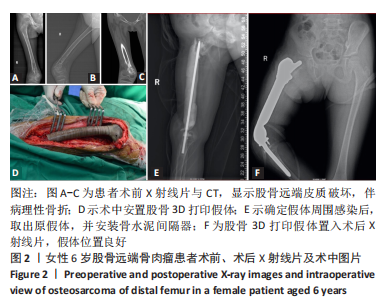
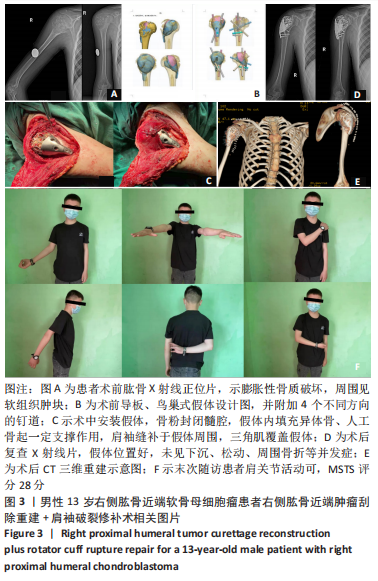
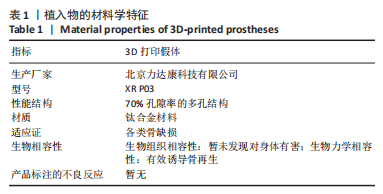
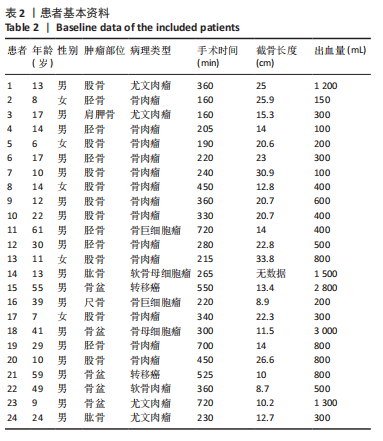
[1] MASQUELET AC, BEGUE T. The concept of induced membrane for reconstruction of long bone defects. Orthop Clin North Am. 2010;41(1): 27-37; table of contents.
[2] PHO RW. Free vascularised fibular transplant for replacement of the lower radius. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1979;61-B(3):362-365.
[3] SHIH HN, CHEN YJ, HUANG TJ, et al. Semistructural allografting in bone defects after curettage. J Surg Oncol. 1998;68(3):159-165.
[4] HENDERSON ER, GROUNDLAND JS, PALA E, et al. Failure mode classification for tumor endoprostheses: retrospective review of five institutions and a literature review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(5): 418-429.
[5] LU M, LI Y, LUO Y, et al. Uncemented three-dimensional-printed prosthetic reconstruction for massive bone defects of the proximal tibia. World J Surg Oncol. 2018;16(1):47.
[6] DAHAKE S, KUTHE A, KULKARNI S, et al. Finite element analysis of customized implant in mandibular reconstruction after tumor resection with and without using customized surgical osteotomy guide. Int J Med Robot. 2018;14(1):10.1002/rcs.1854.
[7] RUGGIERI P, MAVROGENIS AF, PALA E, et al. Long term results of fixed-hinge megaprostheses in limb salvage for malignancy. Knee. 2012; 19(5):543-549.
[8] LI J, CHEN G, LU Y, et al. Factors Influencing Osseous Union Following Surgical Treatment of Bone Tumors with Use of the Capanna Technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(22):2036-2043.
[9] GURSAN O, CELTIK M, YANIK B, et al. Three-Dimensionally-Printed Joint-Preserving Prosthetic Reconstruction of Massive Bone Defects After Malignant Tumor Resection of the Proximal Tibia. Cureus. 2021; 13(3):e13784.
[10] WONG KC, KUMTA SM, GEEL NV, et al. One-step reconstruction with a 3D-printed, biomechanically evaluated custom implant after complex pelvic tumor resection. Comput Aided Surg. 2015;20(1):14-23.
[11] WANG B, HAO Y, PU F, et al. Computer-aided designed, three dimensional-printed hemipelvic prosthesis for peri-acetabular malignant bone tumour. Int Orthop. 2018;42(3):687-694.
[12] WANG J, MIN L, LU M, et al. What are the Complications of Three-dimensionally Printed, Custom-made, Integrative Hemipelvic Endoprostheses in Patients with Primary Malignancies Involving the Acetabulum, and What is the Function of These Patients? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020;478(11):2487-2501.
[13] 闵理,王杰,张瑀琦,等. 3D打印定制一体化半骨盆假体治疗髋臼周围原发恶性骨肿瘤短期疗效的评估[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2021, 10(8):592-600.
[14] DOROZHKIN SV, EPPLE M. Biological and medical significance of calcium phosphates. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2002;41(17):3130-3146.
[15] GUDER WK, HARDES J, GOSHEGER G, et al. Ultra-short stem anchorage in the proximal tibial epiphysis after intercalary tumor resections: analysis of reconstruction survival in four patients at a mean follow-up of 56 months. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(4):481-488.
[16] HOUDEK MT, ROSE PS, MILBRANDT TA, et al. Comparison of Pediatric Intercalary Allograft Reconstructions with and without a Free Vascularized Fibula. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;142(4):1065-1071.
[17] KAA AK, JORGENSEN PH, SOJBJERG JO, et al. Reverse shoulderreplacement after resection of the proximal humerus for bone tumours. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(11):1551-1555.
[18] KING JJ, NYSTROM LM, REIMER NB, et al. Allograft-prosthetic composite reverse total shoulder arthro-plasty for reconstruction of proximal humerus tumor resections.J Shoulder Elb Surg.2016;25(1):45-54.
[19] BONNEVIALLE N, MANSAT P, LEBON J, et al. Reverseshoulder arthroplasty for malignant tumors of proximal humerus.J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2015;24(1):36-44.
[20] LIN CL, FANG JJ, LIN RM. Resection of giant invasive sacral schwannoma using image-based customized osteotomy tools. Eur Spine J. 2016; 25(12):4103-4107.
[21] JEYS LM, GRIMER RJ, CARTER SR, et al. Periprosthetic infection in patients treated for an orthopaedic oncological condition. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(4):842-849.
[22] DOROZHKIN SV, EPPLE M. Biological and medical significance of calcium phosphates. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2002;41(17):3130-3146.
[23] 张昭,朱东泽,党竞医,等.3D打印技术在骨肿瘤精准化治疗中的研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2022,19(3):81-85.
[24] 丁昊,邵显昊,杨强,等.LARS韧带联合3D打印假体在肿瘤切除桡侧半腕关节重建术中的应用研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2022,36(7):822-827.
[25] 黄晓夏,赵岩,彭聪,等.3D打印辅助改良前外侧双肌间隙入路治疗后外侧柱胫骨平台骨折[J].创伤外科杂志,2021,23(10):734-739.
[26] HOLLANDER DA, VON WALTER M, WIRTZ T, et al. Structural,mechanical and in vitro characterization of individually structured Ti-6Al-4V produced by direct laser forming. Biomaterials. 2006;27(7):955-963.
[27] LEE SS, SANTSCHI M, FERGUSON SJ. A Biomimetic Macroporous Hybrid Scaffold with Sustained Drug Delivery for Enhanced Bone Regeneration. Biomacromolecules. 2021;22(6):2460-2471.
[28] HOLLISTER SJ. Scaffold design and manufacturing: from concept to clinic. Adv Mater. 2009;21(32-33):3330-3342.
|