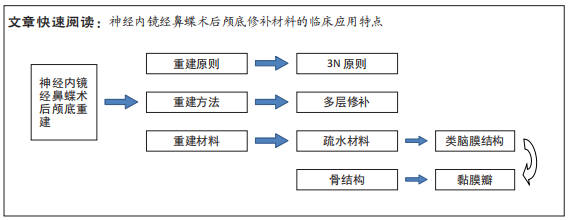
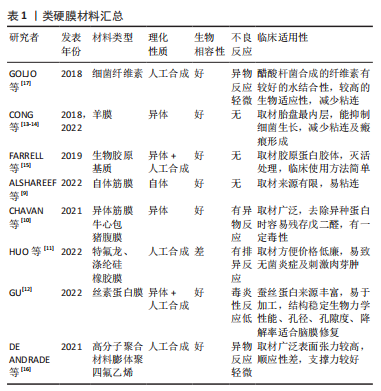
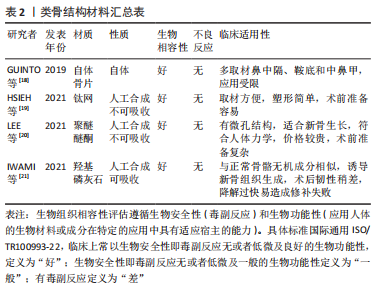
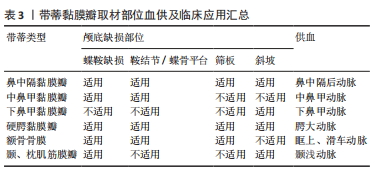
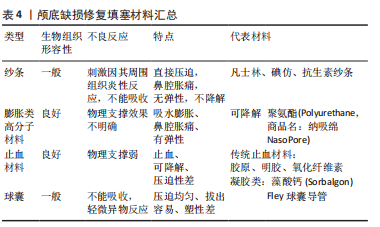
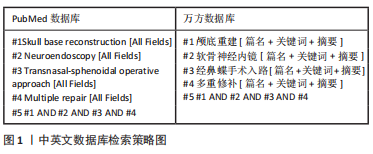
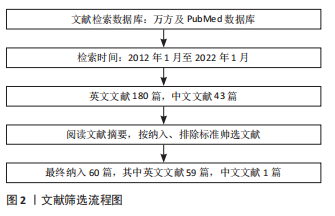
[1] CAI X, YANG J, ZHU J, et al. Reconstruction strategies for intraoperative CSF leak in endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Neurosurg, 2021. doi: 10.1080/02688697.2020.1849548.
[2] AHN S, PARK J, KIM D, et al. Surgical experience in prevention of postoperative csf leaks using abdominal fat grafts in endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary adenomas. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2021;82(5):522-527.
[3] ALBONETTE-FELICIO T, MARTINEZ-PEREZ R, VANKOEVERING K, et al. Soft gasket seal reconstruction after endoscopic endonasal transtuberculum resection of craniopharyngiomas. World Neurosurg. 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.12.058.
[4] BOWEN A, ELTAHIR A, GOATES A, et al. The posterior septal nasal floor mucosal flap for cranial base reconstruction. Laryngoscope. 2022. doi: 10.1002/lary.30079.
[5] CERAUDO M, CAVALLO L, ROSSI D, et al. Role of anterior nasal packing in endoscopic skull base surgery: Italian survey. World Neurosurg. 2021;154:e406-e415.
[6] ALOKBY G, ALAMARI K, ABDULLAH J, et al. Endoscopic reconstruction of skull base defects using tutoplast. Allergy Rhinol. 2021. doi: 10.1177/21526567211009200.
[7] BAUSSART B, RACY E, GAILLARD S. Double pedicled nasoseptal flap for skull base repair after endoscopic expanded endonasal approach. Acta Neurochir. 2022;164(4):1111-1114.
[8] CHASKES M, RABINOWITZ M. Safety of restarting continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy following endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022;8(1):61-65.
[9] ALSHAREEF M, ALROQI A, ALBAHARNA H, et al. Nasoseptal flap and rigid reconstruction in endoscopic endonasal skull base surgeries: the longitudinal experience of a single center. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022.doi:10.1177/01455613221099483.
[10] CHAVAN S, POTDUKHE K, KALE V, et al. A comparitive study of endoscopic skull base reconstruction in CSF rhinorrea using nasoseptal flap with septal cartilage v/s fascia lata with fat. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;73(2):233-239.
[11] HUO C, KING J, GOLDSCHLAGER T, et al. The effects of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) diversion on post-operative CSF leak following extended endoscopic anterior skull base surgery. J Clin Neurosci. 2022;98:194-202.
[12] GU D. Radioanatomical study of the skull base and septum in chinese:implications for using the HBF for endoscopic skull base reconstruction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. doi:10.1155/2022/9940239.
[13] CONG Z, LIU K, WEN G, et al. Universal sellar anatomical reconstruction using the sellar floor flap after endoscopic pituitary adenoma surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;158(4):774-776.
[14] DUAN H, JIANG X, LI C, et al. Application of a three-dimensional printed model to localize a cranial cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report. J Int Med Res. 2022;50(2):3000605221078412.
[15] FARRELL N, KINGDOM T, GETZ A, et al. Development of chronic sphenoid sinusitis after sellar reconstruction with medpor porous polyethylene implant. World Neurosurg. 2019;123:e781-e786.
[16] DE ANDRADE E, ALMEIDA J, BORGHEI-RAZAVI H, et al. Reconstruction after extended endonasal approaches to the anterior cranial base: surgical techniques and current results. J Neurosurg Sci. 2021;65(2): 151-159.
[17] GOLJO E, KINBERG E, STEPAN K, et al. Reconstruction of a skull base defect after endoscopic endonasal resection of a pituitary adenoma: Sphenoid mucosal flaps. Am J Otolaryngol. 2018;39(2):253-256.
[18] GUINTO G, NETTEL B, HERNáNDEZ E, et al. Osseous remodeling technique of the sella turcica:a new surgical option for primary empty sella syndrome. World Neurosurg. 2019;126:e953-e958.
[19] HSIEH Y, GAO X, WANG X, et al. Therapeutic validation of venous pulsatile tinnitus and biomaterial applications for temporal bone reconstruction surgery using multi-sensing platforms and coupled computational techniques. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:777648.
[20] LEE J, WICK E, CHICOINE M, et al. Endonasal free flap reconstruction combined with draf frontal sinusotomy for complex cerebrospinal fluid leak: a technical report & case series. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2021;21(6):478-484.
[21] IWAMI K, FUJII M, JINGUJI S, et al. Skull base reconstruction using a temporoparietal galeal flap in simultaneous transnasal and transcranial surgery for the prevention of carotid blowout syndrome:a report of 3 cases. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2021;82:e236-e242.
[22] JOLLY K, GUPTA K, EGBUJI O, et al. Endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery reconstruction using the fibrin sealant patch Tachosil. Br J Neurosurg. 2021. doi: 10.1080/02688697.2021.1905771.
[23] KAWAGUCHI A, SHIN M, HASEGAWA H, et al. Endoscopic extended transclival approach for lower clival meningioma. World Neurosurg. 2022;164:117.
[24] KUAN E, BIRKENBEUEL J, KOVACS A, et al. Patterns of opioid usage and predictors of utilization following endoscopic skull base surgery. Laryngoscope. 2022. doi:10.1002/lary.30164.
[25] KAWSAR K, LAND T, TSERMOULAS G, et al. Novel surgical treatment of recurrent csf leak by temporoparietal temporalis myofascial flap: a series of 6 cases. World Neurosurg. 2021;147:1-6.
[26] KHATIWALA R, SHASTRI K, PERIS-CELDA M, et al. Endoscopic endonasal reconstruction of high-flow cerebrospinal fluid leak with fascia lata “button” graft and nasoseptal flap: surgical technique and case series. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2020;81(6):645-650.
[27] KIM Y, KANG H, DHO Y, et al. Multi-layer onlay graft using hydroxyapatite cement placement without cerebrospinal fluid diversion for endoscopic skull base reconstruction. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2021;64(4):619-630.
[28] LEHMANN A, VON SNEIDERN M, SHEN S, et al. Does reconstruction affect outcomes following exclusively endoscopic endonasal resection of benign orbital tumors: a systematic review with meta-analysis. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022;8(1):25-35.
[29] LIN F, ZHANG Y, ZHAO P, et al. Grading system and surgical strategy for temporal bone diffuse-type tenosynovial giant cell tumor. Laryngoscope. 2022;132(6):1275-1284.
[30] MARTINEZ-PEREZ R, KUNIGELIS K, WARD R, et al. Hydroxyapatite cement cranioplasty for reconstruction of translabyrinthine approach:aesthetic results, long-term satisfaction, quality of life, and complications. Acta Neurochir. 2022;164(3):669-677.
[31] MAO S, LI M, LI D, et al. Septal floor rotational flap pedicled on ethmoidal arteries for endoscopic skull base reconstruction. Laryngoscope. 2019;129(12):2696-2701.
[32] LUO C, LIU X, XIE S, et al. Experience and modification of skull base reconstruction results in lower complications rates. Acta Neurochir. 2022;164(4):1127-1133.
[33] LIU S, TANG R, LI Z, et al. Analysis of risk factors for delayed iatrogenic cerebrospinal fluid otorrhinorrhea. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;35(12):1111-1114.
[34] LIU Q, WANG H, SUN X, et al. The endoscopic transnasal approach in management of the sinonasal tumor invading the anterior skull base. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;56(1):11-17.
[35] LIN Y, LIN H, CHO D. Tension pneumoventricle after endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery for rathke cleft cyst. World Neurosurg. 2020; 135:228-232.
[36] MATTAVELLI D, FIORENTINO A, TENGATTINI F, et al. Additive manufacturing for personalized skull base reconstruction in endoscopic transclival surgery: a proof-of-concept study. World Neurosurg. 2021; 155:e439-e452.
[37] RAHIMLI T, HIDAYETOV T, RAJABOV T. Endoscopic endonasal approach to multilobular giant pituitary adenoma with cavernous sinus invasion and petroclival extension. World Neurosurg. 2021;147:128-129.
[38] PIPKORN P, LEE J, ZENGA J, et al. Endoscopic adipofascial radial forearm free flap reconstruction of the skull base: a technical update. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2021;82:e243-e247.
[39] PERIS-CELDA M, CHASKES M, LEE D, et al. Optimizing sellar reconstruction after pituitary surgery with free mucosal graft: results from the first 50 consecutive patients. World Neurosurg. 2017;101: 180-185.
[40] PAPAGIANNOPOULOS P, TONG C, BROWN H, et al. Comparison of high-flow CSF leak closure with nasoseptal flap following endoscopic endonasal approach in adult and pediatric populations. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022;12(3):321-323.
[41] PALMA DíAZ M, MARTíNEZ ANDA J, GUERRERO SUAREZ P, et al. Endonasal endoscopic and hybrid surgery techniques for blunt trauma fractures of the skull base with cerebrospinal fluid leaks. J Craniofac Surg. 2021;32(7):2500-2507.
[42] OOSTRA A, KOUTSARNAKIS C, GEORGALAS C. Advances in vascularized flaps for skull base reconstruction. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;29(1):36-43.
[43] MORINAGA Y, AKUTSU H, KINO H, et al. Endoscopic endonasal dural reconstruction for a cerebrospinal fluid leak in the middle cranial fossa of a patient with gorham-stout disease with skull base defect.NMC Case Rep J. 2022;9:55-61.
[44] MISSALE F, IOPPI A, ASCOLI A, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid leak repair:usefulness of intrathecal fluorescein for correct topographic identification of the skull base defects. World neurosurg. 2022;160: e267-e277.
[45] TIANZHI Z, YINGWU S, ZIJIAN Y, et al. A Modified Technique to Harvest Integrated Zygomatic Arch-Temporal Bone Flap:Clinical Experience. Neurol India. 2022;70(1):325-330.
[46] RAMOS-ZúñIGA R, LóPEZ-GONZáLEZ F, SEGURA-DURáN I. Bilaminar chitosan scaffold for sellar floor repair in transsphenoidal surgery. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:122.
[47] REDDY R, GILL A, HWANG J, et al. Surgeon education through a surgical cost feedback system reduces supply cost in endoscopic skull base surgery. J Neurosurg. 2022;136(2):422-430.
[48] STEIERT C, BEHRINGER S, KRAUS L, et al. Augmented reality-assisted craniofacial reconstruction in skull base lesions - an innovative technique for single-step resection and cranioplasty in neurosurgery. Neurosurg Rev. 2022. doi:10.1007/s10143-022-01784-6.
[49] SHELESKO E, CHERNIKOVA N, KRAVCHUK A, et al. Multiple skull base defects:features of pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 2021;85(4):58-63.
[50] SHAMAERAOTAN A, WEI J, MA D, et al. Immediate resection and reconstruction of encephalocele in the craniofacial region. J Craniofac Surg. 2022;33(2):e113-e116.
[51] ROTARIU D, ZIYAD F, BUDU A, et al. The role of osirix based virtual endoscopy in planning endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary adenoma. Turk Neurosurg. 2017;27(3):339-345.
[52] ROCA E, PENN D, SAFAIN M, et al. Abdominal fat graft for sellar reconstruction: retrospective outcomes review and technical note. Oper Neurosurg. 2019;16(6):667-674.
[53] TOSAKA M, PREVEDELLO D, YAMAGUCHI R, et al. Single-layer fascia patchwork closure for the extended endoscopic transsphenoidal transtuberculum transplanum approach: deep suturing technique and preliminary results. World Neurosurg. 2021;155:e271-e284.
[54] TOTTEN D, MANZOOR N, YANCEY K, et al. Comparison of small intestinal submucosal graft and autologous tissue in prevention of CSF leak after posterior fossa craniotomy. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2021;82(6):695-699.
[55] TURRI-ZANONI M, AROSIO A, AGOSTI E, et al. Endoscopic-assisted orbital exenteration: technical feasibility and surgical results from a single-center consecutive series. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2022;50(2): 156-162.
[56] WANG S, QIN Y, XIAO D, et al. Efficacy of sellar opening in the pituitary adenoma resection of transsphenoidal surgery influences the degree of tumor resection. BMC Med Imaging. 2017;17(1):45.
[57] WANG S, QIN Y, XIAO D, et al. Imaging evaluation of the location and fenestration of sellar floor during endonasal transsphenoidal surgery in patients with pituitary adenomas. World Neurosurg. 2018; 116:e232-e238.
[58] WANG Z, XIE Y, YANG R. Rapid reconstruction of craniotomy defects based on surgical navigation. Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. 2021; 45(3):246-249.
[59] ZOGHEIB S, HANNA C, DAOU B, et al. Successful outcomes with flaps for recurrent cerebrospinal fluid leaks: a systematic review of the literature. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2022;75(4):1380-1388.
[60] 王志强.严重颅底缺损模型建立及形状记忆合金支架-生物膜的研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2012:1-103. |