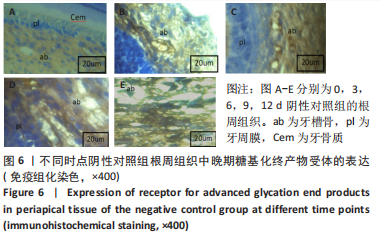
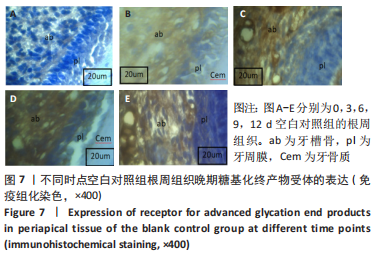
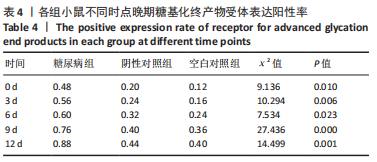
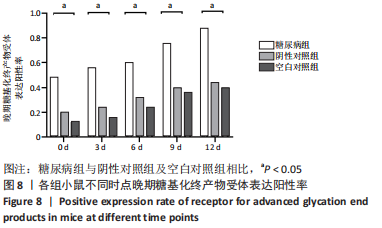
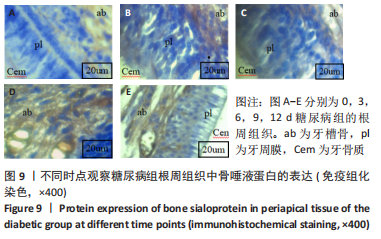
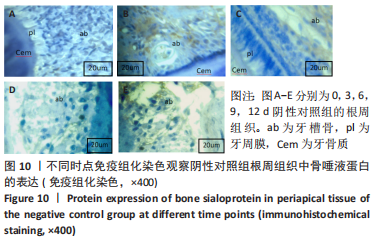
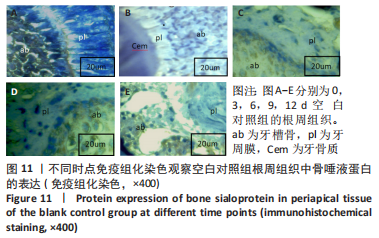
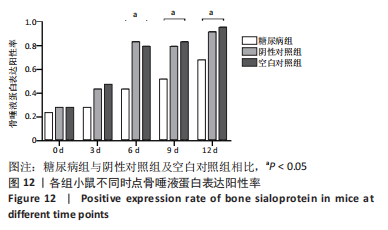
[1] YAMAMOTO M, SUGIMOTO T. Advanced Glycation End Products, Diabetes, and Bone Strength. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016;14(6):320-326.
[2] BORTOLOTTO V, GRILLI M. Every Cloud Has a Silver Lining: Proneurogenic Effects of Aβ Oligomers and HMGB-1 via Activation of the RAGE-NF-κB Axis. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017;16(10):1066-1079.
[3] BYUN K, YOO Y, SON M, et al. Advanced glycation end-products produced systemically and by macrophages: A common contributor toinflammation and degenerative diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;177:44-55.
[4] BOULEFTOUR W, JUIGNET L, BOUET G, et al. The role of the SIBLING, Bone Sialoprotein in skeletal biology - Contribution of mouse experimental genetics. Matrix Biol. 2016;52-54:60-77.
[5] BOUDIFFA M, WADE-GUEYE NM, GUIGNANDON A, et al. Bone Sialoprotein Deficiency Impairs Osteoclastogenesis and Mineral Resorption In Vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(8):1617.
[6] 武婧. 糖尿病对小鼠牙齿伸长运动的影响[D].太原:山西医科大学,2017.
[7] 余佳丽. SPARC、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白在牙齿伸长过程中的表达研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2017.
[8] 邓旎,谢莉莉,何祥一.系统性牙周治疗影响重度慢性牙周炎松动牙转归的临床研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2019,35(6):358-361.
[9] 周婷,徐屹,丁一,等.慢性牙周炎龈下菌斑中五种牙周可疑致病微生物的分布[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2007(5):470-473.
[10] WINNING L, PATTERSON CC, NEVILLE CE, et al. Periodontitis and incident type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study. J Clin Periodontol. 2017;44(3): 266-274.
[11] ACHARYA AB, THAKUR S, MUDDAPUR MV, et al. Cytokine ratios in chronic periodontitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2017; 11(4):277-278.
[12] CHAPPLE IL, GENCO R, WORKING GROUP 2 OF THE JOINT EFP/AAP WORKSHOP. Diabetes and periodontal diseases: consensus report of the Joint EFP/AAP Workshop on Periodontitis and Systemic Diseases. J Periodontol. 2013;84(4 Suppl):S106-112.
[13] DETZEN L, CHENG B, CHEN CY, et al. Soluble Forms of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation Endproducts (RAGE) in Periodontitis. Sci Rep. 2019; 9(1):8170.
[14] MØLVIG J, BAEK L, CHRISTENSEN P, et al. Endotoxin-stimulated human monocyte secretion of interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and prostaglandin E2 shows stable interindividual differences. Scand J Immunol. 1988;27:705-716.
[15] 王刚,孙澎,李娟,等.晚期糖基化终产物受体在2型糖尿病伴慢性牙周炎大鼠牙龈组织内皮细胞中的表达[J].口腔疾病防治,2019,27(7): 428-434.
[16] KATZ J, BHATTACHARYYA I, FARKHONDEH‐KISH F, et al Expression of the receptor of advanced glycation end products in gingival tissues of type 2 diabetes patients with chronic periodontal disease: a study utilizing immunohistochemistry and RT‐PCR J Clin Periodontol. 2005;32(1):40-44.
[17] TAKEDA M, OJIMA M, YOSHIOKA H, et al. Relationship of serum advanced glycation end products with deterioration of periodontitis in type 2 diabetes patients. Periodontol. 2006;77(1):15-20.
[18] NI N, WAGNER RS, LANGER P, et al. New developments in the management of periocular capillary hemangioma in children. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2011;48(5):269-276.
[19] GENNARO G, CLAUDINO M, CESTARI TM, et al. Green tea modulates cytokine expression in the periodontium and attenuates alveolar bone resorption in type 1 diabetic rats. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0134784.
[20] KATAYAMA Y, AKATSU T, YAMAMOTO M, et al. Role of nonenzymatic glycosylation of type 1 collagen in di abetic osteopenia. Bone Miner Res. 1996;11:9312937.
[21] LECKA-CZERNIK B. Diabetes, bone and glucose-lowering agents: basic biology. Diabetologia. 2017;60(7):1163-1169.
[22] ANGELA M, INZERILLO E, SOLOMON E .Osteoporosis and diabetesmellitus. Endocr Metab Disord. 2004;5(2):261.
[23] KANAZAWA I. Interaction between bone and glucose metabolism. Endocr J. 2017;64(11):1043-1053.
[24] YANG Y, CUI Q, SAHAI N. How does bone sialoprotein pro- mote the nucleation of hydroxyapatite? A molecular dynamics study using model peptides of different conformations. Langmuir. 2011;26(12):9848-9859.
[25] NAGASAKI K, CHAVEZ MB, NAGASAKI A, et al. The Bone Sialoprotein RGD Domain Modulates and Maintains Periodontal Development. J Dent Res. 2022;101(10):1238-1247.
[26] AO M, CHAVEZ MB, CHU EY, et al. Overlapping functions of bone sialoprotein and pyrophosphate regulators in directing cementogenesis. Bone. 2017;105:134-147.
[27] GORDON JA, HUNTER GK, GOLDBERG HA. Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by bone sialoprotein regulates osteoblast differentiation. Cells Tissues Organs. 2011;189(1-4):138-143.
[28] YANG Y, HUANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Transcriptional regulation of bone sialoprotein gene expression by Osx. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016; 476(4):574-579.
[29] MALAVAL L, WADE-GUEYE NM, BOUDIFFA M, et al. Bone sialoprotein plays a functional role in bone formation and osteoclastogenesis. J Exp Med. 2008;205(5):1145-1153.
[30] FOSTER BL, AO M, WILLOUGHBY C, et al. Mineralization defects in cementum and craniofacial bone from loss of bone sialoprotein. Bone. 2015;78:150-164.
[31] THOMAS MC, FORBES JM, COOPER ME. Advanced glycation end products and diabetic nephropathy. Am J Ther. 2005;12(6):562-572.
[32] FOSTER BL, SOENJAYA Y, NOCITI FH JR, et al. Deficiency in acellular cementum and periodontal attachment in bsp null mice. J Dent Res. 2013; 92(2):166-172.
|