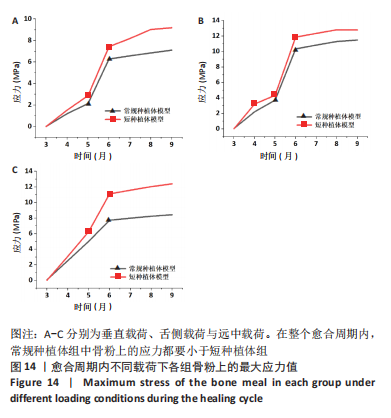
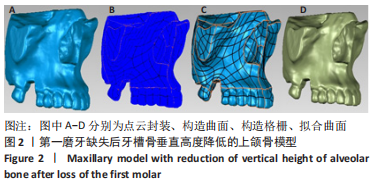
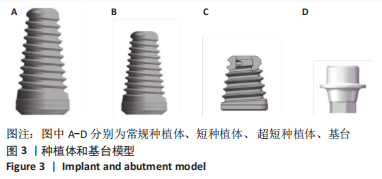
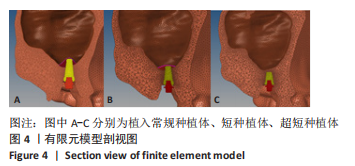
[1] FARINA R, SIMONELLI A, FRANCESCHETTI G, et al. Peri-implant tissue conditions following transcrestal and lateral sinus floor elevation: 3-year results of a bi-center, randomized trial. Clin Oral Invest. 2022; 26(5):3975-3986.
[2] EL-PRINCE O, RAGAB H. Comparison between maxillary sinus lifting in combination with implant placement with versus without bone grafts (clinical and radiographic study). Egypt Dent J. 2020;66(1):113-122.
[3] KHOURY F, HANSER T. Three-Dimensional Vertical Alveolar Ridge Augmentation in the Posterior Maxilla: A 10-year Clinical Study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019;34(2):471-480.
[4] CERNY D, ECKERT S, MOUNAJJED R. Retrospective 9-Year Clinical Outcome Report on Adhesive Post-endodontic Treatment of Anterior Teeth Using Prefabricated Fiber Posts. Int J Prosthodont. 2018;32(1): 14-16.
[5] DONATAS B, GAILĖ B. Short implants without bone augmentation versus long implants with bone augmentation. Systematic review and meta-analysis. Aust Dent J. 2021;66(1):71-81.
[6] LOZANO-CARRASCAL N, ANGLADA-BOSQUED A, SALOMÓ-COLL O, et al. Short implants (<8mm) versus longer implants (≥8mm) with lateral sinus floor augmentation in posterior atrophic maxilla: A meta-analysis of RCT`s in humans. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2020;25(2): e168-e179.
[7] MARCO E, ROBERTO P, CARLO B, et al. Three-year results from a randomised controlled trial comparing prostheses supported by 5-mm long implants or by longer implants in augmented bone in posterior atrophic edentulous jaws Eur J Oral Implantol. 2014;7(4).383-395.
[8] XU X, HUANG J, FU X, et al. Short implants versus longer implants in the posterior alveolar region after an observation period of at least five years: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent. 2020;100:103386.
[9] ESPOSITO M, GRUSOVIN MG, KWAN S, et al. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: bone augmentation techniques for dental implant treatment. Aust Dent J. 2009;54(1):70-71.
[10] GÓMEZ-POLO M, ORTEGA R, GÓMEZ-POLO C, et al. Does Length, Diameter, or Bone Quality Affect Primary and Secondary Stability in Self-Tapping Dental Implants? J Oral Maxil Surg. 2016;74(7):1344-1353.
[11] SOUZA CR, SILVA BM, NOGUEIRA DGAA, et al. Viability of Maxillary Single Crowns Supported by 4-mm Short Implants: A Finite Element Study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2020;35(3):41-50.
[12] FAZEL A, AALAI S, RISMANCHIAN M. Effect of Macro-Design of Immediately Loaded Implants on Micromotion and Stress Distribution in Surrounding Bone Using Finite Element Analysis. Implant Dent. 2009;18(4):345-352.
[13] SAYYEDI A, RASHIDPOUR M, FAYYAZ A, et al. Comparison of Stress Distribution in Alveolar Bone with Different Implant Diameters and Vertical Cantilever Length via the Finite Element Method. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2019;29(1):37-43.
[14] GASHI CB, BOLUKBASI BN, TAYFUN O, et al. The Effect of the Length and Distribution of Implants for Fixed Prosthetic Reconstructions in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla: A Finite Element Analysi. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). 2019;12(16):2556.
[15] HORITA S, SUGIURA T, YAMAMOTO K, et al. Biomechanical analysis of immediately loaded implants according to the “All-on-Four” concept. J Prosthodont Res. 2017;61(2):123-132.
[16] KITAMURA E, STEGAROIU R, NOMURA S, et al. Influence of marginal bone resorption on stress around an implant - a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Oral Rehabil. 2005;32(4):279-286.
[17] 曹敏,王冬梅,王明一,等.半侧上颌骨缺损赝复体修复固位方案的生物力学评价[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(5):484-489.
[18] 丁光兴.基于个性化的长管骨有限元参数化建模及实验验证[D].南京:南京理工大学,2012.
[19] 关振群,石俊,李爱群,等.Mimics辅助快速建立颅上颌复合体的三维有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(43): 7998-8001.
[20] CANTÓ-NAVÉS O, MEDINA-GALVEZ R, MARIMON X, et al. A 3D Finite Element Analysis Model of Single Implant-Supported Prosthesis under Dynamic Impact Loading for Evaluation of Stress in the Crown, Abutment and Cortical Bone Using Different Rehabilitation Materials. Materials. 2021;14(13):3519.
[21] 刘晓芳,胡玲玲,宋光保,等.3种提升材料对闭合式上颌窦底提升术上颌窦黏膜形变影响的力学分析[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2014(6):831-834.
[22] 薛燕青,毓天昊,郑添予,等.种植体根尖部与上颌窦底皮质骨的关系对上颌后牙区种植影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2018,11(1):24-28.
[23] BÁLINT T, NOÉMI G, PÉTER H, et al. Relative performance of various biomaterials used for maxillary sinus augmentation: A Bayesian network meta‐analysis. Clin Oral Implan Res. 2021;32(2):135-153.
[24] EL CHAAR E, SHI Y, ENGEBRETSON S, et al. Bone Ring Allograft: Digitally Guided Placement in the Anterior Esthetic Area. A Retrospective Case Series. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2021;41(6):865-872.
[25] Rues S, Lenz JR, Schierle HP, et al. Simulation of the sinus floor elevation. PAMM. 2004;4(1):368-369.
[26] CRUZ M, WASSALL T, TOLEDO EM, et al. Finite element stress analysis of dental prostheses supported by straight and angled implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24(3):391-403.
[27] VELEZ-MURIEL SM, TALMA E, ROMANYK DL, et al. Biomechanical behavior of an alveolar graft under maxillary therapies. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2021;20(4):1519-1532.
[28] 李璐丽.牙种植体植入扭矩与骨结合失效分析[D].济南:山东大学, 2019.
[29] EL-ANWAR MI, EL-ZAWAHRY MM. A three dimensional finite element study on dental implant desig. J Genet Genomics. 2011;9(1):77-82.
[30] NAGUIB GH, HASHEM AB, NATTO Z, et al. The effect of Implant length and diameter on stress distribution of tooth-implant and implant supported prostheses:An in-vitro finite element study. J Oral Implantol. 2021;26(22):422-431.
[31] BAYRAK A, YARAMANOĞLU P, KıLıÇARSLAN MA, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of a New Triple Cylindrical Implant Design and a Conventional Cylindrical Implant Design on the Mandible by Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2020;35(2):257-264.
[32] BORDIN D, DEL BEL CURY AA, FAOT F. Influence of Abutment Collar Height and Implant Length on Stress Distribution in Single Crowns. Braz Dent J. 2019;30(3):238-243.
[33] JAYAPAL N, RAM SM, MURTHY V, et al. Differentiation between benign and metastatic cervical lymph nodes using ultrasound. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2019;11(6):338.
[34] 阮世捷,李长杰,李海岩,等.种植体长度与直径对下颌骨牙齿种植影响的有限元分析[J].天津科技大学学报,2020,35(4):47-52. |