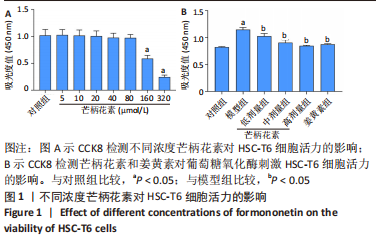
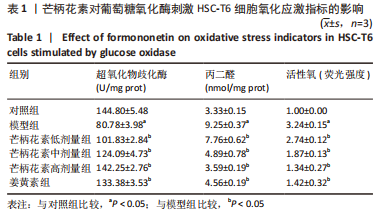
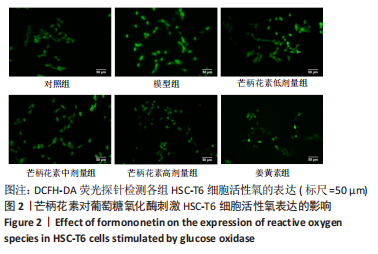
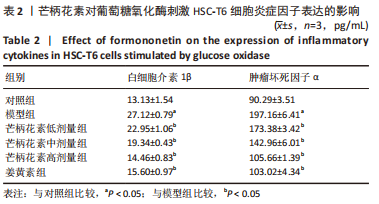
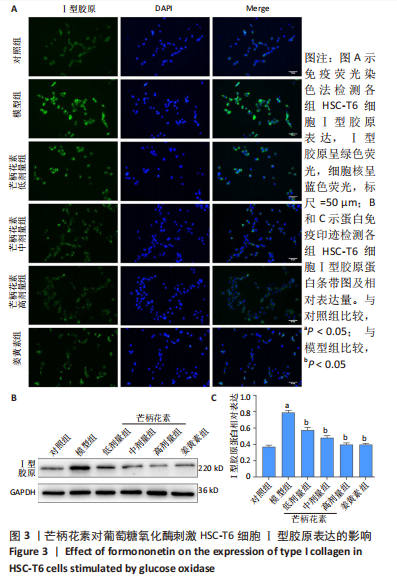
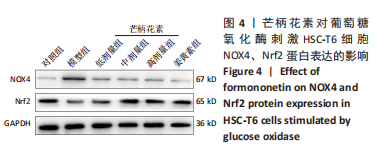
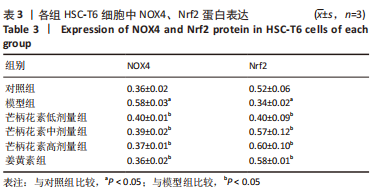
[1] ALTAMIRANO-BARRERA A, BARRANCO-FRAGOSO B, MÉNDEZ-SÁNCHEZ N. Management strategies for liver fibrosis. Ann Hepatol. 2017;16(1):48-56.
[2] AYDIN MM, AKÇALI KC. Liver fibrosis. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2018;29(1):14-21.
[3] LAMBRECHT J, VAN GRUNSVEN LA, TACKE F. Current and emerging pharmacotherapeutic interventions for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020;21(13):1637-1650.
[4] HIGASHI T, FRIEDMAN SL, HOSHIDA Y. Hepatic stellate cells as key target in liver fibrosis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;121:27-42.
[5] RAMOS-TOVAR E, MURIEL P. Molecular Mechanisms That Link Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in the Liver. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(12):1279.
[6] WANG T, ZHOU X, KUANG G, et al. Paeoniflorin modulates oxidative stress, inflammation and hepatic stellate cells activation to alleviate CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis by upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021;73(3):338-346.
[7] 傅月朦,余登香,王淑娜,等.山豆根黄酮类成分药理作用及机制研究进展[J].中草药,2022,53(19):6234-6244.
[8] ZHANG YZ, ZHANG J, TAN L, et al. Preparation and evaluation of temperature and magnetic dual-responsive molecularly imprinted polymers for the specific enrichment of formononetin. J Sep Sci. 2018;41(15):3060-3068.
[9] MACHADO DUTRA J, ESPITIA PJP, ANDRADE BATISTA R. Formononetin: Biological effects and uses - A review. Food Chem. 2021;359:129975.
[10] FANG Y, YE J, ZHAO B, et al. Formononetin ameliorates oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy via the KEAP1-NRF2-GSTP1 axis. Redox Biol. 2020;36:101677.
[11] WANG Y, ZHAO H, LI X, et al. Formononetin alleviates hepatic steatosis by facilitating TFEB-mediated lysosome biogenesis and lipophagy. J Nutr Biochem. 2019;73:108214.
[12] ALAUDDIN, CHATURVEDI S, MALIK MY, et al. Formononetin and biochanin A protects against ritonavir induced hepatotoxicity via modulation of NfκB/pAkt signaling molecules. Life Sci. 2018;213:174-182.
[13] FARZAEI MH, ZOBEIRI M, PARVIZI F, et al. Curcumin in Liver Diseases: A Systematic Review of the Cellular Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress and Clinical Perspective. Nutrients. 2018;10(7): 855.
[14] BOUREBABA N, MARYCZ K. Hepatic stellate cells role in the course of metabolic disorders development - A molecular overview. Pharmacol Res. 2021;170:105739.
[15] CAI X, WANG J, WANG J, et al. Intercellular crosstalk of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis: New insights into therapy. Pharmacol Res. 2020;155:104720.
[16] 赵杰,齐永芬,鱼艳荣.氧化应激在肝纤维化发生发展中的作用[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2019,35(9):2067-2071.
[17] LUO X, SUN D, WANG Y, et al. Cpt1a promoted ROS-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in liver injury via the Nrf2/HO-1 and NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021;99(5):468-477.
[18] TAY KC, TAN LT, CHAN CK, et al. Formononetin: A Review of Its Anticancer Potentials and Mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:820.
[19] 白月,王红芳,黄怀鹏.芒柄花素药理作用的研究进展[J].现代药物与临床, 2022,37(2):425-432.
[20] 李军,熊琨,龚元,等.基于信号转导通路的姜黄素抗氧化机制研究进展[J].中草药,2016,47(13):2373-2380.
[21] REZZANI R, FRANCO C, RODELLA LF. Curcumin as a Therapeutic Strategy in Liver Diseases. Nutrients. 2019;11(10):2498.
[22] 王丽,何萍,孙建超,等.蓝莓花青素对氧化应激诱导肝星状细胞活化、增殖和凋亡的影响及机制探讨[J].山东医药,2016,56(18):8-11.
[23] LUANGMONKONG T, SURIGUGA S, MUTSAERS HAM, et al. Targeting Oxidative Stress for the Treatment of Liver Fibrosis. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2018;175:71-102.
[24] 吕艳杭,吴姗姗,王振常,等.中医药调控活性氧(ROS)抗肝纤维化的研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊,2021,39(6):117-121.
[25] SUN J, WU Y, LONG C, et al. Anthocyanins isolated from blueberry ameliorates CCl4 induced liver fibrosis by modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation and stellate cell activation in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018;120:491-499.
[26] DE SOUZA BASSO B, HAUTE GV, ORTEGA-RIBERA M, et al. Methoxyeugenol deactivates hepatic stellate cells and attenuates liver fibrosis and inflammation through a PPAR-ɣ and NF-kB mechanism. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;280:114433.
[27] RODRÍGUEZ MJ, SABAJ M, TOLOSA G, et al. Maresin-1 Prevents Liver Fibrosis by Targeting Nrf2 and NF-κB, Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Cells. 2021;10(12):3406.
[28] 罗方云,黄晨恺,朱萱. NOX4相关信号通路在肝纤维化发病机制中的作用[J].医学研究生学报,2019,32(3):298-302.
[29] JIMÉNEZ-URIBE AP, GÓMEZ-SIERRA T, APARICIO-TREJO OE, et al. Backstage players of fibrosis: NOX4, mTOR, HDAC, and S1P; companions of TGF-β. Cell Signal. 2021; 87:110123.
[30] DU JJ, SUN JC, LI N, et al. β-Arrestin2 deficiency attenuates oxidative stress in mouse hepatic fibrosis through modulation of NOX4. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021; 42(7):1090-1100.
[31] ZHOU M, ZHAO X, LIAO L, et al. Forsythiaside A Regulates Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells by Inhibiting NOX4-Dependent ROS. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022; 2022:9938392.
[32] SAJADIMAJD S, KHAZAEI M. Oxidative Stress and Cancer: The Role of Nrf2. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2018;18(6):538-557.
[33] 曹玲娟,龚慧,颜苗,等. Nrf2-ARE信号通路参与肝脏疾病病理机制研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2015,31(8):1057-1061.
[34] YAMAMOTO M, KENSLER TW, MOTOHASHI H. The KEAP1-NRF2 System: a Thiol-Based Sensor-Effector Apparatus for Maintaining Redox Homeostasis. Physiol Rev. 2018; 98(3):1169-1203. |