脊髓间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠脊髓损伤的影响及作用机制[J].中药药理与临床,2022, 38(5):2-7.
[39] 李传根,王文升.复元活血汤加减联合电针对脊髓损伤神经功能康复的作用及对神经营养因子和炎症因子的影响研究[J].贵州医药, 2022,46(8):1239-1240.
[40] 刘永辉,赵烨,王向阳,等.愈瘫胶囊对脊髓损伤模型大鼠血清IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α的影响[J].中医药导报,2020,26(15):40-43.
[41] 颜浪辉,鄢来军,林庆宾,等.通督活血汤对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后炎症反应影响[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2020,22(4):51-54.
[42] 张世磊,潘东晟,丁坦,等.神经节苷脂治疗脊髓损伤患者的疗效及对血清肿瘤坏死因子-α白细胞介素-8水平的影响[J].山西医药杂志,2020,49(23):3297-3299.
[43] 梁雪松,宁百乐,吴倩,等.电针对脊髓损伤大鼠血清外泌体及脊髓组织促炎因子表达的影响[J].针刺研究,2023,48(2):192-198.
[44] 李元鑫,邹永艳,王乐荣,等.针灸结合康复治疗对脊髓损伤患者神经功能的影响研究[J].中医临床研究,2021,13(26):83-85.
[45] 蒙法科,梁丽红,卢庆弘.后路减压椎弓根钉内固定术治疗腰椎骨折并发脊髓损伤的效果及对hs-CRP、IL-10、TNF-α的影响[J].解放军医药杂志,2022,34(5):36-38.
[46] 徐乾,梁威,李鹏,等.艾司氯胺酮通过调控miR-148a-3p/KLF4通路减轻脊髓损伤大鼠的炎症反应[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2022,38(9): 965-970.
|