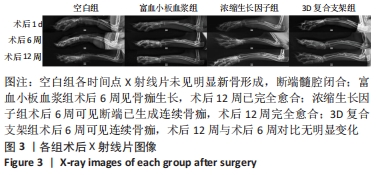
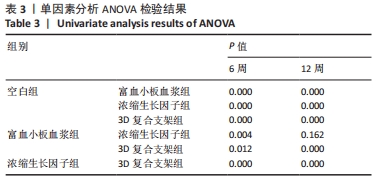
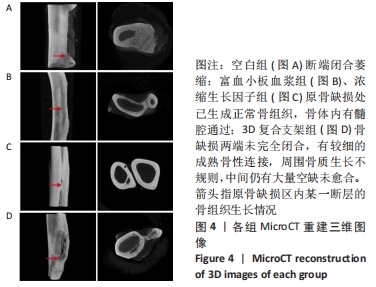
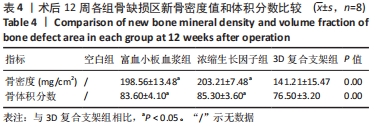
[1] BLOKHUIS TJ, ARTS JJ. Bioactive and osteoinductive bone graft substitutes: definitions, facts and myths. Injury. 2011;42 Suppl 2:S26-S29.
[2] CALORI GM, MAZZA E, COLOMBO M, et al. The use of bone-graft substitutes in large bone defects: any specific needs? Injury. 2011;42 Suppl 2:S56-S63.
[3] BRYDONE AS, MEEK D, MACLAINE S. Bone grafting, orthopaedic biomaterials, and the clinical need for bone engineering. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2010;224(12): 1329-1343.
[4] STAHL A, YANG YP. Regenerative Approaches for the Treatment of Large Bone Defects. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020;6(27):539-547.
[5] MARX RE, CARLSON ER, EICHSTAEDT RM, et al. Platelet-rich plasma: Growth factor enhancement for bone grafts. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998;85(6):638-646.
[6] LE ADK, ENWEZE L, DEBAUN MR, et al. Current Clinical Recommendations for Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2018;11(4):624-634.
[7] EMER J. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Current Applications in Dermatology. Skin Therapy Lett. 2019;24(5):1-6.
[8] LANG S, LOIBL M, HERRMANN M. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Tissue Engineering: Hype and Hope. Eur Surg Res. 2018;59(3-4):265-275.
[9] ORYAN A, ALIDADI S, MOSHIRI A. Platelet-rich plasma for bone healing and regeneration. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016;16(2):213-232.
[10] SHAHID M, KUNDRA R. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for knee disorders. EFORT Open Rev. 2017;2(1):28-34.
[11] DONG K, HAO P, ZHOU W, et al. Concentrate Growth Factors Regulate Osteogenic Dysfunction of MC3T3-E1 Cells Induced by High Glucose Through PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Implant Dent. 2019;28(5):478-483.
[12] LI G, WANG J, REN G, et al. Morphological Observation on Critical-Sized Cranial Defect Repaired by Icariin and Autologous Concentrate Growth Factors in Rabbits. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:2373-2381.
[13] LEE JW, CHO DW. 3D Printing technology over a drug delivery for tissue engineering. Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(12):1606-1617.
[14] SHIRAZI SF, GHAREHKHANI S, MEHRALI M, et al. A review on powder-based additive manufacturing for tissue engineering: selective laser sintering and inkjet 3D printing. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2015;16(3):33502.
[15] CHEN L, MCCRATE JM, LEE JC, et al. The role of surface charge on the uptake and biocompatibility of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles with osteoblast cells. Nanotechnology. 2011;22(10):105708.
[16] ROOZBAHANI M, ALEHOSSEINI M, KHARAZIHA M, et al. Nanocalcium phosphate bone cement based on Si-stabilized alpha-tricalcium phosphate with improved mechanical properties. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;81:532-541.
[17] ZHONGXING L, SHAOHONG W, JINLONG L, et al. Three-dimensional printed hydroxyapatite bone tissue engineering scaffold with antibacterial and osteogenic ability. J Biol Eng. 2021;15(1):21.
[18] CHIU CH, LEI KF, YEH WL. Development of a co-culture device for the study of human tenocytes in response to the combined stimulation of electric field and platelet rich plasma (PRP). Biomed Microdevices. 2017;19(3):69.
[19] MOHAMMADI R, MEHRTASH M, MEHRTASH M, et al. Effect of Platelet Rich Plasma Combined with Chitosan Biodegradable Film on Full-Thickness Wound Healing in Rat Model. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2016;4(1):29-37.
[20] WANG P, YING J, LUO C, et al. Osthole Promotes Bone Fracture Healing through Activation of BMP Signaling in Chondrocytes. Int J Biol Sci. 2017;13(8):996-1007.
[21] KIM TH, KIM SH, SANDOR GK, et al. Comparison of platelet-rich plasma (PRP), platelet-rich fibrin (PRF), and concentrated growth factor (CGF) in rabbit-skull defect healing. Arch Oral Biol. 2014;59(5):550-558.
[22] 李东亚, 郑欣, 邱旭升, 等. 新西兰兔桡骨骨缺损动物模型的制作[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(9):2012.
[23] JI C, BI L, LI J, et al. Salvianolic Acid B-Loaded Chitosan/hydroxyapatite Scaffolds Promotes The Repair Of Segmental Bone Defect By Angiogenesis And Osteogenesis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:8271-8284.
[24] KASTEN P, BEVERUNGEN M, LORENZ H, et al. Comparison of platelet-rich plasma and VEGF-transfected mesenchymal stem cells on vascularization and bone formation in a critical-size bone defect. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012;196(6):523-533.
[25] YU Y, WANG Y, ZHANG W, et al. Biomimetic periosteum-bone substitute composed of preosteoblast-derived matrix and hydrogel for large segmental bone defect repair. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:317-327.
[26] MASUKI H, OKUDERA T, WATANEBE T, et al. Growth factor and pro-inflammatory cytokine contents in platelet-rich plasma (PRP), plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF), advanced platelet-rich fibrin (A-PRF), and concentrated growth factors (CGF). Int J Implant Dent. 2016;2(1):19.
[27] MIJIRITSKY E, ASSAF HD, PELEG O, et al. Use of PRP, PRF and CGF in Periodontal Regeneration and Facial Rejuvenation-A Narrative Review. Biology (Basel). 2021; 10(4):317.
[28] BORNFELDT KE, RAINES EW, GRAVES LM, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor. Distinct signal transduction pathways associated with migration versus proliferation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995;766:416-430.
[29] BAE YJ, CHO CH, LEE WJ, et al. Optimization of recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB encapsulated in Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres for applications in wound healing. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;13(1):13-20.
[30] TSAY RC, VO J, BURKE A, et al. Differential growth factor retention by platelet-rich plasma composites. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;63(4):521-528.
[31] 陈鹏, 颜林淋, 李杨, 等. 富含血小板的血浆(PRP)促进伤口愈合和血管生成[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(5):2286-2291.
[32] RODELLA LF, FAVERO G, BONINSEGNA R, et al. Growth factors, CD34 positive cells, and fibrin network analysis in concentrated growth factors fraction. Microsc Res Tech. 2011;74(8):772-777.
[33] ROCHIRA A, SICULELLA L, DAMIANO F, et al. Concentrated Growth Factors (CGF) Induce Osteogenic Differentiation in Human Bone Marrow Stem Cells. Biology (Basel). 2020;9(11):370.
[34] EVERDING J, STOLBERG-STOLBERG J, RASCHKE MJ, et al. Stimulation of fracture healing by growth factors and cell-based technologies. Unfallchirurg. 2019;122(7):534-543.
[35] SUNDMAN EA, COLE BJ, FORTIER LA. Growth factor and catabolic cytokine concentrations are influenced by the cellular composition of platelet-rich plasma. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(10):2135-2140.
[36] ARICAN G, OZMERIC A, FIRAT A, et al. Micro-ct findings of concentrated growth factors (cgf) on bone healing in masquelet’s technique-an experimental study in rabbits. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;142:83-90.
[37] HU Y, CHEN J, FAN T, et al. Biomimetic mineralized hierarchical hybrid scaffolds based on in situ synthesis of nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan/chondroitin sulfate/hyaluronic acid for bone tissue engineering. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017; 157:93-100.
[38] PASURI J, HOLOPAINEN J, KOKKONEN H, et al. Osteoclasts in the interface with electrospun hydroxyapatite. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;135:774-783.
[39] XIE C, LU X, HAN L, et al. Biomimetic Mineralized Hierarchical Graphene Oxide/Chitosan Scaffolds with Adsorbability for Immobilization of Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(3):1707-1717.
[40] CROWDER SW, PRASAI D, RATH R, et al. Three-dimensional graphene foams promote osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Nanoscale. 2013;5(10):4171-4176.
[41] BRASSOLATTI P, BOSSINI PS, ANDRADE A, et al. Comparison of two different biomaterials in the bone regeneration (15, 30 and 60 days) of critical defects in rats. Acta Cir Bras. 2021;36(6):e360605.
[42] HU B, MENG ZD, ZHANG YQ, et al. Sr-HA scaffolds fabricated by SPS technology promote the repair of segmental bone defects. Tissue Cell. 2020;66:101386.
[43] MURUGAN S, PARCHA SR. Fabrication techniques involved in developing the composite scaffolds PCL/HA nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;32(8):93.
[44] TIAN B, WANG N, JIANG Q, et al. The immunogenic reaction and bone defect repair function of epsilon-poly-L-lysine (EPL)-coated nanoscale PCL/HA scaffold in rabbit calvarial bone defect. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;32(6):63.
[45] CHEN T, ZOU Q, DU C, et al. Biodegradable 3D printed HA/CMCS/PDA scaffold for repairing lacunar bone defect. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;116:111148.
[46] ZHU S, ZHANG X, CHEN X, et al. Nano-Hydroxyapatite Scaffold Based on Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 and Its Application in Bone Defect Repair. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2021;17(7): 1330-1338.
[47] WANG H, FAN HX, CHENG HZ, et al. Evaluation of the effect of 3D printed HAP-GEL scaffold combined with BMSCs and HUVECs in repairing rabbit skull defect. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2021;30(1): 28-32.
|