中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (35): 5596-5601.doi: 10.12307/2022.911
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
温针灸调控膝骨关节炎模型兔关节软骨中PI3K/Akt信号通路的变化
武永利1,2,刘 娣1,王 铎3,刘君伟1,马遇原3
- 1宁夏医科大学总医院中医骨伤科,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004;2宁夏医科大学回医药现代化教育部重点实验室,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004;3宁夏医科大学中医学院,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004
Effect of warm acupuncture on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in articular cartilage of a rabbit knee osteoarthritis model
Wu Yongli1, 2, Liu Di1, Wang Duo3, Liu Junwei1, Ma Yuyuan3
- 1Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology of Traditional Chinese Medicine, the General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 2Key Laboratory of Hui Ethnic Medicine Modernization, Ministry of Education, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 3School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
软骨细胞凋亡:作为细胞程序性死亡中的一种,在骨关节炎的发病中具有重要影响,该过程对软骨的破坏和重建起到重要作用,是造成软骨退行性病理改变的主要因素。
温针灸:温针灸疗法作为中医特色疗法中的一种,具有舒筋止痛、温经通络的作用,对于治疗早、中期膝骨关节炎患者疗效确切,在中医骨伤治疗膝骨关节炎中应用广泛。
背景:温针灸临床治疗膝骨关节炎疗效显著,但基础治疗机制尚未明确。
目的:观察温针灸对兔膝骨关节炎模型关节软骨中PI3K/Akt信号通路及其下游因子Bcl-2、Bax表达的影响。
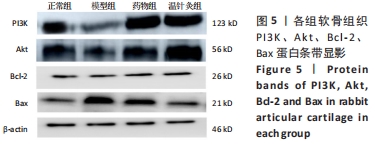
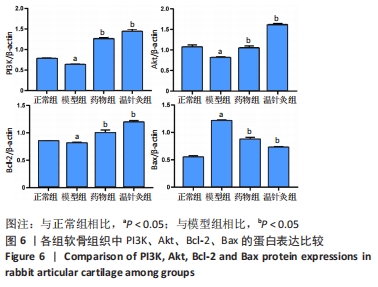
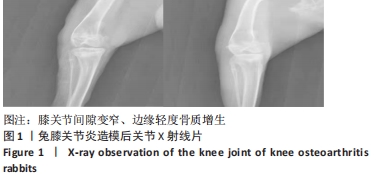
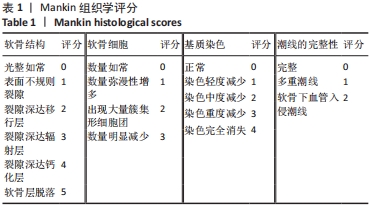
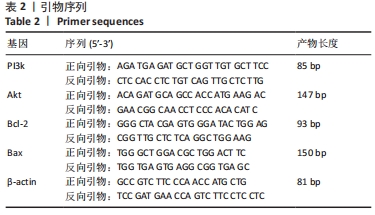
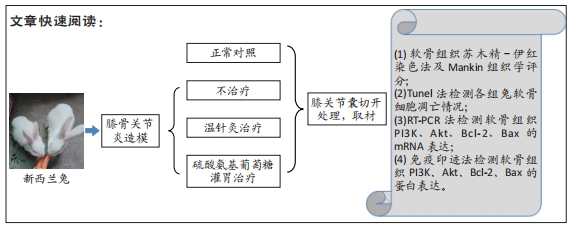
方法:取6月龄新西兰兔40只,采用随机数字表法分为正常组、模型组、药物组、温针灸组,每组10只。模型组、药物组、温针灸组兔右后肢膝关节伸直位以石膏管型固定4周,制备膝骨关节炎模型。造模成功后,模型组每日置于兔架上固定15 min,药物组每天行硫酸氨基葡萄糖灌胃治疗(77 mg/kg,1次/d),温针灸组每天行温针灸治疗(15 min/次,1次/d)。连续治疗28 d后,利用苏木精-伊红染色观察软骨损伤程度,Tunel法检测软骨细胞凋亡,RT-PCR法检测软骨组织中PI3K、Akt、Bcl-2、Bax的mRNA表达,Western blot法检测软骨组织中PI3K、Akt、Bcl-2、Bax 的蛋白表达。
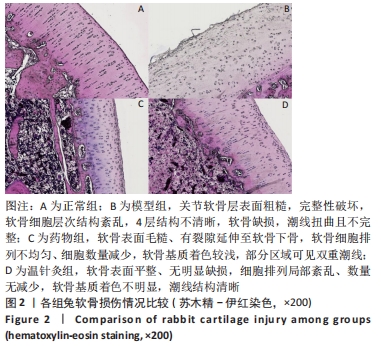
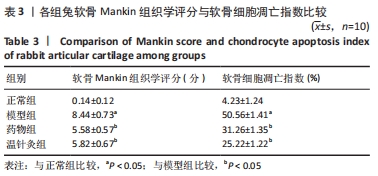
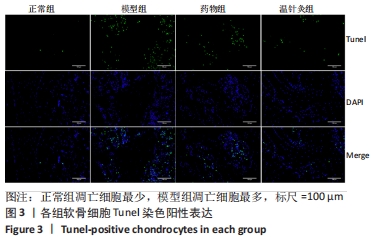
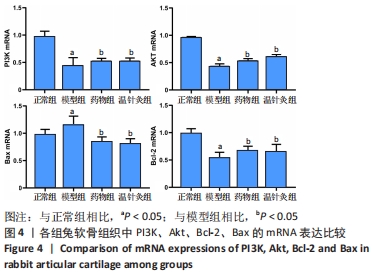
结果与结论:①苏木精-伊红染色显示,模型组软骨细胞数量减少,细胞排列无序,层次紊乱,软骨面被破坏,Mankin评分显著升高;药物组与温针灸组软骨细胞数量明显增多,基质着色深,Mankin评分降低;②与正常组相比,模型组软骨细胞凋亡率增高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,药物组、温针灸组软骨细胞凋亡率降低(P < 0.05);③RT-PCR与Western blot检测显示,与正常组相比,模型组PI3K、Akt、Bcl-2的mRNA与蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05),Bax的mRNA与蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,温针灸组与药物组PI3K、Akt、Bcl-2的mRNA与蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),Bax的mRNA与蛋白降低(P < 0.05);④结果表明温针灸可通过调控PI3K/Akt信号通路引起下游因子Bcl-2表达升高、Bax表达降低,进而抑制软骨细胞过度凋亡,达到保护关节软骨的作用。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9774-453X(武永利)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: