中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (26): 4154-4160.doi: 10.12307/2023.189
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
复方双氯芬酸钠对骨关节炎大鼠软骨形态及氧化应激的影响
周志洁,张兰云,李凤国,张国辉
- 衡水市人民医院关节骨科运动医学科,河北省衡水市 053000
Effects of compound diclofenac sodium on cartilage morphology and oxidative stress in osteoarthritis rats
Zhou Zhijie, Zhang Lanyun, Li Fengguo, Zhang Guohui
- Department of Orthopedics and Sports Medicine, Hengshui People’s Hospital, Hengshui 053000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
Wistar大鼠:是一种大鼠,1970年由美国维斯塔尔研究所养育而成,现已经是世界各国实验室中常见的大鼠,也是中国使用相对较广泛、用量最大的一种鼠,其主要特点为头宽耳长、尾短、繁殖力强、产仔多、生长发育快、性情温顺、抗感染能力强;自发性肿瘤发生率较低。
基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinase,MMPs):因需要Ca、Zn等金属离子做为辅助因子而得名。其家族成员具有相似的结构,一般由5个功能不同的结构域组成。各种MMPs之间具有一定的底物特异性,同一种MMPs可降解各种细胞外基质成分,而某一种细胞外基质成分又可被多种MMPs降解。
背景:复方双氯芬酸钠是镇痛解热、非类固醇药物,其被广泛用于缓解轻至中度疼痛,治疗类风湿关节炎、骨关节炎和强直性脊柱炎、骨关节炎、肌肉骨骼损伤等,但目前关于其对骨关节炎的作用机制报道较少。
目的:探究复方双氯芬酸钠对骨关节炎大鼠基质金属蛋白酶1、软骨形态及氧化应激的影响。
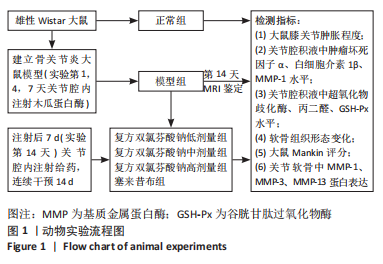
方法:采用木瓜蛋白酶关节腔内注射建立骨关节炎大鼠模型,将Wistar大鼠随机分为空白组,骨关节炎模型组、复方双氯芬酸钠低、中、高剂量组、塞来昔布组。测量各组大鼠右侧膝关节的肿胀程度;ELISA检测关节积液中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、基质金属蛋白酶1水平,并检测氧化应激指标超氧化物歧化酶、丙二醛、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶含量;比较各组大鼠关节软骨组织形态和Mankin评分;蛋白质印迹法检测关节软骨中基质金属蛋白酶1、基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13蛋白表达。
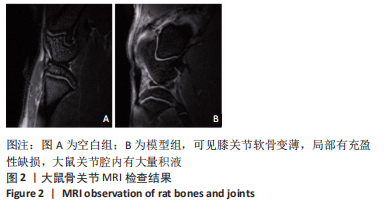
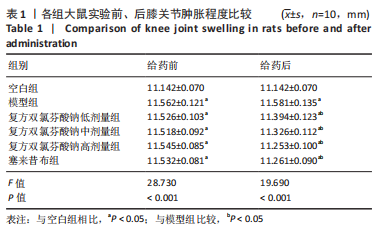
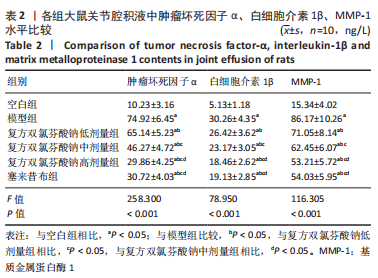
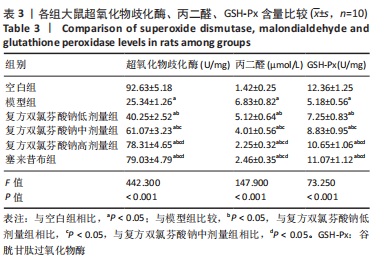
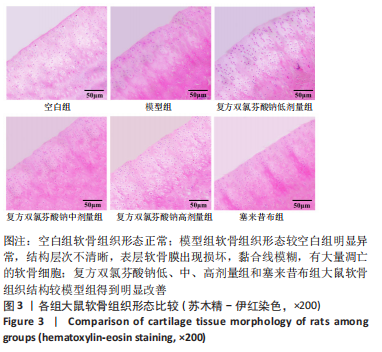
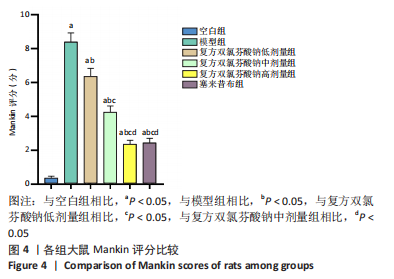
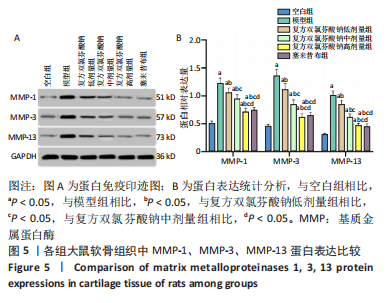
结果与结论:①在造模后和给药前,和空白组相比,模型组大鼠右膝关节均出现了不同程度的红肿,但无紫红色斑和结节等变化;给药后,和模型组相比,复方双氯芬酸钠低、中、高剂量组和塞来昔布组大鼠右膝关节红肿程度明显减轻(P < 0.05);②模型组大鼠关节腔积液中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、基质金属蛋白酶1水平较空白组增加(P < 0.05);低、中、高剂量组和塞来昔布组大鼠关节腔积液中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、基质金属蛋白酶1水平均低于模型组(P < 0.05);③和空白组相比,模型组大鼠超氧化物歧化酶活性和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶含量均显著降低,丙二醛浓度升高(P < 0.05);和模型组相比,各给药组大鼠超氧化物歧化酶活性和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶含量均升高,丙二醛浓度均降低,且复方双氯芬酸钠高剂量组变化最显著(P < 0.05);④模型组大鼠Mankin评分高于空白组(P < 0.05);和模型组相比,各给药组大鼠Mankin评分均显著降低,且复方双氯芬酸钠高剂量组降低最显著(P < 0.05);⑤模型组大鼠软骨组织中基质金属蛋白酶1、基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13蛋白表达高于空白组(P < 0.05);各给药组大鼠软骨组织中3种基质金属蛋白酶蛋白表达均低于模型组(P < 0.05);⑥结果说明,复方双氯芬酸钠可以改善骨关节炎大鼠软骨形态,降低氧化应激损伤,抑制软骨组织中基质金属蛋白酶1表达,进而对骨关节起到治疗作用。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9238-1183(周志洁)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: