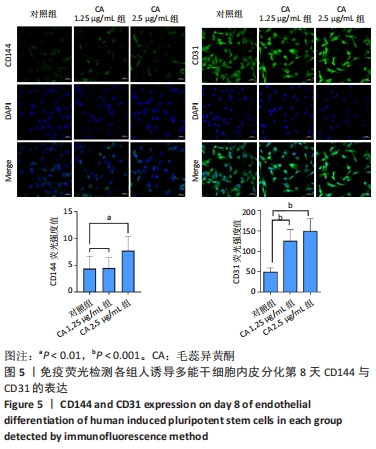
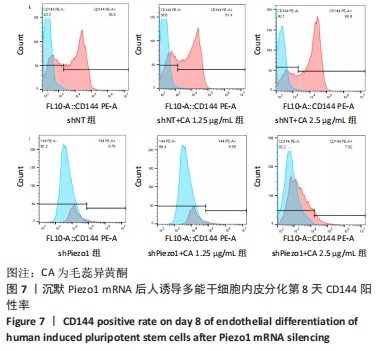
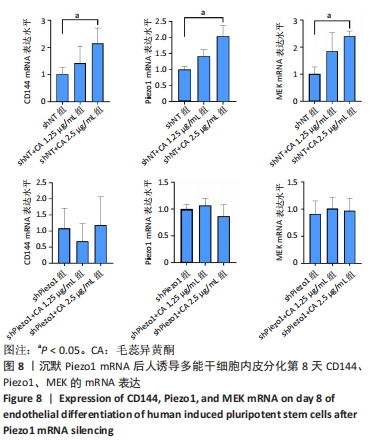
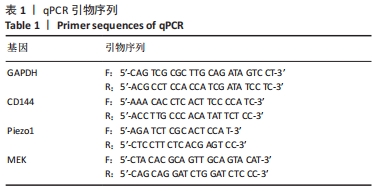
[1] 数据“说”全球心血管疾病负担[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2023, 31(3):5.
[2] GAĆ P, CZERWIŃSKA K, MACEK P, et al. The importance of selenium and zinc deficiency in cardiovascular disorders. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021;82:103553.
[3] 彭阿建,欧阳范馨,张熙,等.黄芪甲苷干预的EPC-Exos对高糖诱导损伤间充质干细胞向内皮分化的影响[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2022,24(4):1593-1602.
[4] 曹雪洁,陶佳平,曲爱娟,等.血管壁干细胞与血管重塑相关性疾病[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2022,30(11):921-929.
[5] VIDONI C, FERRARESI A, SECOMANDI E, et al. Autophagy drives osteogenic differentiation of human gingival mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2019;17(1):98.
[6] POETSCH MS, STRANO A, GUAN K. Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells: From Cell Origin, Genomic Stability, and Epigenetic Memory to Translational Medicine. Stem Cells. 2022;40(6):546-555.
[7] MAROTTA D, RAO C, FOSSATI V. Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSC) Handling Protocols: Maintenance, Expansion, and Cryopreservation. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2454:1-15.
[8] 陶军,谭红梅.机械门控阳离子通道Piezo1与动脉粥样硬化研究进展[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2023,31(1):9-16,33.
[9] 刘轩辰,帖晓瑛,刘玉林,等.何首乌提取物对失重小鼠骨质疏松和骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2021,47(6):1386-1396.
[10] 首健,霍云龙.机械力信号与部分心血管疾病的发生[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2023,31(1):34-40.
[11] SOLIS AG, BIELECKI P, STEACH HR, et al. Mechanosensation of cyclical force by PIEZO1 is essential for innate immunity. Nature. 2019; 573(7772):69-74.
[12] SHINGE SAU, ZHANG D, DIN AU, et al. Emerging Piezo1 signaling in inflammation and atherosclerosis; a potential therapeutic target. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(3):923-941.
[13] LUO C, LÜ D, ZHENG L, et al. Hepatic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells by coupling substrate stiffness and microtopography. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(10):3776-3790.
[14] DENG M, CHEN H, LONG J, et al. Calycosin: a Review of its Pharmacological Effects and Application Prospects. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2021;19(7):911-925.
[15] PAN L, ZHANG XF, WEI WS, et al. The cardiovascular protective effect and mechanism of calycosin and its derivatives. Chin J Nat Med. 2020; 18(12):907-915.
[16] TANG JY, LI S, LI ZH, et al. Calycosin promotes angiogenesis involving estrogen receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway in zebrafish and HUVEC. PLoS One. 2010;5(7): e11822.
[17] GU M. Efficient Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells to Endothelial Cells. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2018;98(1):e64.
[18] HARDING A, CORTEZ-TOLEDO E, MAGNER NL, et al. Highly Efficient Differentiation of Endothelial Cells from Pluripotent Stem Cells Requires the MAPK and the PI3K Pathways. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4):909-919.
[19] 桑婉玥,李耀东.人诱导多能干细胞在心血管疾病中的应用及研究进展[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2022,30(12):1020-1024.
[20] 冯芳.聚多巴胺-多肽粗糙表面调控人诱导多能干细胞体外生长及成骨向诱导分化的研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2022.
[21] 邵文桂,张阳,阮海文,等.人源诱导多能干细胞体外定向分化为功能性肝细胞的方法研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2023,23(2):225-231.
[22] 徐佳佳,李洋洋,仲光尚,等.人诱导多能干细胞体外定向分化为多巴胺能神经元祖细胞[J].南方医科大学学报,2023,43(2):175-182.
[23] MARCHEQUE J, BUSSOLATI B, CSETE M, et al. Concise Reviews: Stem Cells and Kidney Regeneration: An Update. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(1):82-92.
[24] BAHMAD HF, ELAJAMI MK, DAOUK R, et al. Stem Cells: In Sickness and in Health. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;16(3):262-276.
[25] 巩婷婷,司凯,刘会平,等. MAPK级联调控细胞生长及其在免疫、炎症及癌症中作用的研究进展[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2022, 47(12):1721-1728.
[26] KIDDER BL. Direct Reprogramming of Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts to Induced Trophoblast Stem Cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2117: 285-292.
[27] 刘博,冯潇,赵洁,等.转录因子Jun在小鼠睾丸发育过程中的表达及定位[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2022,31(1):11-15.
[28] 张蕊,张同存.整合素integrinβ4调控VEGF诱导的骨髓间充质 干细胞向内皮细胞分化[J].天津科技大学学报,2017,32(1):13-17.
[29] 李鹏,周长勇,尹磊,等.低氧对人脐带间充质干细胞活性和内皮分化能力的影响及VEGF的干预作用[J].中南大学学报(医学版), 2013,38(4):329-340.
[30] 汪雁归,毛萧萧,杨天伦.体外定向诱导胚胎干细胞分化为内皮细胞及其与脐静脉内皮细胞的比较[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2017, 42(4):374-379.
[31] 曹百川,曾高峰,高云兵,等.热休克内皮细胞诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向血管内皮细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(19): 3023-3028.
[32] HU Z, WU Y, ZHOU M, et al. Generation of reporter hESCs by targeting EGFP at the CD144 locus to facilitate the endothelial differentiation. Dev Growth Differ. 2018;60(4):205-215.
[33] 刘莲,汪萍萍,肖晓,等.VEGF、FGF2和BMP4联合通过ERK通路高效诱导hiPSCs向内皮细胞分化[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2022,31(1):1-10.
[34] 左芯萌,王振华,高利平.血管细胞外基质胶促进骨髓CD34+祖细胞分化为内皮细胞的实验研究[J].天津医药,2023,51(3):225-229.
[35] ZHANG Y, ZHANG JQ, ZHANG T, et al. Calycosin Induces Gastric Cancer Cell Apoptosis via the ROS-Mediated MAPK/STAT3/NF-κB Pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2021;14:2505-2517.
[36] GAO J, LIU ZJ, CHEN T, et al. Pharmaceutical properties of calycosin, the major bioactive isoflavonoid in the dry root extract of Radix astragali. Pharm Biol. 2014;52(9):1217-1222.
[37] MOUSAWI F, PENG H, LI J, et al. Chemical activation of the Piezo1 channel drives mesenchymal stem cell migration via inducing ATP release and activation of P2 receptor purinergic signaling. Stem Cells. 2020;38(3):410-421. |